Abstract
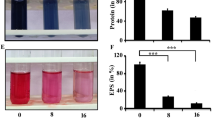
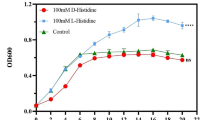
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm lifestyle exhibits multidrug resistance in chronic bacterial infections. Alternative antimicrobial compounds or combination drug therapies must be urgently developed. In this work, the antibiofilm effect of Ag nanoparticle (AgNP) combined with the quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) 4-nitropyridine N-oxide (4NPO) on P. aeruginosa biofilms was investigated. The biofilm biomass of P. aeruginosa was considerably reduced by 1.56–50 mg/L AgNP. However, 4NPO enhanced the ability of AgNP to inhibit P. aeruginosa biofilm formation (P < 0.05). The combination of AgNP with 4NPO could continuously inhibit biofilm development after 12 h, and 50 mg/L AgNP combined with 6.25 mg/L 4NPO thoroughly suppressed biofilm growth. The expression levels of QS genes and exopolysaccharide genes of biofilm treated with the combination of AgNP with 4NPO (AgNP–4NPO combination) were lower than those treated with AgNP alone (P < 0.05). Additional extracellular proteins and polysaccharides were determined in the samples treated with AgNP–4NPO combination. Based on proteomic analysis, this result was attributed to cell rupture caused by antimicrobial agents and intracellular materials released. The combination of the two antimicrobial agents could weaken the swimming ability of bacterial cells by damaging bacterial flagella and blocking rhlA gene expression. Thus, AgNP combined with QSI showed stronger antibiofilm ability than AgNP alone. These results may contribute to the development of antimicrobial agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurore V, Caldana F, Blanchard M, Kharoubi HS, Lannes N, Mantel PY, Filgueira L, Walch M (2018) Silver-nanoparticles increase bactericidal activity and radical oxygen responses against bacterial pathogens in human osteoclasts. Nanomedicine-UK 14(2):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2017.11.006
Bernardes EVT, Charron-Mazenod L, Reading DJ, Reckseidler-Zenteno SL, Lewenza S (2017) Exopolysaccharide-repressing small molecules with antibiofilm and antivirulence activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Ch 61:e01997–e01165. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01997-16
Bhargava A, Pareek V, Choudhury SR, Panwar J, Karmakar S (2018) Superior bactericidal efficacy of fucose-functionalized silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and prevention of its colonization on urinary catheters. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(35):29325–29337. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09475
Boursier ME, Moore JD, Heitman KM, Shepardson-Fungairino SP, Combs JB, Koenig LC, Shin D, Brown EC, Nagarajan R, Blackwell HE (2018) Structure-function analyses of the N-butanoyl l-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal define features critical to activity in RhlR. ACS Chem Biol 13(9):2655–2662. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.8b00577
Burkart M, Toguchi A, Harshey RM (1998) The chemotaxis system, but not chemotaxis, is essential for swarming motility in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(5):2568–2573
Chen M, Yu Q, Sun H (2013) Novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of biofilm related infections. Int J Mol Sci 14(9):18488–18501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140918488
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Edit 52(6):1636–1653. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205923
Choi O, Yu C, Fernandez GE, Hu Z (2010) Interactions of nanosilver with Escherichia coli cells in planktonic and biofilm cultures. Water Res 44(20):6095–6103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.069
Dakal TC, Kumar A, Majumdar RS, Yadav V (2016) Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front Microbiol 7:1831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831
Davies J, Spiegelman GB, Yim G (2006) The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Curr Opin Microbiol 9(5):445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2006.08.006
Deziel E, Lepine F, Milot S, Villemur R (2003) rhlA is required for the production of a novel biosurfactant promoting swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 3-(3-hydroxyalkanoyloxy)alkanoic acids (HAAs), the precursors of rhamnolipids. Microbiol-SGM 149(8):2005–2013. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.26154-0
Flemming H, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2415
Flemming H, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2016) Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14(9):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
Folkesson A, Jelsbak L, Yang L, Johansen HK, Ciofu O, Hoiby N, Molin S (2012) Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis airway: an evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(12):841–851. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2907
Franci G, Falanga A, Galdiero S, Palomba L, Rai M, Morelli G, Galdiero M (2015) Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20(5):8856–8874. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20058856
Franklin MJ, Nivens DE, Weadge JT, Howell PL (2011) Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular polysaccharides, alginate, Pel, and Psl. Front Microbiol 2(167). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2011.00167
Gutierrez M, Choi MH, Tian B, Xu J, Rho JK, Kim MO, Cho Y, Yoon SC (2013) Simultaneous inhibition of rhamnolipid and polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthesis and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by 2-bromoalkanoic acids: effect of inhibitor alkyl-chain-length. PLoS One 8(e739869):e73986. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073986
Habash MB, Goodyear MC, Park AJ, Surette MD, Vis EC, Harris RJ, Khursigara CM (2017) Potentiation of tobramycin by silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Ch 61:e00415–e01711. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00415-17
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):95–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro821
Hassett DJ, Korfhagen TR, Irvin RT, Schurr MJ, Sauer K, Lau GW, Sutton MD, Yu H, Hoiby N (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections in cystic fibrosis: insights into pathogenic processes and treatment strategies. Expert Opin Ther Tar 14(2):117–130. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728220903454988
Hayat S, Muzammil S, Shabana AB, Siddique MH, Saqalein M, Nisar MA (2019) Quorum quenching: role of nanoparticles as signal jammers in Gram-negative bacteria. Future Microbiol 14(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2018-0257
Kim K, Kim YU, Koh BH, Hwang SS, Kim SH, Lepine F, Cho YH, Lee GR (2010) HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Immunology 129(4):578–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03160.x
Le Ouay B, Stellacci F (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: a surface science insight. Nano Today 10(3):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2015.04.002
Lee J, Zhang L (2015) The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 6(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
Li WR, Ma YK, Xie XB, Shi QS, Wen X, Sun TL, Peng H (2018) Diallyl disulfide from garlic oil inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing systems and corresponding virulence factors. Front Microbiol 9:3222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.03222
Lin L, Rosenberg M, Taylor KG, Doyle RJ (1995) Kinetic analysis of ammonium sulfate dependent aggregation of bacteria. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 5(3):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7765(95)01189-P
Lok C, Ho C, Chen R, He Q, Yu W, Sun H, Tam PK, Chiu J, Che C (2007) Silver nanoparticles: partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem 12(4):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-007-0208-z
Loo CY, Young PM, Cavaliere R, Whitchurch CB, Lee WH, Rohanizadeh R (2014) Silver nanoparticles enhance Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm detachment. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 40(6):719–729. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2013.780182
Mampel J, Spirig T, Weber SS, Haagensen J, Molin S, Hilbi H (2006) Planktonic replication is essential for biofilm formation by Legionella pneumophila in a complex medium under static and dynamic flow conditions. Appl Environ Microb 72(4):2885–2895. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.4.2885-2895.2006
Mikutta R, Baumgartner A, Schippers A, Haumaier L, Guggenberger G (2012) Extracellular polymeric substances from Bacillus subtilis associated with minerals modify the extent and rate of heavy metal sorption. Environ Sci Technol 46(7):3866–3873. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204471x
Miller KP, Wang L, Benicewicz BC, Decho AW (2015) Inorganic nanoparticles engineered to attack bacteria. Chem Soc Rev 44(21):7787–7807. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00041f
Niu C, Gilbert ES (2004) Colorimetric method for identifying plant essential oil components that affect biofilm formation and structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(12):6951–6956. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.12.6951-6956.2004
Nowack B, Krug HF, Height M (2011) 120 years of nanosilver history: implications for policy makers. Environ Sci Technol 45(4):1177–1183. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103316q
O’Loughlin CT, Miller LC, Siryaporn A, Drescher K, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL (2013) A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(44):17981–17986. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1316981110
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microb 73(6):1712–1720. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Panmanee W, Charoenlap N, Atichartpongkul S, Mahavihakanont A, Whiteside MD, Winsor G, Brinkman FSL, Mongkolsuk S, Hassett DJ (2017) The OxyR-regulated phnW gene encoding 2-aminoethylphosphonate:pyruvate aminotransferase helps protect Pseudomonas aeruginosa from tert-butyl hydroperoxide. PLoS One 12(12):e189066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189066
Radzig MA, Nadtochenko VA, Koksharova OA, Kiwi J, Lipasova VA, Khmel IA (2013) Antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles on gram-negative bacteria: influence on the growth and biofilms formation, mechanisms of action. Colloid Surface B 102:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.039
Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A (2009) Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
Sharma IM, Petchiappan A, Chatterji D (2014) Quorum sensing and biofilm formation in mycobacteria: role of c-di-GMP and methods to study this second messenger. IUBMB Life 66(12):823–834. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1339
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006) Chemical-equilibrium-based model for describing the strength of sludge: taking hydrogen-producing sludge as an example. Environ Sci Technol 40(4):1280–1285
Singh N, Rajwade J, Paknikar KM (2018) Transcriptome analysis of silver nanoparticles treated Staphylococcus aureus reveals potential targets for biofilm inhibition. Colloids Surf B 175:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.032
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(1):177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012
Surmeneva MA, Sharonova AA, Chernousova S, Prymak O, Loza K, Tkachev MS, Shulepov IA, Epple M, Surmenev RA (2017) Incorporation of silver nanoparticles into magnetron-sputtered calcium phosphate layers on titanium as an antibacterial coating. Colloid Surface B 156:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.016
Voogd CE, van der Stel JJ, Jacobs JJ (1980) The mutagenic action of quindoxin, carbadox, olaquindox and some other N-oxides on bacteria and yeast. Mutat Res 78(3):233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(80)90104-4
Xiao X, Zhu W, Liu Q, Yuan H, Li W, Wu L, Li Q, Yu H (2016) Impairment of biofilm formation by TiO2 photocatalysis through quorum quenching. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11895–11902. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6603134
Xiong J, Koopal LK, Tan W, Fang L, Wang M, Zhao W, Liu F, Zhang J, Weng L (2013) Lead binding to soil fulvic and humic acids: NICA-Donnan modeling and XAFS spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 47(20):11634–11642. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402123v
Yim G, Wang H, Davies J (2006) The truth about antibiotics. Int J Med Microbiol 296(2–3):163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.039
Zeng Z, Qian L, Cao L, Tan H, Huang Y, Xue X, Shen Y, Zhou S (2008) Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(1):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1406-5
Zhang P, Xu X, Chen Y, Xiao M, Feng B, Tian K, Chen Y, Dai Y (2018a) Protein corona between nanoparticles and bacterial proteins in activated sludge: characterization and effect on nanoparticle aggregation. Bioresour Technol 250:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.008
Zhang P, Guo J, Yan P, Chen Y, Wang W, Dai Y, Fang F, Wang G, Shen Y (2018b) Dynamic dispersal of surface layer biofilm induced by nanosized TiO2 based on surface plasmon resonance and waveguide. Appl Environ Microb 84(9):e00047–e00018. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00047-18
Zhang P, Chen Y, Qiu J, Dai Y, Feng B (2019) Imaging the microprocesses in biofilm matrices. Trends Biotechnol 37(2):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.07.006
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51708475), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (2018JJ3496), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, China (819MS139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 361 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Li, JH., Zi, SF. et al. AgNP combined with quorum sensing inhibitor increased the antibiofilm effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 6195–6204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09905-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09905-w