Abstract
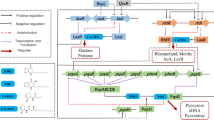
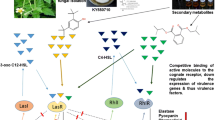
Pseudomonas aeruginosa depends on its quorum sensing (QS) system for its virulence factors’ production and biofilm formation. Biofilms of P. aeruginosa on the surface of indwelling catheters are often resistant to antibiotic therapy. Alternative approaches that employ QS inhibitors alone or in combination with antibiotics are being developed to tackle P. aeruginosa infections. Here, we have studied the mechanism of action of 3-Phenyllactic acid (PLA), a QS inhibitory compound produced by Lactobacillus species, against P. aeruginosa PAO1. Our study revealed that PLA inhibited the expression of virulence factors such as pyocyanin, protease, and rhamnolipids that are involved in the biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PAO1. Swarming motility, another important criterion for biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PAO1, was also inhibited by PLA. Gene expression, mass spectrometric, functional complementation assays, and in silico data indicated that the quorum quenching and biofilm inhibitory activities of PLA are attributed to its ability to interact with P. aeruginosa QS receptors. PLA antagonistically binds to QS receptors RhlR and PqsR with a higher affinity than its cognate ligands N-butyryl-l-homoserine lactone (C4–HSL) and 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS; Pseudomonas quinolone signal). Using an in vivo intraperitoneal catheter-associated medaka fish infection model, we proved that PLA inhibited the initial attachment of P. aeruginosa PAO1 on implanted catheter tubes. Our in vitro and in vivo results revealed the potential of PLA as anti-biofilm compound against P. aeruginosa.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allesen-Holm M, Barken KB, Yang L, Klausen M, Webb JS, Kjelleberg S, Molin S, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2006) A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 59:1114–1128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.05008.x
Babic F, Venturi V, Maravic-Vlahovicek G (2010) Tobramycin at subinhibitory concentration inhibits the RhlI/R quorum sensing system in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa environmental isolate. BMC Infect Dis 10:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-10-148
Bauer JS, Hauck N, Christof L, Mehnaz S, Gust B, Gross H (2016) The systematic investigation of the quorum sensing system of the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp. aurantiaca PB-St2 unveils aurI to be a biosynthetic origin for 3-oxo-homoserine lactones. PLoS One 11:e0167002. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167002
Baysse C, Cullinane M, Denervaud V, Burrowes E, Dow JM, Morrissey JP, Tam L, Trevors JT, O'Gara F (2005) Modulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through alteration of membrane properties. Microbiology 151:2529–2542. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28185-0
Bhattacharya M, Wozniak DJ, Stoodley P, Hall-Stoodley L (2015) Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 13(12):1499–1516. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.2015.1100533
Chatterjee M, Anju CP, Biswas L, Anil-Kumar V, Gopi-Mohan C, Biswas R (2016) Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alternative therapeutic options. Int J Med Microbiol 306:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2015.11.004
Chifiriuc MC, Ditu LM, Banu O, Bleotu C, Dracea O, Bucur M, Larion C, Israil AM, Lazar V (2009) Subinhibitory concentrations of phenyl lactic acid interfere with the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol 68:27–33
Conibear TC, Collins SL, Webb JS (2009) Role of mutation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. PLoS One 4:e6289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006289
Das T, Manefield M (2012) Pyocyanin promotes extracellular DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One 7:e46718. https://doi.org/10.1371/ journal.pone.0046718
Davey ME, Caiazza NC, O'Toole GA (2003) Rhamnolipid surfactant production affects biofilm architecture in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 185:1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.185.3.1027-1036.2003
Dekimpe V, Deziel E (2009) Revisiting the quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the transcriptional regulator RhlR regulates LasR-specific factors. Microbiology 155:712–723. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.022764-0
Deligianni E, Pattison S, Berrar D, Ternan NG, Haylock RW, Moore JE, Elborn SJ, Dooley JS (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolates of similar RAPD genotype exhibit diversity in biofilm forming ability in vitro. BMC Microbiol 10:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-38
Diggle SP, Stacey RE, Dodd C, Camara M, Williams P, Winzer K (2006) The galactophilic lectin, LecA, contributes to biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol 8:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.001001.x
El-Mowafy SA, Shaaban MI, Abd El Galil KH (2014) Sodium ascorbate as a quorum sensing inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 117:1388–1399. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12631
Fothergill JL, Neill DR, Loman N, Winstanley C, Kadioglu A (2014) Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation in the nasopharyngeal reservoir leads to migration and persistence in the lungs. Nat Commun 5:4780. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5780
Glessner A, Smith RS, Iglewski BH, Robinson JB (1999) Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of twitching motility. J Bacteriol 181:1623–1629
Gnanadhas DP, Elango M, Datey A, Chakravortty D (2015) Chronic lung infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm is cured by L-methionine in combination with antibiotic therapy. Sci Rep 5:16043. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16043
Ilangovan A, Fletcher M, Rampioni G, Pustelny C, Rumbaugh K, Heeb S, Camara M, Truman A, Chhabra SR, Emsley J, Williams P (2013) Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR). PLoS Pathog 9:e1003508. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003508
Jakobsen TH, van Gennip M, Phipps RK, Shanmugham MS, Christensen LD, Alhede M, Skindersoe ME, Rasmussen TB, Friedrich K, Uthe F, Jensen PO, Moser C, Nielsen KF, Eberl L, Larsen TO, Tanner D, Hoiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M (2012) Ajoene, a sulfur-rich molecule from garlic, inhibits genes controlled by quorum sensing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:2314–2325. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.05919-11
Janissen R, Murillo DM, Niza B, Sahoo PK, Nobrega MM, Cesar CL, Temperini ML, Carvalho HF, de Souza AA, Cotta MA (2015) Spatiotemporal distribution of different extracellular polymeric substances and filamentation mediate Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm formation. Sci Rep 5:9856. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09856
Jayaseelan S, Ramaswamy D, Dharmaraj S (2014) Pyocyanin: production, applications, challenges and new insights. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1552-5
Jimenez PN, Koch G, Thompson JA, Xavier KB, Cool RH, Quax WJ (2012) The multiple signaling systems regulating virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:46–65. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.05007-11
Kim HS, Park HD (2013) Ginger extract inhibits biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. PLoS One 8:e76106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076106
Kim K, Kim YU, Koh BH, Hwang SS, Kim SH, Lepine F, Cho YH, Lee GR (2009) HHQ and PQS, two Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecules, down-regulate the innate immune responses through the nuclear factor-KB pathway. Immunology 129:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03160.x
Kim T, Duong T, Wu CA, Choi J, Lan N, Kang SW, Lokanath NK, Shin D, Hwang HY, Kim KK (2014) Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of Escherichia coli SdiA, a quorum-sensing receptor. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70:694–707. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713032355
Kim HS, Lee SH, Byun Y, Park HD (2015) 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci Rep 5:8656. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08656
Kiruthika V, Maya S, Suresh MK, Kumar VA, Jayakumar R, Biswas R (2015) Comparative efficacy of chloramphenicol loaded chondroitin sulfate and dextran sulfate nanoparticles to treat intracellular Salmonella infections. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 127:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.01.012
Kohler T, Curty LK, Barja F, van Delden C, Pechere JC (2000) Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J Bacteriol 182:5990–5996. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.182.21.5990-5996.2000
Lee J, Zhang L (2015) The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 6:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
Lee JH, Kim YG, Cho MH, Kim JA, Lee J (2012) 7-Fluoroindole as an antivirulence compound against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 329:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02500.x
Leidal KG, Munson KL, Denning GM (2001) Small molecular weight secretory factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa have opposite effects on IL-8 and RANTES expression by human airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.25.2.4273
Liang H, Li L, Dong Z, Surette MG, Duan K (2008) The YebC family protein PA0964 negatively regulates the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal system and pyocyanin production. J Bacteriol 190:6217–6227. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00428-08
Lister JL, Horswill AR (2014) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:178. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2014.00178
Malvi P, Chaube B, Singh SV, Mohammad N, Pandey V, Vijayakumar MV, Radhakrishnan RM, Vanuopadath M, Nair SS, Nair BG, Bhat MK (2016) Weight control interventions improve therapeutic efficacy of dacarbazine in melanoma by reversing obesity-induced drug resistance. Cancer Metab 4:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40170-016-0162-8
Maya S, Indulekha S, Sukhithasri V, Smitha KT, Nair SV, Jayakumar R, Biswas R (2012) Efficacy of tetracycline encapsulated O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles against intracellular infections of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Biol Macromol 51:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.06.009
McKnight SL, Iglewski BH, Pesci EC (2000) The Pseudomonas quinolone signal regulates rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 182:2702–2708
Mohammad N, Singh SV, Malvi P, Chaube B, Athavale D, Vanuopadath M, Nair SS, Nair B, Bhat MK (2015) Strategy to enhance efficacy of doxorubicin in solid tumor cells by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin: involvement of p53 and Fas receptor ligand complex. Sci Rep 5:11853. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11853
Moscoso JA, Jaeger T, Valentini M, Hui K, Jenal U, Filloux A (2014) The diguanylate cyclase SadC is a central player in Gac/Rsm-mediated biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 196:4081–4088. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01850-14
Mulcahy H, Charron-Mazenod L, Lewenza S (2008) Extracellular DNA chelates cations and induces antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000213. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000213
Nair SV, Baranwal G, Chatterjee M, Sachu A, Vasudevan AK, Bose C, Banerji A, Biswas R (2016) Antimicrobial activity of plumbagin, a naturally occurring naphthoquinone from Plumbago rosea, against Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. Int J Med Microbiol 306:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.05.004
O'Loughlin CT, Miller LC, Siryaporn A, Drescher K, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL (2013) A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17981–17986. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1316981110
O'May C, Tufenkji N (2011) The swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is blocked by cranberry proanthocyanidins and other tannin-containing materials. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3061–3067. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02677-10
Prithiviraj B, Bais HP, Weir T, Suresh B, Najarro EH, Dayakar BV, Schweizer HP, Vivanco JM (2005) Down regulation of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by salicylic acid attenuates its virulence on Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans. Infect Immun 73:5319–5328. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.9.5319-5328.2005
Rada B, Jendrysik MA, Pang L, Hayes CP, Yoo DG, Park JJ, Moskowitz SM, Malech HL, Leto TL (2013) Pyocyanin-enhanced neutrophil extracellular trap formation requires the NADPH oxidase. PLoS One 8:e54205. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054205
Rasmussen TB, Skindersoe ME, Bjarnsholt T, Phipps RK, Christensen KB, Jensen PO, Andersen JB, Koch B, Larsen TO, Hentzer M, Eberl L, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2005) Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 151:1325–1340. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27715-0
Saint-Cricq P, Deshayes S, Zink JI, Kasko AM (2015) Magnetic field activated drug delivery using thermodegradable azo-functionalised PEG-coated core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nano 7:13168–13172. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr03777h
Sarabhai S, Sharma P, Capalash N (2013) Ellagic acid derivatives from Terminalia chebula Retz. downregulate the expression of quorum sensing genes to attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 virulence. PLoS One 8:e53441. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053441
Steindler L, Bertani I, De Sordi L, Schwager S, Eberl L, Venturi V (2009) LasI/R and RhlI/R quorum sensing in a strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa beneficial to plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5131–5140. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02914-08
Stiefel P, Schmidt-Emrich S, Maniura-Weber K, Ren Q (2015) Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol 15:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-015-0376-x
Tielen P, Rosenau F, Wilhelm S, Jaeger KE, Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) Extracellular enzymes affect biofilm formation of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 156:2239–2252. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.037036-0
Ueda A, Wood TK (2009) Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase TpbA (PA3885). PLoS Pathog 5:e1000483. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000483
Varma P, Nisha N, Dinesh KR, Kumar AV, Biswas R (2011) Anti-infective properties of Lactobacillus fermentum against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 20:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1159/000328512
Voggu L, Schlag S, Biswas R, Rosenstein R, Rausch C, Gotz F (2006) Microevolution of cytochrome bd oxidase in Staphylococci and its implication in resistance to respiratory toxins released by Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol 188:8079–8086. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00858-06
Wilhelm S, Gdynia A, Tielen P, Rosenau F, Jaeger KE (2007) The autotransporter esterase EstA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for rhamnolipid production, cell motility, and biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 189:6695–6703. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00023-07
Wu H, Song Z, Hentzer M, Andersen JB, Molin S, Givskov M, Hoiby N (2004) Synthetic furanones inhibit quorum-sensing and enhance bacterial clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. J Antimicrob Chemother 53:1054–1061. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkh223
Wu AM, Wu JH, Singh T, Liu JH, Tsai MS, Gilboa-Garber N (2006) Interactions of the fucose-specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin, PA-IIL, with mammalian glycoconjugates bearing polyvalent Lewis(a) and ABH blood group glycotopes. Biochimie 88:1479–1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.05.004
Wu H, Moser C, Wang HZ, Hoiby N, Song ZJ (2015) Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. Int J Oral Sci 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2014.65
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Gaurav Baranwal for his technical support and Centre for Nanosciences and Molecular Medicine, AIMS-Cochin, India, for infrastructural support. C.G.M. is grateful to Centre for Nanosciences and Molecular Medicine, AIMS-Cochin for computational infrastructure support. The authors acknowledge Amrita Agilent Analytical Research Centre, Amrita School of Biotechnology, Kollam, India, for mass spectrometric data collection and analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) grant (SR/S0/HS/0011/2012) from the Department of Science and Technology, India to R.B. and Indian Council of Medical Research SRF fellowship (3/1/2/16/2013-Nut.) to M.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Ethical statement
All experiments using medaka fish were conducted after obtaining approval from the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Cochin-682041, Kerala, India. All animal experimental guidelines were strictly followed and all efforts were made to minimize animal suffering.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 417 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, M., D’Morris, S., Paul, V. et al. Mechanistic understanding of Phenyllactic acid mediated inhibition of quorum sensing and biofilm development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 8223–8236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8546-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8546-4