Abstract
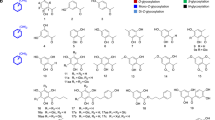
Glycosyltransferase 1 from Bacillus cereus (BcGT1) catalyzes the transfer of a glucosyl moiety from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to various acceptors; it was expressed and characterized. The specificity of acceptors was found to be broad: more than 20 compounds classified into O-, S-, and N-linkage glucosides can be prepared with BcGT1 catalysis. Based on this work, we conclude that the corresponding acceptors of these compounds must possess the following features: (1) the acceptors must contain at least one aromatic or fused-aromatic or heteroaromatic ring; (2) the reactive hydroxyl or sulfhydryl or amino group can attach either on the aromatic ring or on its aliphatic side chain; and (3) the acceptors can be a primary, secondary, or even a tertiary amine. Four representative acceptors—fluorescein methyl ester, 17-β-estradiol, 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin, and 6-benzylaminopurine—were chosen as a candidate acceptor for O-, S-, and N-glucosidation, respectively. These enzymatic products were purified and the structures were confirmed with mass and NMR spectra. As all isolated glucosides are β-anomers, BcGT1 is confirmed to be an inverting enzyme. This study not only demonstrates the substrate promiscuity of BcGT1 but also showed the great application prospect of this enzyme in bioconversion of valuable bioactive molecules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aumiller JJ, Mabashi-Asazuma H, Hillar A, Shi X, Jarvis DL (2012) A new glycoengineered insect cell line with an inducibly mammalianized protein N-glycosylation pathway. Glycobiology 22(3):417–428. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwr160
Bai Y, Mao QQ, Qin J, Zheng XY, Wang YB, Yang K, Shen HF, Xie LP (2010) Resveratrol induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human T24 bladder cancer cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Sci 101(2):488–493. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01415.x
Bate N, Butler AR, Smith IP, Cundliffe E (2000) The mycarose-biosynthetic genes of Streptomyces fradiae, producer of tylosin. Microbiology 146(Pt 1):139–146. doi:10.1099/00221287-146-1-139
Buchheit D, Dragan CA, Schmitt EI, Bureik M (2011) Production of ibuprofen acyl glucosides by human UGT2B7. Drug Metabolism and Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals 39(12):2174–2181. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.041640
Bureik M, Buchheit D, Dragan C (2010) Drug metabolism. EP Patent 2:166,088
Burke DG, Heales SJ, Vellodi A (2015) Lysosomal β-glucosidase (GBA1) and non-lysosomal β-glucosidase (GBA2): potential involvement in the pathogenesis of Gaucher disease/Parkinson disease. Mol Genet Metab 114(2):S26. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.12.040
Campbell JA, Davies GJ, Bulone V, Henrissat B (1997) A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 326(Pt 3):929. doi:10.1042/bj3260929u
Chen Y, Zhou J, Wang H, Xia Y, Yang ZY, Xia P (2008) Synthesis and anti-HBV activity of S-substituted 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin analogs. Chin Chem Lett 19(8):925–927. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2008.05.043
Cowley D, Duke C, Liepa A, MacLeod J, Letham D (1978) The structure and synthesis of cytokinin metabolites. 1. The 7-and 9-β-D-glucofuranosides and pyranosides of zeatin and 6-benzylaminopurine. Aust J Chem 31(5):1095–1111. doi:10.1071/CH9781095
Dasgupta F, Garegg PJ (1989) Synthesis of ethyl and phenyl 1-thio-1,2-trans-D-glycopyranosides from the corresponding per-O-acetylated glycopyranoses having a 1,2-trans-configuration using anhydrous ferric-chloride as a promoter. Acta Chem Scand 43(5):471–475. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.43-0471
Discher S, Burse A, Tolzin-Banasch K, Heinemann SH, Pasteels JM, Boland W (2009) A versatile transport network for sequestering and excreting plant glycosides in leaf beetles provides an evolutionary flexible defense strategy. Chembiochem: A European Journal of Chemical Biology 10(13):2223–2229. doi:10.1002/cbic.200900226
Du W, Hu Y (2004) Synthesis of fully protected N-arylglycosylamines and factors affecting the configuration of C1-substituents of N-arylglycosylamines. Synth Commun 34(16):2987–2992. doi:10.1081/SCC-200026656
Eichholzer J, MacLeod J, Summons R (1978) Studies of the thermal N 3 to N 9 rearrangement of the 3-β-D-glucoside of the cytokinin, 6-benzylaminopurine. Aust J Chem 31(4):893–899. doi:10.1071/CH9780893
Frebort I, Kowalska M, Hluska T, Frebortova J, Galuszka P (2011) Evolution of cytokinin biosynthesis and degradation. J Exp Bot 62(8):2431–2452. doi:10.1093/jxb/err004
Gantt RW, Goff RD, Williams GJ, Thorson JS (2008) Probing the aglycon promiscuity of an engineered glycosyltransferase. Angew Chem 47(46):8889–8892. doi:10.1002/anie.200803508
Gao Y, Zhao G, Liu W, Wang Y, Xu W, Wang J (2010) Thiadiazole-based thioglycosides as sodium-glucose Co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Chin J Chem 28(4):605–612. doi:10.1002/cjoc.201090120
Green MD, King CD, Mojarrabi B, Mackenzie PI, Tephly TR (1998) Glucuronidation of amines and other xenobiotics catalyzed by expressed human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 A3. Drug Metab Dispos 26(6):507–512
Hirohara S, Obata M, Alitomo H, Sharyo K, Ando T, Tanihara M, Yano S (2009) Synthesis, photophysical properties and sugar-dependent in vitro photocytotoxicity of pyrrolidine-fused chlorins bearing S-glycosides. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B, Biology 97(1):22–33. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.07.007
Hsieh YC, Chiu HH, Huang YC, Fun HK, Lu CY, Li YK, Chen CJ (2014) Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of glycosyltransferase-1 from Bacillus cereus. Acta Crystallographica Section F, Structural Biology Communications 70(Pt 9):1228–1231. doi:10.1107/S2053230X14014629
Hyung Ko J, Gyu Kim B, Joong-Hoon A (2006) Glycosylation of flavonoids with a glycosyltransferase from Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258(2):263–268. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00226.x
Ikeda Y, Furukawa K, Yamada H (2002) Simultaneous regioselective protection of phenyl 1-thioglucosides at the C-3 and C-6 or at the C-2 and C-6 hydroxy groups. Carbohydr Res 337(16):1499–1501. doi:10.1016/S0008-6215(02)00168-4
Jaeken J, Matthijs G (2007) Congenital disorders of glycosylation: a rapidly expanding disease family. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 8:261–278. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092327
Jaki B, Sticher O, Veit M, Fröhlich R, Pauli GF (2002) Evaluation of glucoiberin reference material from Iberis amara by spectroscopic fingerprinting. J Nat Prod 65(4):517–522. doi:10.1021/np0100800
Jung CM, Heinze TM, Schnackenberg LK, Mullis LB, Elkins SA, Elkins CA, Steele RS, Sutherland JB (2009) Interaction of dietary resveratrol with animal-associated bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 297(2):266–273. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01691.x
Katayama H, Asahina Y, Hojo H (2011) Chemical synthesis of the S-linked glycopeptide, sublancin. J Pept Sci 17(12):818–821. doi:10.1002/psc.1406
Kiessling LL, Splain RA (2010) Chemical approaches to glycobiology. Annu Rev Biochem 79:619–653. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.070606.100917
Kleeblatt D, Siyo B, Hein M, Iaroshenko VO, Iqbal J, Villinger A, Langer P (2013) Synthesis of N,N′-diglycosylated isoindigos. Org Biomol Chem 11(6):886–895. doi:10.1039/c2ob25866h
Kudo F, Kasama Y, Hirayama T, Eguchi T (2007) Cloning of the pactamycin biosynthetic gene cluster and characterization of a crucial glycosyltransferase prior to a unique cyclopentane ring formation. The Journal of Antibiotics 60(8):492–503. doi:10.1038/ja.2007.63
Letham D, Palni L, Tao G-Q, Gollnow B, Bates C (1983) Regulators of cell division in plant tissues XXIX. The activities of cytokinin glucosides and alanine conjugates in cytokinin bioassays. J Plant Growth Regul 2(1–4):103–115. doi:10.1007/BF02042238
Letham D, Wilson M, Parker C, Jenkins I, MacLeod J, Summons R (1975) Regulators of cell division in plant tissues: XXIII. The identity of an unusual metabolite of 6-benzylaminopurine. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 399(1):61–70. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(75)90211-1
Li T, Du Y, Cui Q, Zhang J, Zhu W, Hong K, Li W (2013) Cloning, characterization and heterologous expression of the indolocarbazole biosynthetic gene cluster from marine-derived Streptomyces sanyensis FMA. Mar Drugs 11(2):466–488. doi:10.3390/md11020466
Lim EK (2005) Plant glycosyltransferases: their potential as novel biocatalysts. Chemistry-A European Journal 11(19):5486–5494. doi:10.1002/chem.200500115
Lim EK, Bowles DJ (2004) A class of plant glycosyltransferases involved in cellular homeostasis. The EMBO Journal 23(15):2915–2922. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600295
Lomino JV, Naegeli A, Orwenyo J, Amin MN, Aebi M, Wang LX (2013) A two-step enzymatic glycosylation of polypeptides with complex N-glycans. Bioorg Med Chem 21(8):2262–2270. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.02.007
Lu C, Bai L, Shen Y (2004) A novel amide N-glycoside of ansamitocins from Actinosynnema pretiosum. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 57(5):348–350. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.57.348
MacDougall JM, Zhang XD, Polgar WE, Khroyan TV, Toll L, Cashman JR (2004) Design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of thiosaccharide analogues of morphine- and codeine-6-glucuronide. J Med Chem 47(23):5809–5815. doi:10.1021/jm049554t
Margraf-Schonfeld S, Bohm C, Watzl C (2011) Glycosylation affects ligand binding and function of the activating natural killer cell receptor 2B4 (CD244) protein. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 286(27):24142–24149. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.225334
Martin GD, Tan LT, Jensen PR, Dimayuga RE, Fairchild CR, Raventos-Suarez C, Fenical W (2007) Marmycins A and B, cytotoxic pentacyclic C-glycosides from a marine sediment-derived actinomycete related to the genus Streptomyces. J Nat Prod 70(9):1406–1409. doi:10.1021/np060621r
Mohorko E, Glockshuber R, Aebi M (2011) Oligosaccharyltransferase: the central enzyme of N-linked protein glycosylation. J Inherit Metab Dis 34(4):869–878. doi:10.1007/s10545-011-9337-1
Mulichak AM, Losey HC, Walsh CT, Garavito RM (2001) Structure of the UDP-glucosyltransferase GtfB that modifies the heptapeptide aglycone in the biosynthesis of vancomycin group antibiotics. Structure 9(7):547–557. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00616-5
Mydock LK, Demchenko AV (2010) Mechanism of chemical O-glycosylation: from early studies to recent discoveries. Org Biomol Chem 8(3):497–510. doi:10.1039/b916088d
Nandi V, Soine WH (1997) HPLC analysis for amobarbital N-glycosides in urine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 15(8):1187–1195. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(96)01936-X
Nomura S, Sakamaki S, Hongu M, Kawanishi E, Koga Y, Sakamoto T, Yamamoto Y, Ueta K, Kimata H, Nakayama K (2010) Discovery of canagliflozin, a novel C-glucoside with thiophene ring, as sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (1). J Med Chem 53(17):6355–6360. doi:10.1021/jm100332n
Ogiso M, Fujimoto Y, Ikekawa N, Ohnishi E (1986) Glucosidation of estradiol-17β in the cultured ovaries of the silkworm,Bombyx mori. Gen Comp Endocrinol 61(3):393–401. doi:10.1016/0016-6480(86)90225-X
Okkels FT, Ward JL, Joersbo M (1997) Synthesis of cytokinin glucuronides for the selection of transgenic plant cells. Phytochemistry 46(5):801–804. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00373-7
Pamplona R, Bellmunt MJ, Portero M, Riba D, Prat J (1995) Chromatographic evidence for amadori product formation in rat liver aminophospholipids. Life Sci 57(9):873–879. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(95)02020-J
Razavi SM, Zahri S, Zarrini G, Nazemiyeh H, Mohammadi S (2009) Biological activity of quercetin-3-O-glucoside, a known plant flavonoid. Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry 35(3):376–378. doi:10.1134/S1068162009030133
Šardzík R, Both P, Flitsch SL (2011) Post-translational modifications: S-linked sugars lost and found. Nat Chem Biol 7(2):69–70. doi:10.1038/nchembio.516
Schroeder C, Lutterbach R, Stöckigt J (1996) Preparative biosynthesis of natural glucosides and fluorogenic substrates for β-glucosidases followed by in vivo 13C NMR with high density plant cell cultures. Tetrahedron 52(3):925–934. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(95)00930-2
Shimoda K, Kubota N, Taniuchi K, Sato D, Nakajima N, Hamada H, Hamada H (2010) Biotransformation of naringin and naringenin by cultured Eucalyptus perriniana cells. Phytochemistry 71(2–3):201–205. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.09.035
Shipkova M, Armstrong VW, Oellerich M, Wieland E (2003) Acyl glucuronide drug metabolites: toxicological and analytical implications. Ther Drug Monit 25(1):1–16. doi:10.1097/00007691-200302000-00001
Sinclair AM, Elliott S (2005) Glycoengineering: the effect of glycosylation on the properties of therapeutic proteins. J Pharm Sci 94(8):1626–1635. doi:10.1002/jps.20319
Stege PW, Messina GA, Bianchi G, Olsina RA (2010) Determination of the β-glucosidase activity in different soils by pre capillary enzyme assay using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Fluoresc 20(2):517–523. doi:10.1007/s10895-009-0575-7
Sweeney AT, Tangpricha V, Weinberg J, Malabanan AO, Chimeh FN, Holick MF (2006) Comparison of the effects of a new conjugated oral estrogen, estradiol-3-beta-glucoside, with oral micronized 17-beta-estradiol in postmenopausal women. Translational Research: the Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 148(4):164–170. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2006.05.002
Talisman IJ, Kumar V, Deschamps JR, Frisch M, Malhotra SV (2011) Application of silver N-heterocyclic carbene complexes in O-glycosidation reactions. Carbohydr Res 346(15):2337–2341. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2011.07.025
Tanaka T, Matsumoto T, Noguchi M, Kobayashi A, Shoda S (2009) Direct transformation of unprotected sugars to aryl 1-thio-β-glycosides in aqueous media using 2-chloro-1, 3-dimethylimidazolinium chloride. Chem Lett 38(5):458–459. doi:10.1246/cl.2009.458
Tawara JN, Johnston JJ, Goodall MJ (1996) Degradation of 3-chloro-p-toluidine hydrochloride in watermelon bait. Identification and chemical characterization of novel N-glucoside and oxopropanimine. J Agric Food Chem 44(12):3983–3988. doi:10.1021/Jf960044k
Thibodeaux CJ, Melancon CE, Liu HW (2007) Unusual sugar biosynthesis and natural product glycodiversification. Nature 446(7139):1008–1016. doi:10.1038/nature05814
Valliere-Douglass JF, Eakin CM, Wallace A, Ketchem RR, Wang W, Treuheit MJ, Balland A (2010) Glutamine-linked and non-consensus asparagine-linked oligosaccharides present in human recombinant antibodies define novel protein glycosylation motifs. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 285(21):16012–16022. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.096412
Wang H, van der Donk WA (2011) Substrate selectivity of the sublancin S-glycosyltransferase. J Am Chem Soc 133(41):16394–16397. doi:10.1021/ja2075168
Wang W, Rattananakin P, Goekjian PG (2003) Synthesis of N-glycoside analogs via thionolactones. J Carbohydr Chem 22(7–8):743–751. doi:10.1081/CAR-120026472
Wirth DD, Baertschi SW, Johnson RA, Maple SR, Miller MS, Hallenbeck DK, Gregg SM (1998) Maillard reaction of lactose and fluoxetine hydrochloride, a secondary amine. J Pharm Sci 87(1):31–39. doi:10.1021/js9702067
Wright GD (2005) Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(10):1451–1470. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2005.04.002
Xiang S, Ma J, Gorityala BK, Liu XW (2011) Stereoselective synthesis of β-N-glycosides through 2-deoxy-2-nitroglycal. Carbohydr Res 346(18):2957–2959. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2011.01.032
Xu S, Yan X, Zhang Q, Xia P, Chen Y (2007) Unexpected rearrangement in the reaction of 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin with 1-mono-and 1, 1-dimethyl propargyl alcohols. Synth Commun 37(21):3801–3808. doi:10.1080/00397910701571615
Yang F, Lian G, Yu B (2010) Synthesis of raphanuside, an unusual oxathiane-fused thioglucoside isolated from the seeds of Raphanus sativus L. Carbohydr Res 345(2):309–314. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2009.11.020
Yoon SH, Fulton DB, Robyt JF (2010) Enzymatic synthesis of L-dopa alpha-glycosides by reaction with sucrose catalyzed by four different glucansucrases from four strains of Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Carbohydr Res 345(12):1730–1735. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2010.05.001
Zhao P, Bai L, Ma J, Zeng Y, Li L, Zhang Y, Lu C, Dai H, Wu Z, Li Y (2008a) Amide N-glycosylation by Asm25, an N-glycosyltransferase of ansamitocins. Chemistry & Biology 15(8):863–874. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.06.007
Zhao P, Wang M, Zhang SP, Shao SC, Sun XY, Yao SD, Wang SL (2008b) Photochemical properties of a new kind of anti-cancer drug: N-glycoside compound. Sci China Ser B 51(9):872–877. doi:10.1007/s11426-008-0091-7
Zhou M, Hamza A, Zhan CG, Thorson JS (2013) Assessing the regioselectivity of OleD-catalyzed glycosylation with a diverse set of acceptors. J Nat Prod 76(2):279–286. doi:10.1021/np300890h
Zhou M, Thorson JS (2011) Asymmetric enzymatic glycosylation of mitoxantrone. Org Lett 13(10):2786–2788. doi:10.1021/ol200977u
Zitzmann N, Block T, Methta A, Rudd P, Burton D, Wilson I, Platt F, Butters T, Dwek RA (2005) Glycosylation: disease targets and therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol 564:1–2. doi:10.1007/0-387-25515-X_1
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Chia-Yu Lu, Ms. Ko-Jen Su for enzyme preparation, Dr. Hsing-Pang Hsieh (National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan) for providing BPR2P0064S0, Mr. Chang-Lin Yang for isolating 7-mercapto-4-methylcoumarin 7-S-glucoside, Dr. Kuang-Po Chen, Ms. Chloe Chang and Dr. Li-Ching Shen for the NMR analysis, Ms. Yun-Ming Li (Mass Laboratory, Center for Advanced Instrumentation at National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan) for mass analysis, and Dr. Yu-Kuo Wang (Department of Biological Science and Technology, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan) for MALDI-TOF-MS peptide-mapping analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan (101-2113-M-009-012-MY3).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1.67 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, HH., Shen, MY., Liu, YT. et al. Diversity of sugar acceptor of glycosyltransferase 1 from Bacillus cereus and its application for glucoside synthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 4459–4471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7270-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7270-1