Abstract
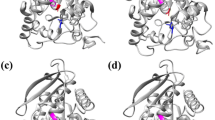
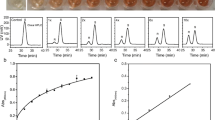
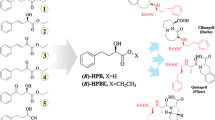
Methyl (R)-o-chloromandelate (R-CMM) is an intermediate for the platelet aggregation inhibitor clopidogrel. Its preparation through enzymatic resolution of the corresponding ester has been hindered by the lack of an enzyme with satisfying enantioselectivity and activity. In the present work, we aimed to improve the enzymatic enantioselectivity towards methyl (S)-o-chloromandelate (S-CMM) by rational design, using esterase BioH as a model enzyme. Based on the differences in the binding mode of S- and R-enantiomers at the active cavity of the enzyme, the steric and electronic interactions between the key amino acids of BioH and the enantiomers were finely tuned. The enantioselectivity of esterase BioH towards S-CMM was improved from 3.3 (the wild type) to 73.4 (L123V/L181A/L207F). Synergistic interaction was observed between point mutations, and insight into the source of enzymatic enantioselectivity was gained by molecular dynamics simulations. The results can provide a reference for the enzyme design of other enzymes towards S-CMM for the enhancement of enantioselectivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SN, Kazlauskas RJ, Morinville AH, Grochulski P, Schrag JD, Cygler M (1994) Enantioselectivity of Candida rugosa lipase toward carboxylic acids: a predictive rule from substrate mapping and X-ray crystallography. Biocatal Biotransfor 9:209–225. doi:10.3109/10242429408992121
Barrozo A, Borstnar R, Marloie G, Kamerlin SCL (2012) Computational protein engineering: bridging the gap between rational design and laboratory evolution. Int J Mol Sci 13:12428–12460. doi:10.3390/ijms131012428
Bartsch S, Kourist R, Bornscheuer UT (2008) Complete inversion of enantioselectivity towards acetylated tertiary alcohols by a double mutant of a Bacillus subtilis esterase. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:1508–1511. doi:10.1002/anie.200704606
Dantas G, Kuhlman B, Callender D, Wong M, Baker D (2003) A large scale test of computational protein design: folding and stability of nine completely redesigned globular proteins. J Mol Biol 332:449–460. doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00888-x
Ema T, Kobayashi J, Maeno S, Sakai T, Utaka M (1998) Origin of the enantioselectivity of lipases explained by a stereo-sensing mechanism operative at the transition state. B Chem Soc Jpn 71:443–453. doi:10.1246/bcsj.71.443
Ema T, Fujii T, Ozaki M, Korenaga T, Sakai T (2005) Rational control of enantioselectivity of lipase by site-directed mutagenesis based on the mechanism. Chem Commun 0:4650-4651. doi: 10.1039/b508244g
Ema T, Ide S, Okita N, Sakai T (2008) Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of methyl (R)-o-chloromandelate, a key intermediate for clopidogrel, via asymmetric reduction with recombinant Escherichia coli. Adv Synth Catal 350:2039–2044. doi:10.1002/adsc.200800292
Ema T, Kamata S, Takeda M, Nakano Y, Sakai T (2010) Rational creation of mutant enzyme showing remarkable enhancement of catalytic activity and enantioselectivity toward poor substrates. Chem Commun 46:5440–5442. doi:10.1039/c001561j
Ema T, Nakano Y, Yoshida D, Kamata S, Sakai T (2012) Redesign of enzyme for improving catalytic activity and enantioselectivity toward poor substrates: manipulation of the transition state. Org Biomol Chem 10:6299–6308. doi:10.1039/c2ob25614b
Engström K, Nyhlén J, Sandström AG, Bäckvall JE (2010) Directed evolution of an enantioselective lipase with broad substrate scope for hydrolysis of α-substituted esters. J Am Chem Soc 132:7038–7042. doi:10.1021/ja100593j
Godinho LF, Reis CR, Rozeboom HJ, Dekker FJ, Dijkstra BW, Poelarends GJ, Quax WJ (2012) Enhancement of the enantioselectivity of carboxylesterase A by structure-based mutagenesis. J Biotechnol 158:36–43. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.12.026
Gu JL, Yu HW (2012) The role of residue S139 of mandelate racemase: synergistic effect of S139 and E317 on transition state stabilization. J Biomol Struct Dyn 30:585–593. doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.687524
Gu J, Liu M, Guo F, Xie W, Lu W, Ye L, Chen Z, Yuan S, Yu H (2014) Virtual screening of mandelate racemase mutants with enhanced activity based on binding energy in the transition state. Enzyme Microb Technol 55:121–127. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.10.008
Guo F, Franzen S, Ye L, Gu J, Yu H (2014) Controlling enantioselectivity of esterase in asymmetric hydrolysis of aryl prochiral diesters by introducing aromatic interactions. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.25249
Hosangadi BD, Dave RH (1996) An efficient general method for esterification of aromatic carboxylic acids. Tetrahedron Lett 37:6375–6378. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(96)01351-2
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:10. doi:10.1063/1.445869
Kiss G, Çelebi-Ölçüm N, Moretti R, Baker D, Houk KN (2013) Computational enzyme design. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:5700–5725. doi:10.1002/anie.201204077
Lin S, Hanson RE, Cronan JE (2010) Biotin synthesis begins by hijacking the fatty acid synthetic pathway. Nat Chem Biol 6:682–688. doi:10.1038/NCHEMBIO.420
Ma H, Yang L, Ni Y, Zhang J, Li CX, Zheng GW, Yang H, Xu JH (2012a) Stereospecific reduction of methyl o-chlorobenzoylformate at 300 gL−1 without additional cofactor using a carbonyl reductase mined from Candida glabrata. Adv Synth Catal 354:1765–1772. doi:10.1002/adsc.201100366
Ma J, Wu L, Guo F, Gu J, Tang X, Jiang L, Liu J, Zhou J, Yu H (2012b) Enhanced enantioselectivity of a carboxyl esterase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides by directed evolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol:1-10. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4396-2
Morley KL, Kazlauskas RJ (2005) Improving enzyme properties: when are closer mutations better? Trends Biotechnol 23:231–237. doi:10.1016/j.tiblech.2005.03.005
Padhi SK, Fujii R, Legatt GA, Fossum SL, Berchtold R, Kazlauskas RJ (2010) Switching from an esterase to a hydroxynitrile lyase mechanism requires only two amino acid substitutions. Chem Biol 17:863–871. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.06.013
Reetz MT, Sanchis J (2008) Constructing and analyzing the fitness landscape of an experimental evolutionary process. Chembiochem 9:2260–2267. doi:10.1002/cbic.200800371
Reetz MT, Zonta A, Schimossek K, Jaeger KE, Liebeton K (1997) Creation of enantioselective biocatalysts for organic chemistry by in vitro evolution. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 36:2830–2832. doi:10.1002/anie.199728301
Rong F, Feng XG, Yuan CW, Fu DG, Li P (2006) Chiral separation of mandelic acid and its derivatives by thin-layer chromatography using molecularly imprinted stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 29:2593–2602. doi:10.1080/10826070600915213
Rothlisberger D, Khersonsky O, Wollacott AM, Jiang L, DeChancie J, Betker J, Gallaher JL, Althoff EA, Zanghellini A, Dym O, Albeck S, Houk KN, Tawfik DS, Baker D (2008) Kemp elimination catalysts by computational enzyme design. Nature 453:190-195. doi:http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v453/n7192/suppinfo/nature06879_S1.html
Saggu M, Levinson NM, Boxer SG (2011) Direct measurements of electric fields in weak OH··· π hydrogen bonds. J Am Chem Soc 133:17414–17419. doi:10.1021/ja2069592
Sanishvili R, Yakunin AF, Laskowski RA, Skarina T, Evdokimova E, Doherty-Kirby A, Lajoie GA, Thornton JM, Arrowsmith CH, Savchenko A (2003) Integrating structure, bioinformatics, and enzymology to discover function BioH, a new carboxylesterase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 278:26039–26045. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303867200
Siegel JB, Zanghellini A, Lovick HM, Kiss G, Lambert AR, St.Clair JL, Gallaher JL, Hilvert D, Gelb MH, Stoddard BL, Houk KN, Michael FE, Baker D (2010) Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction. Science 329:309–313. doi:10.1126/science.1190239
Uhm KN, Lee SJ, Kim H, Kang HY, Lee Y (2007) Enantioselective resolution of methyl 2-chloromandelate by Candida antarctica lipase A in a solvent-free transesterification reaction. J Mol Catal B Enzym 45:34–38. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2006.10.006
van Langen LM, van Rantwijk F, Sheldon RA (2003) Enzymatic hydrocyanation of a sterically hindered aidehyde. Optimization of a chemoenzymatic procedure for (R)-2-chloromandelic acid. Org Process Res Dev 7:828–831. doi:10.1021/op0340964
van Langen LM, Selassa RP, van Rantwijk F, Sheldon RA (2004) Cross-linked aggregates of (R)-oxynitrilase: a stable, recyclable biocatalyst for enantioselective hydrocyanation. Org Lett 7:327–329. doi:10.1021/ol047647z
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174. doi:10.1002/jcc.20035
Wang J, Wang W, Kollman PA, Case DA (2006a) Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J Mol Graph Model 25:247–260. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2005.12.005
Wang PY, Chen TL, Tsai SW (2006b) Kinetic resolution of (R, S)-ethyl 2-chloromandelate in biphasic media using hydrolase of Klebsiella oxytoca. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:930–935. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.01.028
Wang PY, Tsai SW, Chen TL (2008) Improvements of enzyme activity and enantioselectivity via combined substrate engineering and covalent immobilization. Biotechnol Bioeng 101:460–469. doi:10.1002/bit.21916
Wang B, Jiang L, Wang J, Ma J, Liu M, Yu H (2011) A tandem and fully enzymatic procedure for the green resolution of chiral alcohols: acylation and deacylation in non-aqueous media. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 22:980–985. doi:10.1016/j.tetasy.2011.05.022
Wu Q, Soni P, Reetz MT (2013) Laboratory evolution of enantiocomplementary Candida antarctica lipase B mutants with broad substrate scope. J Am Chem Soc 135:1872–1881. doi:10.1021/ja310455t
Zhang CS, Zhang ZJ, Li CX, Yu HL, Zheng GW, Xu JH (2012) Efficient production of (R)-o-chloromandelic acid by deracemization of o-chloromandelonitrile with a new nitrilase mined from Labrenzia aggregata. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:91–99. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-3993-4
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21176215), the Program for Zhejiang Leading Team of S&T Innovation (Grant No. 2011R50007), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2014QNA4025), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LQ14B060005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supporting information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Synthetic primers used for site-directed mutagenesis, geometry of the hydrogen bonds between the mutants and R- or S-CMM, the catalytic activities of the wild-type BioH and mutants towards S- and R-CMM, energy contribution (kcal/mol) of key amino acids at the active cavity for the designed mutants and the wild type in R-complex and S-complex, geometry of the hydrogen bonds formed between the R-CMM or S-CMM and residue H233 for mutants L207C and L207S are shown in the supporting information. (PDF 616 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Ye, L., Guo, F. et al. Rational design of esterase BioH with enhanced enantioselectivity towards methyl (S)-o-chloromandelate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 1709–1718 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5995-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5995-x