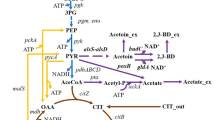
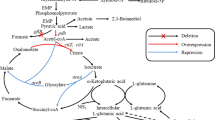
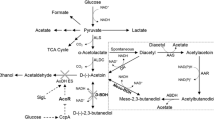
Abstract
Bacillus licheniformis WX-02 is a well-studied strain to produce poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) with numerous applications. This study is to improve WX-02 strain’s capability of assimilating glycerol, a major byproduct of biofuels industries, through metabolic manipulation. Through gene knockout, the GlpK pathway was identified as the sole functional glycerol catabolism pathway, while the DhaK pathway was inactive for this strain under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. The enhancement of glycerol utilization was attempted by substituting the native glpFK promoter with the constitutive promoter (P43), ytzE promoter (PytzE), and bacABC operon promoter (PbacA), respectively. The glycerol consumptions of the corresponding mutant strains WX02-P43glpFK, WX02-PytzEglpFK, and WX02-PbacAglpFK were 30.9, 26.42, and 18.8% higher than that of the WX-02 strain, respectively. The γ-PGA concentrations produced by the three mutant strains were 33.71, 23.39, and 30.05% higher than that of WX-02 strain, respectively. When biodiesel-derived crude glycerol was used as the carbon source, the mutant WX02-P43glpFK produced 16.63 g L−1 of γ-PGA, with a productivity of 0.35 g L−1 h−1. Collectively, this study demonstrated that glycerol can be used as an effective substrate for producing γ-PGA by metabolic engineering B. licheniformis strains.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj I, Singhal R (2011) Poly (glutamic acid)—an emerging biopolymer of commercial interest. Bioresour Technol 102:5551–5561. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.047
Bizzini A, Zhao C, Budin-Verneuil A, Sauvageot N, Giard J, Auffray Y, Hartke A (2010) Glycerol is metabolized in a complex and strain-dependent manner in Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 192:779–785. doi:10.1128/JB.00959-09
Chen Y, Li S, Xiong J, Li Z, Bai J, Zhang L, Ye Q, Ouyang P, Ying H (2010) The mechanisms of citrate on regulating the distribution of carbon flux in the biosynthesis of uridine 5′-monophosphate by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:75–81. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2287-y
Chen Z, Liu D, (2016) Toward glycerol biorefinery: metabolic engineering for the production of biofuels and chemicals from glycerol. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:205
Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2013) Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol: a platform for renewable fuels and chemicals. Trends Biotechnol 31:20–28. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.10.006
Cromwick AM, Birrer GA, Gross RA (1996) Effects of pH and aeration on gamma-poly(glutamic acid) formation by Bacillus licheniformis in controlled batch fermentor cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 50:222–227. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19960420)50:2<222::AID-BIT10>3.0.CO;2-P
da Silva GP, Mack M, Contiero J (2009) Glycerol: a promising and abundant carbon source for industrial microbiology. Biotechnol Adv 27:30–39. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.07.006
Daniel R, Stuertz K, Gottschalk G (1995) Biochemical and molecular characterization of the oxidative branch of glycerol utilization by Citrobacter freundii. J Bacteriol 177:4392–4401. doi:10.1128/jb.177.15.4392-4401.1995
Darbon E, Servant P, Poncet S, Deutscher J (2002) Antitermination by GlpP, catabolite repression via CcpA and inducer exclusion triggered by P-GlpK dephosphorylation control Bacillus subtilis glpFK expression. Mol Microbiol 43:1039–1052. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02800.x
Dobson R, Gray V, Rumbold K (2012) Microbial utilization of crude glycerol for the production of value-added products. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:217–226. doi:10.1007/s10295-011-1038-0
Du G, Yang G, Qu Y, Chen J, Lun S (2005) Effects of glycerol on the production of poly(γ-glutamic acid) by Bacillus licheniformis. Process Biochem 40:2143–2147. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.08.005
EC L (1976) Glycerol dissimilation and its regulation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 30:535–578. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002535
Goto A, Kunioka M (1992) Biosynthesis and hydrolysis of poly(gamma-glutamic acid) from Bacillus subtilis IF03335. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 56:1031–1035. doi:10.1271/bbb.56.1031
Gutknecht R, Beutler R, Garcia-Alle LF, Baumann U, Erni B (2001) The dihydroxyacetone kinase of Escherichia coli utilizes a phosphoprotein instead of ATP as phosphoryl donor. The EMBO J 20:2480–2486. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.10.2480
Holmberg C, Beijer L, Rutberg B, Rutberg L (1990) Glycerol catabolism in Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence of the genes encoding glycerol kinase (glpK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (glpD). J Gen Microbiol 136:2367–2375. doi:10.1099/00221287-136-12-2367
Jacobs NJ, VanDemark PJ (1960) Comparison of the mechanism of glycerol oxidation in aerobically and anaerobically grown Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 79:532–538
Jeong JH, Kim JN, Wee YJ, Ryu HW (2010) The statistically optimized production of poly(gamma-glutamic acid) by batch fermentation of a newly isolated Bacillus subtilis RKY3. Bioresour Technol 101:4533–45339. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.080
Ko YH, Gross RA (1998) Effects of glucose and glycerol on gamma-poly(glutamic acid) formation by Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 9945a. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:430–437. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19980220)57:4<430::AID-BIT6>3.0.CO;2-N
Li X, Gou X, Long D, Ji Z, Hu L, Xu D, Liu J, Chen S (2014) Physiological and metabolic analysis of nitrate reduction on poly-gamma-glutamic acid synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. Arch Microbiol 196:791–799. doi:10.1007/s00203-014-1014-y
Luo Z, Guo Y, Liu J, Qiu H, Zhao M, Zou W, Li S (2016) Microbial synthesis of poly-gamma-glutamic acid: current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:134. doi:10.1186/s13068-016-0537-7
Mattam AJ, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R, Yazdani SS (2013) Fermentation of glycerol and production of valuable chemical and biofuel molecules. Biotechnol Lett 35:831–842. doi:10.1007/s10529-013-1240-4
Murarka A, Dharmadi Y, Yazdani SS, Gonzalez R (2008) Fermentative utilization of glycerol by Escherichia coli and its implications for the production of fuels and chemicals. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1124–1135. doi:10.1128/AEM.02192-07
Nikel PI, Kim J, de Lorenzo V (2014) Metabolic and regulatory rearrangements underlying glycerol metabolism in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 16:239–254. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12224
Ogunleye A, Bhat A, Irorere VU, Hill D, Williams C, Radecka I (2015) Poly-gamma-glutamic acid: production, properties and applications. Microbiology 161:1–17. doi:10.1099/mic.0.081448-0
Oren A (2017) Glycerol metabolism in hypersaline environments. Environ Microbiol 19:851–863. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13493
Qi G, Kang Y, Li L, Xiao A, Zhang S, Wen Z, Xu D, Chen S (2014) Deletion of meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene budC for enhanced D-2,3-butanediol production in Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:16. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-7-16
Qiu Y, Xiao F, Wei X, Wen Z, Chen S (2014) Improvement of lichenysin production in Bacillus licheniformis by replacement of native promoter of lichenysin biosynthesis operon and medium optimization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8895–8903. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5978-y
Qiu Y, Zhang J, Li L, Wen Z, Nomura CT, Wu S, Chen S (2016) Engineering Bacillus licheniformis for the production of meso-2,3-butanediol. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:117. doi:10.1186/s13068-016-0522-1
Ruffing AM, Chen RR (2011) Citrate stimulates oligosaccharide synthesis in metabolically engineered Agrobacterium sp. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:851–866. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9179-1
Sanda F, Fujiyama T, Endo T (2001) Chemical synthesis of poly-γ-glutamic acid by polycondensation of γ-glutamic acid dimer: synthesis and reaction of poly-γ-glutamic acid methyl ester. J Polym Sci Pol Chem 39:732–741. doi:10.1002/1099-0518(20010301)39:5<732::AID-POLA1045>3.0.CO;2-P
Shih IL, Van YT, Chang YN (2002) Application of statistical experimental methods to optimize production of poly(γ-glutamic acid) by Bacillus licheniformis CCRC 12826. Enzym Microb Technol 31:213–220. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00103-5
Shih IL, Wu PJ, Shieh CJ (2005) Microbial production of a poly(γ-glutamic acid) derivative by Bacillus subtilis. Process Biochem 40:2827–2832. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.12.009
Sonenshein AL (2007) Control of key metabolic intersections in Bacillus subtilis. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:917–927. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1772
Tian G, Fu J, Wei X, Ji Z, Ma X, Qi G, Chen S (2014) Enhanced expression of pgdS gene for high production of poly-γ-glutamic aicd with lower molecular weight in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. J Chem Technol Biotech 89:1825–1832. doi:10.1002/jctb.4261
Tsau JL, Guffanti AA, Montville TJ (1992) Conversion of pyruvate to acetoin helps to maintain pH homeostasis in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 5:891–894
Wang Q, Chen S, Zhang J, Sun M, Liu Z, Yu Z (2008) Co-producing lipopeptides and poly-gamma-glutamic acid by solid-state fermentation of Bacillus subtilis using soybean and sweet potato residues and its biocontrol and fertilizer synergistic effects. Bioresour Technol 99:3318–3323. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.05.052
Wang J, Yuan H, Wei X, Chen J, Chen S (2016) Enhancement of poly-γ-glutamic acid production by alkaline pH stress treatment in Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. J Chem Technol Biotech 91:2399–2403. doi:10.1002/jctb.4822
Wang Y, Tao F, Xin B, Liu H, Gao Y, Zhou NY, Xu P (2017) Switch of metabolic status: redirecting metabolic flux for acetoin production from glycerol by activating a silent glycerol catabolism pathway. Metab Eng 39:90–101. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2016.10.020
Wei X, Ji Z, Chen S (2010) Isolation of halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis WX-02 and regulatory effects of sodium chloride on yield and molecular sizes of poly-gamma-glutamic acid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:1332–1340. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8681-1
Wu Q, Xu H, Shi N, Yao J, Li S, Ouyang P (2008) Improvement of poly(gamma-glutamic acid) biosynthesis and redistribution of metabolic flux with the presence of different additives in Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 0833. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 79:527–535. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1462-x
Wu Q, Xu H, Liang J, Yao J (2010) Contribution of glycerol on production of poly(gamma-glutamic acid) in Bacillus subtilis NX-2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:386–392. doi:10.1007/s12010-008-8320-2
Xue GP, Johnson JS, Dalrymple BP (1999) High osmolarity improves the electro-transformation efficiency of the gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis. J Microbiol Meth 34:183–191
Yang F, Hanna M, Sun R (2012) Value-added uses for crude glycerol—a byproduct of biodiesel production. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:13. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-5-13
Yangtse W, Zhou Y, Lei Y, Qiu Y, Wei X, Ji Z, Qi G, Yong Y, Chen L, Chen S (2012) Genome sequence of Bacillus licheniformis WX-02. J Bacteriol 194:3561–3562. doi:10.1128/JB.00572-12
Yao J, Xu H, Shi N, Cao X, Feng X, Li S, Ouyang P (2010) Analysis of carbon metabolism and improvement of gamma-polyglutamic acid production from Bacillus subtilis NX-2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:2332–2341. doi:10.1007/s12010-009-8798-2
Yao R, Liu Q, Hu H, Wood TK, Zhang X (2015) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance acetol production from glycerol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:7945–7952. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6732-9
Yazdani SS, Gonzalez R (2007) Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol: a path to economic viability for the biofuels industry. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:213–219. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2007.05.002
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, No. 2015CB150505), and the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (No.2013AA102801-52).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C Zhu and S Chen designed and supervised the study. Y Zhan and B Sheng performed the experiments. Y Zhan, C Zhu, D Cai, Q Wang, Z Wen, and S Chen analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
All the strains, plasmids and primers used in this study were listed as the Supplementary Materials (Tables S1-S3). The result of mRNA relative transcription levels of TCA cycle, codY, ccpC, and gltT in WX02-P43glpFK was listed in the Supplementary Materials (Fig. S1).. This information is available free of charge via the Internet http://link.springer.com/journal/253
ESM 1
(PDF 265 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, Y., Zhu, C., Sheng, B. et al. Improvement of glycerol catabolism in Bacillus licheniformis for production of poly-γ-glutamic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7155–7164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8459-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8459-2