Abstract
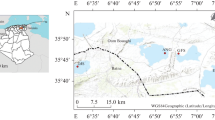
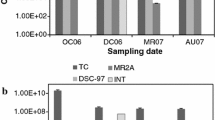
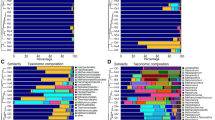
The Arava Valley in is a rock desert within the Great African Rift valley. Soil from this area is covered with a salt crust. Here, we report microbial diversity from arid, naturally saline samples collected near Ein Yahav from the Arava Valley by culture-independent as well as culture-dependent analysis. High-throughput sequencing of the hypervariable region V4 of the 16S rRNA gene revealed that the microbial community consists of halophiles from the domain Bacteria as well as Archaea. Bacterial diversity was mainly represented by the genus Salinimicrobium of the order Flavobacteriales within the phylum Bacteroidetes, from the gammaproteobacterial orders Alteromonadales and Oceanospirillales as well as representatives from the order Bacillales of the phylum Firmicutes. Archaeal diversity was dominated by euryarchaeal Halobacteria from the orders Halobacteriales, Haloferacales, and Natrialbales. But more than 40% of the sequences affiliated with Archaea were assigned to unknown or unclassified archaea. Even if taxonomic resolution of the 16S rRNA gene V4 region for Archaea is limited, this study indicates the need of further and more detailed studies of Archaea. By using culture-dependent analysis, bacteria of the order Bacillales as well as archaea from all three halobacterial orders Halobacteriales, Haloferacales, and Natrialbales including potentially novel species from the genera Halorubrum and Haloparvum were isolated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma Y, Galinski EA, Grant WD, Oren A, Ventosa A (2010) Halophiles 2010: life in saline environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6971–6981
Konings WN, Albers SV, Koning S, Driessen AJM (2002) The cell membrane plays a crucial role in survival of bacteria and archaea in extreme environments. Anton Leeuw 81:61–72
Oren A (2013) Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes. Front Microbiol 4:315. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00315
Pandit AS, Joshi MN, Bhargava P, Shaikh I, Ayachit GN, Raj SR, Saxena AK, Bagatharia SB (2015) A snapshot of microbial communities from the Kutch: one of the largest salt deserts in the World. Extremophiles 19:973–987
Hollister EB, Engledow AS, Hammett AJM, Provin TL, Wilkinson HH, Gentry TJ (2010) Shifts in microbial community structure along an ecological gradient of hypersaline soils and sediments. ISME J 4:829–838
Patel R, Mevada V, Prajapati D, Dudhagara P, Koringa P, Joshi CG (2015) Metagenomic sequence of saline desert microbiota from wild ass sanctuary, Little Rann of Kutch, Gujarat, India. Genomics Data 3:137–139
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Fabros R, Adeolu M (2016) A phylogenomic reappraisal of family-level divisions within the class Halobacteria: proposal to divide the order Halobacteriales into the families Halobacteriaceae, Haloarculaceae fam. nov., and Halococcaceae fam. nov., and the order Haloferacales into the families, Haloferacaceae and Halorubraceae fam. nov. Anton Leeuw 109:565–587
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Baker S (2015) Phylogenomic analyses and molecular signatures for the class Halobacteria and its two major clades: a proposal for division of the class Halobacteria into an emended order Halobacteriales and two new orders, Haloferacales ord. nov and Natrialbales ord. nov., containing the novel families Haloferacaceae fam. nov and Natrialbaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1050–1069
McDuff S, King GM, Neupane S, Myers MR (2016) Isolation and characterization of extremely halophilic CO-oxidizing Euryarchaeota from hypersaline cinders, sediments and soils and description of a novel CO oxidizer, Haloferax namakaokahaiae Mke2.3T, sp. nov. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:fiw028
Chen YG, Cui XL, Zhang YQ, Li WJ, Wang YX, Kim CJ, Lim JM, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2008) Salinimicrobium terrae sp. nov., isolated from saline soil, and emended description of the genus Salinimicrobium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2501–2504
Naghoni A, Emtiazi G, Amoozegar MA, Cretoiu MS, Stal LJ, Etemadifar Z, Fazeli SAS, Bolhuis H (2017) Microbial diversity in the hypersaline Lake Meyghan, Iran. Sci Rep 7:11522
Gibtan A, Park K, Woo M, Shin JK, Lee DW, Sohn JH, Song M, Roh SW, Lee SJ, Lee HS (2017) Diversity of extremely halophilic archaeal and bacterial communities from commercial salts. Front Microbiol 8:799
Selenska-Pobell S, Kampf G, Flemming K, Radeva G, Satchanska G (2001) Bacterial diversity in soil samples from two uranium waste piles as determined by rep-APD, RISA and 16S rDNA retrieval. Anton Leeuw 79:149–161
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:4516–4522
Data Analysis Methodology RTL Genomics. http://www.rtlgenomics.com/docs/Data_Analysis_Methodology.pdf
Robertson CE, Harris JK, Wagner BD, Granger D, Browne K, Tatem B, Feazel LM, Park K, Pace NR, Frank DN (2013) Explicet: graphical user interface software for metadata-driven management, analysis and visualization of microbiome data. Bioinformatics 29:3100–3101
Delong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:5685–5689
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Nedashkovskaya OI, Vancanneyt M, Kim SB, Han J, Zhukova NV, Shevchenko LS (2010) Salinimicrobium marinum sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae, and emended descriptions of the genus Salinimicrobium and Salinimicrobium catena. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2303–2306
Yoon J-H, Kang S-J, Jung Y-T, Oh T-K (2007) Halobacillus campisalis sp. nov., containing mesodiaminopimelic acid in the cell-wall peptidoglycan, and emended description of the genus Halobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2021–2025
Garcia MT, Gallego V, Ventosa A, Mellado E (2005) Thalassobacillus devorans gen. nov., sp nov., a moderately halophilic, phenol-degrading, Gram-positive bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1789–1795
Sanchez-Porro C, Yilmaz P, de la Haba RR, Birbir M, Ventosa A (2011) Thalassobacillus pellis sp nov., a moderately halophilic, Gram-positive bacterium isolated from salted hides. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1206–1210
Gao XH, Gao S, Zhou Y, Guan HL, Zhang YJ, Jia M, Huang HW, Yang DX, Li WJ, Tang SK (2013) Tenuibacillus halotolerans sp nov., a novel bacterium isolated from a soil sample from a salt lake in Xinjiang, China and emended description of the genus Tenuibacillus. Anton Leeuw 103:207–215
Amoozegar MA, Bagheri M, Didari M, Mehrshad M, Schumann P, Sproer C, Sanchez-Porro C, Ventosa A (2014) Aquibacillus halophilus gen. nov., sp nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from a hypersaline lake, and reclassification of Virgibacillus koreensis as Aquibacillus koreensis comb. nov and Virgibacillus albus as Aquibacillus albus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3616–3623
Lim JM, Jeon CO, Park DJ, Kim HR, Yoon BJ, Kim CJ (2005) Pontibacillus marinus sp nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from a solar saltern, and emended description of the genus Pontibacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1027–1031
Podell S, Ugalde JA, Narasingarao P, Banfield JF, Heidelberg KB, Allen EE (2013) Assembly-driven community genomics of a hypersaline microbial ecosystem. PLoS One 8:e61692
Wang ZJ, Liu QQ, Zhao LH, Du ZJ, Chen GJ (2015) Bradymonas sediminis gen. nov., sp nov., isolated from coastal sediment, and description of Bradymonadaceae fam. nov and Bradymonadales ord. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1542–1549
Gutierrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Xue Y, Ma Y, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2007) Halopiger xanaduensis gen. nov., sp nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from saline Lake Shangmatala in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1402–1407
Minegishi H, Shimogaki R, Enomoto S, Echigo A, Kondo Y, Nagaoka S, Shimane Y, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Ohkuma M, Nunoura T, Takai K, Usami R (2016) Halopiger thermotolerans sp nov., a thermo-tolerant haloarchaeon isolated from commercial salt. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4975–4980
Jaakkola ST, Pfeiffer F, Ravantti JJ, Guo QG, Liu Y, Chen XD, Ma HL, Yang CH, Oksanen HM, Bamford DH (2016) The complete genome of a viable archaeum isolated from 123-million-year-old rock salt. Environ Microbiol 18:565–579
Jaakkola ST, Zerulla K, Guo QG, Liu Y, Ma HL, Yang CH, Bamford DH, Chen XD, Soppa J, Oksanen HM (2014) Halophilic archaea cultivated from surface sterilized Middle-Late Eocene rock salt are polyploid. PLoS One 9:e110533
Kondo Y, Minegishi H, Echigo A, Shimane Y, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Ohkuma M, Takahashi-Ando N, Fukushima Y, Yoshida Y, Usami R (2015) Halorubrum gandharaense sp nov., an alkaliphilic haloarchaeon from commercial rock salt. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2345–2350
Cui HL, Li XY, Gao X, Xu XW, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Oren A, Zhou PJ (2010) Halopelagius inordinatus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2089–2093
Vreeland RH, Straight S, Krammes J, Dougherty K, Rosenzweig WD, Kamekura M (2002) Halosimplex carlsbadense gen. nov., sp nov., a unique halophilic archaeon, with three 16S rRNA genes, that grows only in defined medium with glycerol and acetate or pyruvate. Extremophiles 6:445–452
Chen SX, Liu HC, Zhou J, Xiang H (2016) Haloparvum sedimenti gen. nov., sp nov., a member of the family Haloferacaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2327–2334
Robinson CK, Wierzchos J, Black C, Crits-Christoph A, Ma B, Ravel J, Ascaso C, Artieda O, Valea S, Roldan M, Gomez-Silva B, DiRuggiero J (2015) Microbial diversity and the presence of algae in halite endolithic communities are correlated to atmospheric moisture in the hyper-arid zone of the Atacama Desert. Environ Microbiol 17:299–315
Canfora L, Bacci G, Pinzari F, Lo Papa G, Dazzi C, Benedetti A (2014) Salinity and bacterial diversity: to what extent does the concentration of salt affect the bacterial community in a saline soil? PLoS One 9:e106662
Oren A (2008) Microbial life at high salt concentrations: phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst 4:2
Vreeland RH, Litchfield CD, Martin EL, Elliot E (1980) Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salt-tolerant bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:485–495
Lim JM, Jeon CO, Lee SS, Park DJ, Xu LH, Jiang CL, Kim CJ (2008) Reclassification of Salegentibacter catena Ying et al. 2007 as Salinimicrobium catena gen. nov., comb. nov and description of Salinimicrobium xinjiangense sp nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from Xinjiang province in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:438–442
Sella S, Vandenberghe LPS, Soccol CR (2014) Life cycle and spore resistance of spore-forming Bacillus atrophaeus. Microbiol Res 169:931–939
Gu J, Cai H, Yu SL, Qu R, Yin B, Guo YF, Zhao JY, Wu XL (2007) Marinobacter gudaonensis sp nov., isolated from an oil-polluted saline soil in a Chinese oilfield. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:250–254
Jiang JQ, Pan YY, Hu SX, Zhang XX, Hu BZ, Huang HP, Hong S, Meng J, Li C, Wang KB (2014) Halomonas songnenensis sp nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from saline and alkaline soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1662–1669
Quillaguaman J, Hatti-Kaul R, Mattiasson B, Alvarez MT, Delgado O (2004) Halomonas boliviensis sp nov., an alkalitolerant, moderate halophile isolated from soil around a Bolivian hypersaline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:721–725
Hug LA, Baker BJ, Anantharaman K, Brown CT, Probst AJ, Castelle CJ, Butterfield CN, Hernsdorf AW, Amano Y, Ise K, Suzuki Y, Dudek N, Relman DA, Finstad KM, Amundson R, Thomas BC, Banfield JF (2016) A new view of the tree of life. Nat Microbiol 1:16048
Yang Y, Cui HL, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2006) Halobacterium jilantaiense sp nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2353–2355
Zhang WY, Huo YY, Zhang XQ, Zhu XF, Wu M (2013) Halolamina salifodinae sp nov and Halolamina sauna sp nov., two extremely halophilic archaea isolated from a salt mine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4380–4385
Corral P, de la Haba RR, Sanchez-Porro C, Amoozegar MA, Papke RT, Ventosa A (2015) Halorubrum persicum sp nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from sediment of a hypersaline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1770–1778
Rasooli M, Naghoni A, Amoozegar MA, Mirfeizi L, Nikou MM, Fazeli SAS, Minegishi H, Ventosa A (2017) Natrinema soli sp nov., a novel halophilic archaeon isolated from a hypersaline wetland. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2142–2147
Caton TM, Caton IR, Witte LR, Schneegurt MA (2009) Archaeal diversity at the Great Salt Plains of Oklahoma described by cultivation and molecular analyses. Microb Ecol 58:519–528
Angel R, Soares MIM, Ungar ED, Gillor O (2010) Biogeography of soil archaea and bacteria along a steep precipitation gradient. ISME J 4:553–563
Acknowledgements
We thank Osnat Gillor from the Zuckerberg Institute for Water Research, J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research, Ben-Gurion University, Sede Boqer Campus, Israel; Ines M Soares, a former colleague from the Zuckerberg Institute for Water Research, J. Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research, Ben-Gurion University, Sede Boqer Campus, Israel; and Sonja Selenska-Pobell, a former colleague of the Institute of Resource Ecology from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf for collecting and providing the samples. Additionally, we admire the support from the Analytics Group of the Institute of Resource Ecology from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 359 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachran, M., Kluge, S., Lopez-Fernandez, M. et al. Microbial Diversity in an Arid, Naturally Saline Environment. Microb Ecol 78, 494–505 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1301-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1301-2