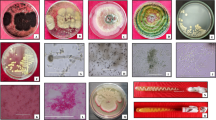
Abstract
Bacterial diversity of soil samples collected from different geographical regions of Himalayan mountains was studied through culturable (13 samples) and culture-independent approaches (5 samples based on abundance of diversity indices in each ecological niche). Shannon–Wiener diversity index and total bacterial count ranged from 1.50 ± 0.1 to 2.57 ± 0.15 and 7.8 ± 1.6 × 105 to 30.9 ± 1.7 × 105 cfu ml−1 of soil, respectively. Based on morphology and pigmentation, 406 isolates were selected by culturing in different cultivable media at various strengths and concentrations. All the strains were subjected to amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis and the representative isolates from each cluster were chosen for 16S rRNA gene sequence-based identification. Soil habitat in Himalayan foot hills was dominated by the genera Arthrobacter, Exiguobacterium, Bacillus, Cedecea, Erwinia, and Pseudomonas. Five 16S rRNA gene libraries from the selected five samples yielded 268 clones and were grouped into 53 phylotypes covering 25 genera including the genus of Ferribacterium, Rothia, and Wautersiella, which were reported for the first time in Himalayan tracks. Principal coordinates analysis indicates that all the clone libraries were clearly separated and found to be significantly different from each other. Further, extracellular investigation of cold-active enzymes showed activity of cellulase (23.71 %), pectinase (20.24 %), amylase (17.32 %), phytase (13.87 %), protease (12.72 %), and lipase (23.71 %) among the isolates. Four isolates namely Exiguobacterium mexicanum (BSa14), Exiguobacterium sibiricum (BZa11), Micrococcus antarcticus (BSb10), and Bacillus simplex (BZb3) showed multiple enzyme activity for five different types of enzymes. In addition, various genera like Exiguobacterium, Erwinia, Mycetecola, Cedecea, Pantoea, and Trichococcus have also shown novel hydrolytic enzyme activity in the Himalayan foothills.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pradhan S, Srinivas TNR, Pindi P, Kishore KH, Begum Z, Singh P, Singh A, Pratibha MS, Yasala A, Reddy GSN, Shivaji S (2010) Bacterial biodiversity from Roopkund Glacier, Himalayan mountain ranges, India. Extremophiles 14(4):377–395. doi:10.1007/s00792-010-0318-3
Shivaji S, Pratibha MS, Sailaja B, Hara Kishore K, Singh AK, Begum Z, Anarasi U, Prabagaran SR, Reddy GS, Srinivas TN (2011) Bacterial diversity of soil in the vicinity of Pindari glacier, Himalayan mountain ranges, India, using culturable bacteria and soil 16S rRNA gene clones. Extremophiles 15(1):1–22. doi:10.1007/s00792-010-0333-4
Mayilraj S, Prasad GS, Suresh K, Saini HS, Shivaji S, Chakrabarti T (2005) Planococcus stackebrandtii sp. nov., isolated from a cold desert of the Himalayas, India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(Pt 1):91–94. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63290-0
Gangwar P, Alam SI, Singh L (2011) Metabolic characterization of cold active Pseudomonas, Arthrobacter, Bacillus, and Flavobacterium spp. from Western Himalayas. Indian J Microbiol 51(1):70–75. doi:10.1007/s12088-011-0092-7
Skidmore M, Anderson SP, Sharp M, Foght J, Lanoil BD (2005) Comparison of microbial community compositions of two subglacial environments reveals a possible role for microbes in chemical weathering processes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6986–6997. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.11.6986-6997.2005
Gangwar P, Alam SI, Bansod S, Singh L (2009) Bacterial diversity of soil samples from the western Himalayas, India. Can J Microbiol 55(5):564–577. doi:10.1139/w09-011
Nemergut DR, Anderson SP, Cleveland CC, Martin AP, Miller AE, Seimon A, Schmidt SK (2007) Microbial community succession in an unvegetated, recently deglaciated soil. Microb Ecol 53(1):110–122. doi:10.1007/s00248-006-9144-7
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Kang S, Zeng Y, Huang S (2006) Microbial community structure in moraine lakes and glacial meltwaters, Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Lett 265(1):98–105. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00477.x
Xiang SR, Shang TC, Chen Y, Jing ZF, Yao TD (2009) Dominant bacteria and biomass in the Kuytun 51 glacier. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(22):7287–7290. doi:10.1128/Aem.00915-09
Zhang X, Yao T, An L, Tian L, Xu S (2006) A study on the vertical profile of bacterial DNA structure in the Puruogangri (Tibetan Plateau) ice core using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Ann Glaciol 43(1):160–166. doi:10.3189/172756406781811934
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Kang S, Xu B, Zeng Y, Huang S, Liu X (2009) Bacterial diversity in the snow over Tibetan Plateau Glaciers. Extremophiles 13(3):411–423. doi:10.1007/s00792-009-0227-5
Zhang XF, Yao TD, Tian LD, Xu SJ, An LZ (2008) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of bacteria isolated from Puruogangri ice core. Microb Ecol 55(3):476–488. doi:10.1007/s00248-007-9293-3
Zhang S, Hou S, Yang G, Wang J (2010) Bacterial community in the East Rongbuk Glacier, Mt. Qomolangma (Everest) by culture and culture-independent methods. Microbiol Res 165(4):336–345. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2009.08.002
Srinivas TN, Singh SM, Pradhan S, Pratibha MS, Kishore KH, Singh AK, Begum Z, Prabagaran SR, Reddy GS, Shivaji S (2011) Comparison of bacterial diversity in proglacial soil from Kafni Glacier, Himalayan Mountain ranges, India, with the bacterial diversity of other glaciers in the world. Extremophiles 15(6):673–690. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0398-8
Shivaji S, Bhadra B, Rao RS, Pradhan S (2008) Rhodotorula himalayensis sp. nov., a novel psychrophilic yeast isolated from Roopkund Lake of the Himalayan mountain ranges, India. Extremophiles 12(3):375–381. doi:10.1007/s00792-008-0144-z
Mayilraj S, Kroppenstedt RM, Suresh K, Saini HS (2006) Kocuria himachalensis sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from the Indian Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(Pt 8):1971–1975. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63915-0
Negi YK, Prabha D, Garg SK, Kumar J (2010) Genetic diversity among cold-tolerant fluorescent Pseudomonas isolates from Indian Himalayas and their characterization for biocontrol and plant growth-promoting activities. J Plant Growth Regul 30(2):128–143. doi:10.1007/s00344-010-9175-7
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Tian L, Hu A, Yu W, Li S (2011) Microbial diversity in the snow, a moraine lake and a stream in Himalayan glacier. Extremophiles 15(3):411–421. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0372-5
Baghel VS, Tripathi RD, Ramteke PW, Gopal K, Dwivedi S, Jain RK, Rai UN, Singh SN (2005) Psychrotrophic proteolytic bacteria from cold environment of Gangotri glacier, Western Himalaya, India. Enzym Microb Technol 36(5–6):654–659. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2004.09.005
Mayilraj S, Suresh K, Kroppenstedt RM, Saini HS (2006) Dietzia kunjamensis sp. nov., isolated from the Indian Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(Pt 7):1667–1671. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64212-0
Singh NK, Raichand R, Kaur I, Kaur C, Pareek S, Mayilraj S (2013) Exiguobacterium himgiriensis sp. nov. a novel member of the genus Exiguobacterium, isolated from the Indian Himalayas. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103(4):789–796. doi:10.1007/s10482-012-9861-5
Singla AK, Mayilraj S, Kudo T, Krishnamurthi S, Prasad GS, Vohra RM (2005) Actinoalloteichus spitiensis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from a cold desert of the Indian Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(Pt 6):2561–2564. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63720-0
Kishore KH, Begum Z, Pathan AA, Shivaji S (2010) Paenibacillus glacialis sp. nov., isolated from the Kafni glacier of the Himalayas, India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(Pt 8):1909–1913. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.015271-0
Chaturvedi P, Reddy GS, Shivaji S (2005) Dyadobacter hamtensis sp. nov., from Hamta glacier, located in the Himalayas, India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(Pt 5):2113–2117. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63806-0
Reddy GS, Uttam A, Shivaji S (2008) Bacillus cecembensis sp. nov., isolated from the Pindari glacier of the Indian Himalayas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(Pt 10):2330–2335. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65515-0
Chaturvedi P, Shivaji S (2006) Exiguobacterium indicum sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium from the Hamta glacier of the Himalayan mountain ranges of India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(Pt 12):2765–2770. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64508-0
Pindi PK, Kishore KH, Reddy GS, Shivaji S (2009) Description of Leifsonia kafniensis sp. nov. and Leifsonia antarctica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(Pt 6):1348–1352. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.006643-0
Reddy GS, Pradhan S, Manorama R, Shivaji S (2010) Cryobacterium roopkundense sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from glacial soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(Pt 4):866–870. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.011775-0
Reddy GS, Prabagaran SR, Shivaji S (2008) Leifsonia pindariensis sp. nov., isolated from the Pindari glacier of the Indian Himalayas, and emended description of the genus Leifsonia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(Pt 9):2229–2234. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65715-0
Sahay H, Babu BK, Singh S, Kaushik R, Saxena AK, Arora DK (2012) Cold-active hydrolases producing bacteria from two different sub-glacial Himalayan lakes. J Basic Microbiol. doi:10.1002/jobm.201200126
Feller G, Gerday C (2003) Psychrophilic enzymes: hot topics in cold adaptation. Nat Rev Microbiol 1(3):200–208. doi:10.1038/nrmicro773
Dunbar J, Ticknor LO, Kuske CR (2000) Assessment of microbial diversity in four southwestern United States soils by 16S rRNA gene terminal restriction fragment analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(7):2943–2950. doi:10.1128/aem.66.7.2943-2950.2000
McCaig AE, Glover LA, Prosser JI (1999) Molecular analysis of bacterial community structure and diversity in unimproved and improved upland grass pastures. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(4):1721–1730
Cho J-C, Kim S-J (2000) Increase in bacterial community diversity in subsurface aquifers receiving livestock wastewater input. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):956–965. doi:10.1128/aem.66.3.956-965.2000
Chang BioScience, 2004. Shannon–Wiener diversity index/Shannon entropy calculator. <http://www.changbioscience.com/genetics/shannon.html>.
Romano RT, Zhang R, Teter S, McGarvey JA (2009) The effect of enzyme addition on anaerobic digestion of Jose Tall Wheat Grass. Bioresour Technol 100:4564–4571. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.065
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wright ES, Yilmaz LS, Noguera DR (2012) DECIPHER, a search-based approach to chimera identification for 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(3):717–725. doi:10.1128/aem.06516-11
Kim O-S, Cho Y-J, Lee K, Yoon S-H, Kim M, Na H, Park S-C, Jeon YS, Lee J-H, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(Pt 3):716–721. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Tamura K, Peterso K, Peterson N, Stecher G, Masatoshi N, Sudhir K (2011) MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 10(28):2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Kasana RC, Salwan R, Dhar H, Dutt S, Gulati A (2008) A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using gram’s iodine. Curr Microbiol 57(5):503–507. doi:10.1007/s00284-008-9276-8
Lu M, Fang Y, Li H, Liu H, Wang S (2010) Isolation of a novel cold-adapted amylase-producing bacterium and study of its enzyme production conditions. Ann Microbiol 60(3):557–563. doi:10.1007/s13213-010-0090-8
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2009) Methods for detection and characterization of lipases: a comprehensive review. Biotechnol Adv 27(6):782–798. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.06.001
Yoon SJ, Choi YJ, Min HK, Cho KK, Kim JW, Lee SC, Jung YH (1996) Isolation and identification of phytase-producing bacterium, Enterobacter sp. 4, and enzymatic properties of phytase enzyme. Enzym Microb Technol 18(6):449–454. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(95)00131-X
Zhou MY, Chen XL, Zhao HL, Dang HY, Luan XW, Zhang XY, He HL, Zhou BC, Zhang YZ (2009) Diversity of both the cultivable protease-producing bacteria and their extracellular proteases in the sediments of the South China Sea. Microb Ecol 58(3):582–590. doi:10.1007/s00248-009-9506-z
Jacob N, Asha Poorna C, Prema P (2008) Purification and partial characterization of polygalacturonase from Streptomyces lydicus. Bioresour Technol 99(14):6697–6701. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.002
Christner BC, Mosley-Thompson E, Thompson LG, Zagorodnov V, Sandman K, Reeve JN (2000) Recovery and identification of viable bacteria immured in glacial ice. Icarus 144(2):479–485. doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6288
Miteva VI, Sheridan PP, Brenchley JE (2004) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of microorganisms isolated from a deep Greenland glacier ice core. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(1):202–213. doi:10.1128/aem.70.1.202-213.2004
McDougald D, Rice SA, Weichart D, Kjelleberg S (1998) Nonculturability: adaptation or debilitation? FEMS Microbiol Ecol 25(1):1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.1998.tb00455.x
Cho J-C, Tiedje JM (2000) Biogeography and degree of endemicity of fluorescent Pseudomonas strains in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5448–5456. doi:10.1128/aem.66.12.5448-5456.2000
Antibus D, Leff L, Hall B, Baeseman J, Blackwood C (2012) Cultivable bacteria from ancient algal mats from the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Extremophiles 16(1):105–114. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0410-3
Lemos LN, Fulthorpe RR, Triplett EW, Roesch LF (2011) Rethinking microbial diversity analysis in the high throughput sequencing era. J Microbiol Methods 86(1):42–51. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2011.03.014
Michaud L, Cello F, Brilli M, Fani R, Giudice A, Bruni V (2004) Biodiversity of cultivable psychrotrophic marine bacteria isolated from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol Lett 230(1):63–71. doi:10.1016/s0378-1097(03)00857-7
Ravenschlag K, Sahm K, Pernthaler J, Amann R (1999) High bacterial diversity in permanently cold marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(9):3982–3989
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Rea SM, McMeekin TA (2000) The microbial composition of three limnologically disparate hypersaline Antarctic lakes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 183(1):81–88. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb08937.x
Sabbe K, Hodgson DA, Verleyen E, Taton A, Wilmotte A, Vanhoutte K, Vyverman W (2004) Salinity, depth and the structure and composition of microbial mats in continental Antarctic lakes. Freshw Biol 49(3):296–319. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01186.x
Peeters K, Verleyen E, Hodgson D, Convey P, Ertz D, Vyverman W, Willems A (2012) Heterotrophic bacterial diversity in aquatic microbial mat communities from Antarctica. Polar Biol 35(4):543–554. doi:10.1007/s00300-011-1100-4
Brambilla E, Hippe H, Hagelstein A, Tindall BJ, Stackebrandt E (2001) 16S rDNA diversity of cultured and uncultured prokaryotes of a mat sample from Lake Fryxell, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Extremophiles 5(1):23–33. doi:10.1007/s007920000169
Smith J, Tow L, Stafford W, Cary C, Cowan D (2006) Bacterial diversity in three different Antarctic cold desert mineral soils. Microb Ecol 51(4):413–421. doi:10.1007/s00248-006-9022-3
Aislabie J, Lau A, Dsouza M, Shepherd C, Rhodes P, Turner S (2013) Bacterial composition of soils of the Lake Wellman area, Darwin Mountains, Antarctica. Extremophiles:1-12. doi:10.1007/s00792-013-0560-6
Bajerski F, Wagner D (2013) Bacterial succession in Antarctic soils of two glacier forefields on Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85(1):128–142. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12105
Chong CW, Pearce DA, Convey P, Yew WC, Tan IKP (2012) Patterns in the distribution of soil bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequences from different regions of Antarctica. Geoderma 181–182(0):45–55. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.02.017
Cowan D, Russell N, Mamais A, Sheppard D (2002) Antarctic Dry Valley mineral soils contain unexpectedly high levels of microbial biomass. Extremophiles 6(5):431–436. doi:10.1007/s00792-002-0276-5
Chong CW, Convey P, Pearce DA, Tan IKP (2012) Assessment of soil bacterial communities on Alexander Island (in the maritime and continental Antarctic transitional zone). Polar Biol 35(3):387–399. doi:10.1007/s00300-011-1084-0
Roesch LFW, Fulthorpe RR, Pereira AB, Pereira CK, Lemos LN, Barbosa AD, Suleiman AKA, Gerber AL, Pereira MG, Loss A, da Costa EM (2012) Soil bacterial community abundance and diversity in ice-free areas of Keller Peninsula, Antarctica. Appl Soil Ecol 61(0):7–15. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.04.009
Chong CW, Pearce DA, Convey P, Tan GYA, Wong RCS, Tan IKP (2010) High levels of spatial heterogeneity in the biodiversity of soil prokaryotes on Signy Island, Antarctica. Soil Biol Biochem 42(4):601–610. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.12.009
Stewart K, Snape I, Siciliano S (2012) Physical, chemical and microbial soil properties of frost boils at Browning Peninsula, Antarctica. Polar Biol 35(3):463–468. doi:10.1007/s00300-011-1076-0
Powell SM, Bowman JP, Ferguson SH, Snape I (2010) The importance of soil characteristics to the structure of alkane-degrading bacterial communities on sub-Antarctic Macquarie Island. Soil Biol Biochem 42(11):2012–2021. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.07.027
Yergeau E, Newsham KK, Pearce DA, Kowalchuk GA (2007) Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats. Environ Microbiol 9(11):2670–2682. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01379.x
Olivera N, Sequeiros C, Nievas M (2007) Diversity and enzyme properties of protease-producing bacteria isolated from sub-Antarctic sediments of Isla de Los Estados, Argentina. Extremophiles 11(3):517–526. doi:10.1007/s00792-007-0064-3
Vyas P, Rahi P, Gulati A (2009) Stress tolerance and genetic variability of phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent Pseudomonas from the cold deserts of the trans-Himalayas. Microb Ecol 58(2):425–434. doi:10.1007/s00248-009-9511-2
Selvakumar G, Joshi P, Mishra PK, Bisht JK, Gupta HS (2009) Mountain aspect influences the genetic clustering of psychrotolerant phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonads in the Uttarakhand Himalayas. Curr Microbiol 59(4):432–438. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9456-1
Ruckmani A, Chakrabarti T (2011) Analysis of bacterial community composition of a spring water from the Western Ghats, India using culture dependent and molecular approaches. Curr Microbiol 62(1):7–15. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9663-9
Dastager SG, Deepa CK, Puneet SC, Nautiyal CS, Pandey A (2009) Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting strain Pantoea NII-186. From Western Ghat forest soil, India. Lett Appl Microbiol 49(1):20–25. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02616.x
Zhang S, Hou S, Yang G, Wang J (2010) Bacterial community in the East Rongbuk Glacier, Mt. Qomolangma (Everest) by culture and culture-independent methods. Microbiol Res 165(4):336–345. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2009.08.002
Pradhan S, Srinivas TN, Pindi PK, Kishore KH, Begum Z, Singh PK, Singh AK, Pratibha MS, Yasala AK, Reddy GS, Shivaji S (2010) Bacterial biodiversity from Roopkund Glacier, Himalayan mountain ranges, India. Extremophiles 14(4):377–395. doi:10.1007/s00792-010-0318-3
Xiang SR, Shang TC, Chen Y, Jing ZF, Yao T (2009) Dominant bacteria and biomass in the Kuytun 51 Glacier. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(22):7287–7290. doi:10.1128/AEM.00915-09
Xiang SR, Yao TD, An LZ, Xu BQ, Li Z, Wu GJ, Wang YQ, Ma S, Chen XR (2004) Bacterial diversity in Malan ice core from the Tibetan Plateau. Folia Microbiol 49(3):269–275. doi:10.1007/bf02931042
Xiang S, Yao T, An L, Xu B, Wang J (2005) 16S rRNA sequences and differences in bacteria isolated from the Muztag Ata glacier at increasing depths. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(8):4619–4627. doi:10.1128/aem.71.8.4619-4627.2005
Rohini-Kumar M, Osborne J, Saravanan VS (2013) Comparison of soil bacterial communities of Pinus patula of Nilgiris, Western Ghats with other biogeographically distant pine forest clone libraries. Microb Ecol 66(1):132–144. doi:10.1007/s00248-012-0167-y
Janssen PH (2006) Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3):1719–1728. doi:10.1128/aem.72.3.1719-1728.2006
Christner B, Kvitko B II, Reeve J (2003) Molecular identification of Bacteria and Eukarya inhabiting an Antarctic cryoconite hole. Extremophiles 7(3):177–183. doi:10.1007/s00792-002-0309-0
Nold SC, Kopczynski ED, Ward DM (1996) Cultivation of aerobic chemoorganotrophic proteobacteria and gram-positive bacteria from a hot spring microbial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(11):3917–3921
Santegoeds CM, Nold SC, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis used to monitor the enrichment culture of aerobic chemoorganotrophic bacteria from a hot spring cyanobacterial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(11):3922–3928
Simbahan J, Kurth E, Schelert J, Dillman A, Moriyama E, Jovanovich S, Blum P (2005) Community analysis of a mercury hot spring supports occurrence of domain-specific forms of mercuric reductase. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8836–8845. doi:10.1128/aem.71.12.8836-8845.2005
Aminin ALN, Warganegara FM, Aditiawati P, Akhmaloka (2008) Simple enrichment and independent cultures to expand bacterial community analysis from Gedongsongo hot spring. J Biosci Bioeng 106(2):211–214. doi:10.1263/jbb.106.211
Roesch LFW, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AKM, Kent AD, Daroub SH, Camargo FAO, Farmerie WG, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J 1 (4):283-290. doi:http://www.nature.com/ismej/journal/v1/n4/suppinfo/ismej200753s1.html
Kemp PF, Aller JY (2004) Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: what 16S rDNA libraries can tell us. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47(2):161–177. doi:10.1016/s0168-6496(03)00257-5
Feller G (2007) Life at low temperatures: is disorder the driving force? Extremophiles 11(2):211–216. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0050-1
Salwan R, Gulati A, Kasana RC (2010) Phylogenetic diversity of alkaline protease-producing psychrotrophic bacteria from glacier and cold environments of Lahaul and Spiti, India. J Basic Microbiol 50(2):150–159. doi:10.1002/jobm.200800400
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (GOI) for the grant (vide reference No. SR/FT/LS-032/2008) and support by University Grants Commission (GOI) through the Special Assistance Program (SAP) (vide reference NO. F. 3-9/2007-SAP-II). The authors also acknowledge Dr. Muthu Krishnan, Assistant Professor, Department of Linguistics, Bharathiar University, for proof reading the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1627 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkatachalam, S., Gowdaman, V. & Prabagaran, S.R. Culturable and Culture-Independent Bacterial Diversity and the Prevalence of Cold-Adapted Enzymes from the Himalayan Mountain Ranges of India and Nepal. Microb Ecol 69, 472–491 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0476-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0476-4