Abstract
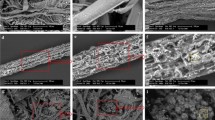
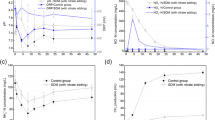
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor is one of the most applied technologies for various high-strength wastewater treatments. The present study analysed the microbial community changes in UASB granules during the transition from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions. Dynamicity of microbial community in granules was analysed using high-throughput sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicons, and the results showed that the temperature strictly determines the diversity of the microbial consortium. It was demonstrated that most of the microbes which were present in the initial mesophilic community were not found in the granules after the transition to thermophilic conditions. More specifically, only members from family Anaerolinaceae managed to tolerate the temperature change and contributed in maintaining the physical integrity of granular structure. On the contrary, new hydrolytic and fermentative bacteria were quickly replacing the old members in the community. A direct result from this abrupt change in the microbial diversity was the accumulation of volatile fatty acids and the concomitant pH drop in the reactor inhibiting the overall anaerobic digestion process. Nevertheless, by maintaining deliberately the pH levels at values higher than 6.5, a methanogen belonging to Methanoculleus genus emerged in the community enhancing the methane production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelidaki I, Sanders W (2004) Assessment of the anaerobic biodegradability of macropollutants. Re/Views Environ Sci {&} Bio/Technology 3:117–129
Angelidaki I, Ellegaard L, Ahring BK (1992) Compact automated displacement gas metering system for measurement of low gas rates from laboratory fermentors. Biotechnol Bioeng 39:351–353
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association
Azman S, Khadem AF, Van Lier JB, Zeeman G, Plugge CM (2015) Presence and role of anaerobic hydrolytic microbes in conversion of lignocellulosic biomass for biogas production. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:2523–2564
Bassani I, Kougias PG, Treu L, Angelidaki I (2015) Biogas upgrading via hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis in two-stage continuous stirred tank reactors at mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Environ Sci Technol 49:12585–12593
Bouallagui H, Haouari O, Touhami Y, Ben Cheikh R, Marouani L, Hamdi M (2004) Effect of temperature on the performance of an anaerobic tubular reactor treating fruit and vegetable waste. Process Biochem 39:2143–2148
Boušková A, Dohanyos M, Schmidt JE, Angelidaki I (2005) Strategies for changing temperature from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions in anaerobic CSTR reactors treating sewage sludge. Water Res 39:1481–1488
Bzducha-Wróbel A, Błażejak S, Molenda M, Reczek L (2015) Biosynthesis of β (1, 3)/(1, 6)-glucans of cell wall of the yeast Candidautilis ATCC 9950 strains in the culture media supplemented with deproteinated potato juice water and glycerol. Eur Food Res Technol 240:1023–1034
Campanaro S, Treu L, Kougias PG, Francisci D, Valle G, Angelidaki I (2016) Metagenomic analysis and functional characterization of the biogas microbiome using high throughput shotgun sequencing and a novel binning strategy. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:1
Carrillo-Reyes J, Celis LB, Alatriste-Mondragón F, Razo-Flores E (2014) Decreasing methane production in hydrogenogenic UASB reactors fed with cheese whey. Biomass Bioenergy 63:101–108
Castrillon L, Vázquez I, Maranon E, Sastre H (2002) Anaerobic thermophilic treatment of cattle manure in UASB reactors. Waste Manag Res 20:350–356
De Francisci D, Kougias PG, Treu L, Campanaro S, Angelidaki I (2015) Microbial diversity and dynamicity of biogas reactors due to radical changes of feedstock composition. Bioresour Technol 176:56–64
Fang H, Lau I (1996) Startup of thermophilic (55UC) UASB reactors using different mesophilic seed sludges. Water Sci Technol 34:445–452
Fang C, Boe K, Angelidaki I (2011) Biogas production from potato-juice, a by-product from potato-starch processing, in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) and expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactors. Bioresour Technol 102:5734–5741
Frank JA, Pan Y, Tooming-Klunderud A, Eijsink VGH, McHardy AC, Nederbragt AJ, Pope PB (2016) Improved metagenome assemblies and taxonomic binning using long-read circular consensus sequence data. Sci. Rep 6:25373
Khemkhao M, Nuntakumjorn B, Techkarnjanaruk S, Phalakornkule C (2012) UASB performance and microbial adaptation during a transition from mesophilic to thermophilic treatment of palm oil mill effluent. J Environ Manag 103:74–82
Kougias PG, De Francisci D, Treu L, Campanaro S, Angelidaki I (2014) Microbial analysis in biogas reactors suffering by foaming incidents. Bioresour Technol 167:24–32
Kougias PG, Boe K, Einarsdottir ES, Angelidaki I (2015) Counteracting foaming caused by lipids or proteins in biogas reactors using rapeseed oil or oleic acid as antifoaming agents. Water Res 79:119–127
Kougias PG, Treu L, Campanaro S, Zhu X, Angelidaki I (2016) Dynamic functional characterization and phylogenetic changes due to long chain fatty acids pulses in biogas reactors. Sci Rep 6:28810
Liu Y, Balkwill DL, Aldrich HC, Drake GR, Boone DR (1999) Characterization of the anaerobic propionate-degrading syntrophs Smithella propionica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Syntrophobacter wolinii. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49:545–556
Lu X, Zhen G, Estrada AL, Chen M, Ni J, Hojo T, Kubota K, Li Y-Y (2015) Operation performance and granule characterization of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating wastewater with starch as the sole carbon source. Bioresour Technol 180:264–273
Luo G, De Francisci D, Kougias PG, Laura T, Zhu X, Angelidaki I (2015) New steady-state microbial community compositions and process performances in biogas reactors induced by temperature disturbances. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:3
Ma K, Liu X, Dong X (2005) Methanobacterium beijingense sp. nov., a novel methanogen isolated from anaerobic digesters. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:325–329
Mao C, Feng Y, Wang X, Ren G (2015) Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew Sust Energ Rev 45:540–555
Martini M, Marcone C, Lee IM, Firrao G (2014) The prokarytoes—Firmicutes and Tenericutes, 4th Editio. Springer, Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London
Ntaikou I, Gavala HN, Kornaros M, Lyberatos G (2008) Hydrogen production from sugars and sweet sorghum biomass using Ruminococcus albus. Int J Hydrog Energy 33:1153–1163
Parawira W, Murto M, Read JS, Mattiasson B (2007) A study of two-stage anaerobic digestion of solid potato waste using reactors under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Environ Technol 28:1205–1216
Parks DH, Beiko RG (2010) Identifying biologically relevant differences between metagenomic communities. Bioinformatics 26:715–721
Pol LWH, de Castro Lopes SI, Lettinga G, Lens PNL (2004) Anaerobic sludge granulation. Water Res 38:1376–1389
Praveckova M, Brennerova MV, Holliger C, De Alencastro F, Rossi P (2016) Indirect evidence link PCB dehalogenation with Geobacteraceae in anaerobic sediment-free microcosms. Front Microbiol 7:933
Rainey FA, Stackebrandt E (1993) Transfer of the type species of the genus Thermobacteroides to the genus Thermoanaerobacter as Thermoanaerobacter acetoethylicus (Ben-Bassat and Zeikus 1981) comb. Nov., description of Coprothermobacter gen. Nov., and Reclassification of Thermobacteroides. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 43:857–859
Satoh H, Miura Y, Tsushima I, Okabe S (2007) Layered structure of bacterial and archaeal communities and their in situ activities in anaerobic granules. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7300–7307
Schink B (1997) Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:262–280
Sieber JR, McInerney MJ, Gunsalus RP (2012) Genomic insights into syntrophy: the paradigm for anaerobic metabolic cooperation. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:429–452
Slobodkin AI, Tourova TP, Kostrikina NA, Lysenko AM, German KE, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Birkeland N-K (2006) Tepidimicrobium ferriphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic, Fe (III)-reducing bacterium of the order Clostridiales. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:369–372
Syutsubo K, Harada H, Ohashi A, Suzuki H (1997) An effective start-up of thermophilic UASB reactor by seeding mesophilically-grown granular sludge. Water Sci Technol 36:391–398
Vlyssides A, Barampouti EM, Mai S (2008) Granulation mechanism of a UASB reactor supplemented with iron. Anaerobe 14:275–279
Wang H, Fotidis IA, Angelidaki I (2015) Ammonia effect on hydrogenotrophic methanogens and syntrophic acetate-oxidizing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:11
Yamada T, Sekiguchi Y (2009) Cultivation of uncultured Chloroflexi subphyla: significance and ecophysiology of formerly uncultured Chloroflexi ‘subphylum I’ with natural and biotechnological relevance. Microbes Environ 24:205–216
Yamada T, Sekiguchi Y, Imachi H, Kamagata Y, Ohashi A, Harada H (2005) Diversity, localization, and physiological properties of filamentous microbes belonging to Chloroflexi subphylum I in mesophilic and thermophilic methanogenic sludge granules. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7493–7503
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H, Whitman WB, Euzéby J, Amann R, Rosselló-Móra R (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:635–645
Yu D, Liu J, Sui Q, Wei Y (2016) Biogas-pH automation control strategy for optimizing organic loading rate of anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating high COD wastewater. Bioresour Technol 203:62–70
Zhang Y, Wang X, Hu M, Li P (2015) Effect of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on the biodegradation of trichloroethylene wastewater and anaerobic bacterial community in the UASB reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1977–1987
Acknowledgements
We thank Hector Garcia and Hector Diaz for technical assistance. X. Zhu acknowledges the financial support provided by the Integrated Water Technology (InWaTech) project, research collaboration between the Technical University of Denmark and the Korean Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (DTU-KAIST, http://www.inwatech.org). This work was supported by the Danish Council for Strategic Research under the project “SYMBIO – Integration of biomass and wind power for biogas enhancement and upgrading via hydrogen assisted anaerobic digestion”, contract 12-132654. Illumina sequencing was performed at the Ramaciotti Centre for Genomics (Sydney, Australia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 80 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Kougias, P.G., Treu, L. et al. Microbial community changes in methanogenic granules during the transition from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 1313–1322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8028-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8028-0