Abstract
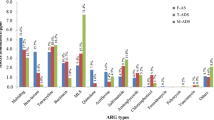
This study investigated the use of thermophilic anaerobic digestion for removing antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) from residual municipal wastewater solids. Four laboratory-scale anaerobic digesters were operated in 8-day batch cycles at temperatures of 40, 56, 60, and 63 °C. Two tetracycline resistance genes (tet(W) and tet(X)), a fluoroquinolone resistance gene (qnrA), the integrase gene of class 1 integrons (intI1), 16S rRNA genes of all Bacteria, and 16S rRNA genes of methanogens were quantified using real-time quantitative PCR. ARG and intI1 quantities decreased at all temperatures and were described well by a modified form of the Collins-Selleck disinfection kinetic model. The magnitudes of Collins-Selleck kinetic parameters were significantly greater at thermophilic temperatures compared to 40 °C, but few statistically significant differences were observed among these parameters for the thermophilic anaerobic digesters. This model allows for the direct comparison of different operating conditions (e.g., temperature) on anaerobic digestion performance in mitigating the quantity of ARGs in wastewater solids and could be used to design full-scale anaerobic digesters to specifically treat for ARGs as a “pollutant” of concern.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold S, Gassner B, Giger T, Zwahlen R (2004) Banning antimicrobial growth promoters in feedstuffs does not result in increased therapeutic use of antibiotics in medicated feed in pig farming. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 13:323–331
Aminov RI, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance: development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:22–32
Auerbach EA, Seyfried EE, McMahon KD (2007) Tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 41:1143–1151
Beecher N, Crawford K, Goldstein N, Kester G, Lono-Batura M, Dziezyk E, Peckenham J, Cheng T (2007) Final report: a national biosolids regulation, quality, end use, & disposal survey. Tamworth, NH, North East Biosolids and Residuals Association
Burch TR, Sadowsky MJ, LaPara TM (2013a) Aerobic digestion reduces the quantity of antibiotic resistance genes in residual municipal wastewater solids. Front Microbiol 4:17
Burch TR, Sadowsky MJ, LaPara TM (2013b) Air-drying beds reduce the quantities of antibiotic resistance genes and class 1 integrons in residual municipal wastewater solids. Environ Sci Technol 47:9965–9971
Burch TR, Sadowsky MJ, LaPara TM (2014) Fate of antibiotic resistance genes and Class 1 integrons in soil microcosms following the application of treated residual municipal wastewater solids. Environ Sci Technol 48:5620–5627
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/index.html
Cook RD, Weisberg S (1999) Applied regression including computing and graphics. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ
Crittenden JC, Trussell RR, Hand DW, Howe KJ, Tchobanoglous G (2005) Water treatment: principles and design, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ
Cummings DE, Archer KF, Arriola DJ, Baker PA, Faucett KG, Laroya JB, Pfeil KL, Ryan CR, Ryan KRU, Zuill DE (2011) Broad dissemination of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in sediments of two urban coastal wetlands. Environ Sci Technol 45:447–454
Davies J (2012) Sewage recycles antibiotic resistance. Nature 487:302
Diehl DL, LaPara TM (2010) Effect of temperature on the fate of genes encoding tetracycline resistance and the integrase of class 1 integrons within anaerobic and aerobic digesters treating municipal wastewater solids. Environ Sci Technol 44:9128–9133
Edgar R, Friedman N, Molshanski-Mor S, Qimron U (2012) Reversing bacterial resistance to antibiotics by phage-mediated delivery of dominant sensitive genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:744–751
Ghosh S, Ramsden SJ, LaPara TM (2009) The role of anaerobic digestion in controlling the release of tetracycline resistance genes and class 1 integrons from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:791–796
Gillings MR, Gaze WH, Pruden A, Smalla K, Tiedje JM, Zhu T-G (2014) Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J 9:1269–1279
Goldstein C, Lee MD, Sanchez S, Hudson C, Phillips B, Regester B, Grady M, Liebert C, Summers AO, White DG, Maurer JJ (2001) Incidence of class 1 and 2 integrases in clinical and commensal bacteria from livestock, companion animals, and exotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:723–726
Graham DW, Collignon P, Davies J, Larsson DGJ, Snape J (2014) Underappreciated role of regionally poor water quality on globally increasing antibiotic resistance. Environ Sci Technol 48:11746–11747
Guiney DG, Hasegawa P, Davis CE (1984) Expression in Escherichia coli of cryptic tetracycline resistance genes from Bacteroides R plasmids. Plasmid 11:248–252
Jabes D (2011) The antibiotic R&D pipeline: an update. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:564–569
Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Collins JJ (2010) How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:423–435
LaPara TM, Burch TR, McNamara PJ, Tan DT, Yan M, Eichmiller JJ (2011) Tertiary-treated municipal wastewater is a significant point source of antibiotic resistance genes into Duluth-Superior Harbor. Environ Sci Technol 45:9543–9549
Levy SB, Marshall B (2004) Antibacterial resistance worldwide: causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med 10:S122–S129
Levy SB, McMurry LM, Barbosa TM, Burdett V, Courvalin P, Hillen W, Roberts MC, Rood JI, Taylor DE (1999) Nomenclature for new tetracycline resistance determinants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1523–1524
Ma Y, Wilson CA, Novak JT, Riffat R, Aynur S, Murthy S, Pruden A (2011) Effect of various sludge digestion conditions on sulfonamide, macrolide, and tetracycline resistance genes and class I integrons. Environ Sci Technol 45:7855–7861
Mazel D (2006) Integrons: agents of bacterial evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:608–620
Munir M, Wong K, Xagoraki I (2011) Release of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in the effluent and biosolids of five wastewater utilities in Michigan. Water Res 45:681–693
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nelson DK, LaPara TM, Novak PJ (2010) Effects of ethanol-based fuel contamination: microbial community changes, production of regulated compounds, and methane generation. Environ Sci Technol 44:4525–4530
Pruden A, Larsson DGJ, Amezquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Lazorchak JM, Suzuki S, Silley P, Snape JR, Topp E, Zhang T, Zhu YG (2013) Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect 121:878–885
Pruden A, Pei R, Storteboom H, Carlson KH (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 40:7445–7450
Rizzo L, Manaia C, Merlin C, Schwartz T, Dagot C, Ploy MC, Michael I, Fatta-Kassinos D (2013) Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 447:345–360
Roberts MC (2005) Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:195–203
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Selleck RE, Collins HF, Saunier BM (1978) Kinetics of bacterial deactivation with chlorine. J Environ Eng Div ASCE 104:1197–1212
Speer BS, Bedzyk L, Salyers AA (1991) Evidence that a novel tetracycline resistance gene found on two Bacteroides transposons encodes an NADP-requiring oxidoreductase. J Bacteriol 173:176–183
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel HD (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. Metcalf and Eddy, Inc, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill, Boston
Wierup M (2001) The Swedish experience of the 1986 year ban of antimicrobial growth promoters, with special reference to animal health, disease prevention, productivity, and usage of antimicrobials. Microb Drug Resist 7:183–190
Zhang T, Yang Y, Pruden A (2015) Effect of temperature on removal of antibiotic resistance genes by anaerobic digestion of activated sludge revealed by metagenomic approach. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6688-9
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Science Foundation (CBET-0967176).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 669 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burch, T.R., Sadowsky, M.J. & LaPara, T.M. Modeling the fate of antibiotic resistance genes and class 1 integrons during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of municipal wastewater solids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1437–1444 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7043-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7043-x