Abstract
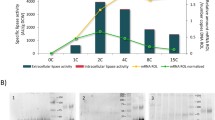
The methylotrophic yeast Komagataella phaffii is among the most popular hosts for recombinant protein synthesis. Most recombinant proteins have been expressed in the wild-type Mut+ host strain from the methanol-inducible alcohol oxidase (AOX) promoter PAOX1. Since methanol metabolism has undesirable consequences, two additional host strains, Muts (Δaox1) and Mut− (Δaox1Δaox2), were introduced which consume less methanol and reportedly also express recombinant protein better than Mut+. Both results follow from a simple model based on two widespread assumptions, namely methanol is transported by diffusion and the sole inducer of PAOX1. To test this model, we studied 14C-methanol uptake in the Mut− strain and β-galactosidase expression in all three strains. We confirmed that methanol is transported by diffusion, but in contrast to the literature, Mut+ expressed β-galactosidase 5- and 10-fold faster than Muts and Mut−. These results imply that methanol is not the sole inducer of PAOX1—metabolites downstream of methanol also induce PAOX1. We find that formate or/and formaldehyde are probably true inducers since both induce PAOX1 expression in Mut− which cannot synthesize intracellular methanol from formate or formaldehyde. Formate offers a promising substitute for methanol since it does not appear to suffer from the deficiencies that afflict methanol.
Key points
• This is the first study to systematically compare all three Mut phenotypes as host strains.
• Mut+ strain expresses 5- and 10-fold faster than Muts and Mut− strains.
• Methanol is transported by diffusion in Komagataella phaffii.
• Formate and formaldehyde are true and strong inducers of PAOX1 expression





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LE, McClure WO (1973) An improved scintillation cocktail of high-solubilizing power. Anal Biochem 51(1):173–179
Andrews JF (1968) A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 10(6):707–723
Arnau C, Casas C, Valero F (2011) The effect of glycerol mixed substrate on the heterologous production of a Rhizopus oryzae lipase in Pichia pastoris system. Biochem Eng J 57:30–37
Brierley RA, Bussineau C, Kosson R, Melton A, Siegel RS (1990) Fermentation development of recombinant Pichia pastoris expressing the heterologous gene: bovine lysozyme. Ann N Y Acad Sci 589(1):350–362
Chiruvolu V, Cregg JM, Meagher MM (1997) Recombinant protein production in an alcohol oxidase-defective strain of Pichia pastoris in fedbatch fermentations. Enzym Microb Technol 21(4):277–283
Clare JJ, Rayment FB, Ballantine SP, Sreekrishna K, Romanos MA (1991) High-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple tandem integrations of the gene. Biotechnol 9(5):455
Cos O, Serrano A, Montesinos JL, Ferrer P, Cregg JM, Valero F (2005) Combined effect of the methanol utilization (Mut) phenotype and gene dosage on recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris fed-batch cultures. J Biotechnol 116(4):321–335
Cregg JM, Russell KA (1998) Transformation. In: Pichia protocols Humana Press, pp 27–39
Cregg JM, Madden KR, Barringer KJ, Thill GP, Stillman CA (1989) Functional characterization of the two alcohol oxidase genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris. Mol Cell Biol 9(3):1316–1323
Cregg JM, Tschopp JF, Stillman C, Siegel R, Akong M, Craig WS, Buckholz RG, Madden KR, Kellaris PA, Davis GR, Smiley BL, Cruze J, Torregrossa R, Velicȩlebi G, Thill GP (1987) High–level expression and efficient assembly of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Nat Biotechnol 5 (5):479–485
Cregg JM, Cereghino JL, Shi J, Higgins DR (2000) Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Mol Biotechnol 16(1):23–52
Digan ME, Lair SV, Brierley RA, Siegel RS, Williams ME, Ellis SB, Kellaris PA, Provow SA, Craig WS, Velicelebi G, Harpold MM, Thill GP (1989) Continuous production of a novel lysozyme via secretion from the yeast, Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol 7(2):160–164
Eggeling L, Sahm H (1980) Regulation of alcohol oxidase synthesis in Hansenula polymorpha: oversynthesis during growth on mixed substrates and induction by methanol. Arch Microbial 127(2):119–124
Eggeling L, Sahm H, Wagner F (1977) Induction of FMN adenylyltransferase in the methanol utilizing yeast Candida boidinii. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1(4):205–209
Fricke UWE (1975) Tritosol: a new scintillation cocktail based on triton X-100. Anal Biochem 63(2):555–558
Giuseppin ML, van Eijk HM, Verduyn C, Bante I, van Dijken JP (1988) Production of catalase-free alcohol oxidase by Hansenula polymorpha. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28(1):14–19
Giuseppin ML, Almkerk JW, Heistek JC, Verrips CT (1993) Comparative study on the production of guar alpha-galactosidase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SU50B and Hansenula polymorpha 8/2 in continuous cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(1):52–59
Guijarro JM, Lagunas R (1984) Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not accumulate ethanol against a concentration gradient. J Bacteriol 160(3):874–878
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166(4):557–580
Higgins DR, Cregg JM (1998) Introduction to Pichia pastoris. In: Pichia protocols. Humana Press, pp 1–15
Inan M, Meagher MM (2001) Non-repressing carbon sources for alcohol oxidase (AOX1) promoter of Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 92(6):585–589
Invitrogen IM, 2010 Pichia expression kit, catalog no. K1710-01
Jungo C, Rérat C, Marison IW, von Stockar U (2006) Quantitative characterization of the regulation of the synthesis of alcohol oxidase and of the expression of recombinant avidin in a Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain. Enzym Microb Technol 39(4):936–944
Jungo C, Marison I, von Stockar U (2007a) Mixed feeds of glycerol and methanol can improve the performance of Pichia pastoris cultures: a quantitative study based on concentration gradients in transient continuous cultures. J Biotechnol 128(4):824–837
Jungo C, Marison I, von Stockar U (2007b) Regulation of alcohol oxidase of a recombinant Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain in transient continuous cultures. J Biotechnol 130(3):236–246
Jungo C, Schenk J, Pasquier M, Marison IW, von Stockar U (2007c) A quantitative analysis of the benefits of mixed feeds of sorbitol and methanol for the production of recombinant avidin with Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 131(1):57–66
Kamihira M, Taniguchi M, Kobayashi T (1987) Sterilization of microorganisms with supercritical carbon dioxide. Agric Biol Chem 51(2):407–412
Kim SJ, Lee JA, Kim YH, Song BK (2009) Optimization of the functional expression of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase in Pichia pastoris by varying the host and promoter. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(9):966–971
Kippert F (1995) A rapid permeabilization procedure for accurate quantitative determination of β-galactosidase activity in yeast cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128(2):201–206
Krainer FW, Dietzsch C, Hajek T, Herwig C, Spadiut O, Glieder A (2012) Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris strains with an engineered methanol utilization pathway. Microb Cell Factories 11(1):22
Kunert R, Gach J, Katinger H (2008) Expression of a fab fragment in CHO and Pichia pastoris. Bioprocess Int 6(6):34–40
Kurtzman CP (2005) Description of Komagataella phaffii sp. nov. and the transfer of Pichia pseudopastoris to the methylotrophic yeast genus Komagataella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(2):973–976
Loueiro V, Ferreira HG (1983) Intracellular accumulation of ethanol in yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 25(9):2263–2269
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22(4):249–270
Mattanovich D, Graf A, Stadlmann J, Dragosits M, Redl A, Maurer M, Kleinheinz M, Sauer M, Altmann F, Gasser B (2009) Genome, secretome and glucose transport highlight unique features of the protein production host Pichia pastoris. Microb Cell Factories 8(1):29
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor
Pedro AQ, Oppolzer D, Bonifacio MJ, Maia CJ, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2015) Evaluation of Muts and Mut+ Pichia pastoris strains for membrane-bound catechol-O-methyltransferase biosynthesis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(8):3840–3855
Peng L, Zhong X, Ou J, Zheng S, Liao J, Wang L, Xu A (2004) High-level secretory production of recombinant bovine enterokinase light chain by Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 108(2):185–192
Pfeffer M, Maurer M, Köllensperger G, Hann S, Graf AB, Mattanovich D (2011) Modeling and measuring intracellular fluxes of secreted recombinant protein in Pichia pastoris with a novel 34 S labeling procedure. Microb Cell Factories 10(1):47
Pla IA, Damasceno LM, Vannelli T, Ritter G, Batt CA, Shuler ML (2006) Evaluation of Mut+ and Muts Pichia pastoris phenotypes for high level extracellular scFv expression under feedback control of the methanol concentration. Biotechnol Prog 22(3):881–888
Potvin G, Ahmad A, Zhang Z (2012) Bioprocess engineering aspects of heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris: a review. Biochem Eng J 64:91–105
Sahm H (1977) Metabolism of methanol by yeasts. In: Advances in biochemical engineering, 6th edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 77–103
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (Vol 1, 2, 3), 3rd edn. Cold spring harbor laboratory press, New York
Schroder LA, Glick BS, Dunn WA (2007) Identification of pexophagy genes by restriction enzyme-mediated integration. In: Pichia Protocols. Humana Press, pp 203–218
Schwarzhans JP, Wibberg D, Winkler A, Luttermann T, Kalinowski J, Friehs K (2016) Non-canonical integration events in Pichia pastoris encountered during standard transformation analysed with genome sequencing. Sci Rep 6:38952
Shimizu S, Ishida M, Kato N, Tani Y, Ogata K (1977) Derepression of FAD pyrophosphorylase and flavin changes during growth of Kloeckera sp. no. 2201 on methanol. Agric Biol Chem 41(11):2215–2220
Sreekrishna K, Brankamp RG, Kropp KE, Blankenship DT, Tsay JT, Smith PL, Wierschke JD, Subramaniam A, Birkenberger LA (1997) Strategies for optimal synthesis and secretion of heterologous proteins in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Gene 190(1):55–62
Tschopp JF, Brust PF, Cregg JM, Stillman CA, Gingeras TR (1987a) Expression of the lacZ gene from two methanol-regulated promoters in Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res 15(9):3859–3876
Tschopp JF, Sverlow G, Kosson R, Craig W, Grinna L (1987b) High-level secretion of glycosylated invertase in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol 5(12):1305
Tyurin O, Kozlov D (2013) Novel inductor for the promoters of the methanol utilization pathway. In: Abstr. 26th Int. Conf. Yeast Genet Mol Biol, p. 211
Tyurin OV, Kozlov DG (2015) Deletion of the FLD gene in methylotrophic yeasts Komagataella phaffii and Komagataella kurtzmanii results in enhanced induction of the AOX1 promoter in response to either methanol or formate. Microbiol 84(3):408–411
Funding
The authors received funding from the Department of Biotechnology (Government of India) (grant BT/PR13831/BBE/117/68/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS and AN conceived and designed the research. AS performed the experiments. AS and AN wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that no human participants or animals were used for the purpose of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2.20 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Narang, A. The Mut+ strain of Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) expresses PAOX1 5 and 10 times faster than Muts and Mut− strains: evidence that formaldehyde or/and formate are true inducers of PAOX1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 7801–7814 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10793-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10793-8