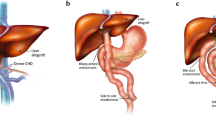
Abstract
Background
Although biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation represent a common source of morbidity and mortality, decreasing graft survival, consensus is lacking on their management in the pediatric population.
Objective
The aim of this study was to present the prevalence of such biliary complications and their interventional radiologic management with representative images.
Materials and methods
This retrospective study reports our experience with percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography in the management of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation in pediatric patients. This study enrolled all pediatric patients (<18 years old) who underwent percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography for the management of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation at a tertiary care center between January 2010 and December 2020. Diagnosis of biliary complications and indication to perform percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography were based on clinical, laboratory or radiologic data.
Results
Among the 301 orthotopic liver transplantations, 78 (26%) developed biliary complications that were managed by interventional radiology: these included 52 (17.3%) biliary strictures, 19 (6.3%) bile leaks, 5 (1.7%) biliary stones, 1 (0.3%) iatrogenic biliary obstruction and 1 (0.3%) vanishing syndrome. The median time interval between orthotopic liver transplantation and the diagnosis of biliary complications was 6.0 years (interquartile range [IQR] 8.2 years). Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and biliary duct catheterization were successful in all cases, with low rates of complications that were variable among subgroups.
Conclusion
A wide spectrum of biliary complications can occur after pediatric orthotopic liver transplantation. In this large single-center experience, we highlight the value of percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography in their diagnosis and management. Percutaneous treatments in pediatric patients are safe and effective, providing resolution or serving as a bridge to surgery, including re-transplantation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohli R, Cortes M, Heaton ND, Dhawan A (2018) Liver transplantation in children: state of the art and future perspectives. Arch Dis Child 103:192–198
Goss JA, Shackleton CR, Maggard M et al (1998) Liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure in the pediatric patient. Arch Surg 133:839–844
Adam R, Karam V, Cailliez V et al (2018) 2018 annual report of the European Liver Transplant Registry (ELTR) — 50-year evolution of liver transplantation. Transpl Int 31:1293–1317
Ryu CH, Lee SK (2011) Biliary strictures after liver transplantation. Gut Liver 5:133–142
Colledan M, D'Antiga L (2014) Biliary complications after pediatric liver transplantation: the endless heel. Pediatr Transplant 18:786–787
Laurence JM, Sapisochin G, DeAngelis M et al (2015) Biliary complications in pediatric liver transplantation: incidence and management over a decade. Liver Transpl 21:1082–1090
Sansotta N, De Luca E, Nicastro E et al (2021) Incidence of cholangitis and sepsis associated with percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography in pediatric liver transplant recipients. Antibiotics 10:282
Feier FH, Chapchap P, Pugliese R et al (2014) Diagnosis and management of biliary complications in pediatric living donor liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl 20:882–892
Racadio JM, Kukreja K (2010) Pediatric biliary interventions. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 13:244–249
Feier FH, da Fonseca EA, Seda-Neto J, Chapchap P (2015) Biliary complications after pediatric liver transplantation: risk factors, diagnosis and management. World J Hepatol 7:2162–2170
Sansotta N, Agazzi R, Sonzogni A et al (2020) Subclinical biliary strictures as a cause of long-term allograft dysfunction in children who underwent liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 21:391–399
Horvat N, Marcelino ASZ, Horvat JV et al (2017) Pediatric liver transplant: techniques and complications. Radiographics 37(6):1612–1631
Pilleul F, Guibaud L, Dugougeat F et al (2000) MR cholangiography in biliary complications after liver transplantation in children. J Radiol 81:793–798
Kinner S, Dechêne A, Paul A et al (2011) Detection of biliary stenoses in patients after liver transplantation: is there a different diagnostic accuracy of MRCP depending on the type of biliary anastomosis? Eur J Radiol 80:e20–e28
Salvolini L, Urbinati C, Valeri G et al (2012) Contrast-enhanced MR cholangiography (MRCP) with GDEOB-DTPA in evaluating biliary complications after surgery. Radiol Med 117:354–368
De Cobelli F, Marra P, Diana P et al (2017) Therapeutic EUS: biliary drainage — the interventional radiologist's perspective. Endosc Ultrasound 6:127–131
Giurazza F, Corvino F, Contegiacomo A et al (2019) Safety and effectiveness of ultrasound-guided percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: a multicenter experience. J Ultrasound 22:437–445
Miraglia R, Maruzzelli L, Caruso S et al (2008) Percutaneous management of biliary strictures after pediatric liver transplantation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:993–998
Sharma S, Gurakar A, Jabbour N (2008) Biliary strictures following liver transplantation: past, present and preventative strategies. Liver Transpl 14:759–769
Sunku B, Salvalaggio PR, Donaldson JS et al (2006) Outcomes and risk factors for failure of radiologic treatment of biliary strictures in pediatric liver transplantation recipients. Liver Transpl 12:821–826
Moreira AM, Carnevale FC, Tannuri U et al (2010) Long-term results of percutaneous bilioenteric anastomotic stricture treatment in liver-transplanted children. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:90–96
Mauri G, Michelozzi C, Melchiorre F et al (2016) Benign biliary strictures refractory to standard bilioplasty treated using polydoxanone biodegradable biliary stents: retrospective multicentric data analysis on 107 patients. Eur Radiol 26:4057–4063
Hsiao CY, Ho CM, Wu YM et al (2019) Biliary complication in pediatric liver transplantation: a single-center 15-year experience. J Gastrointest Surg 23:751–759
Moy BT, Birk JW (2019) A review on the management of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. J Clin Transl Hepatol 7:61–71
Sheng R, Ramirez CB, Zajko AB, Campbell WL (1996) Biliary stones and sludge in liver transplant patients: a 13-year experience. Radiology 198:243–247
Paterno F, Khan A, Cavaness K et al (2011) Malpositioned transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the common hepatic duct leading to biliary obstruction and liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 17:344–346
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2021) LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548715/. Accessed 27 August 2021. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda
Greca RD, Cunha-Silva M, Costab LBE et al (2020) Vanishing bile duct syndrome related to DILI and Hodgkin lymphoma overlap: a rare and severe case. Ann Hepatol 19:107–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dulcetta, L., Marra, P., Carbone, F.S. et al. Biliary complications in pediatric liver transplantation: findings of percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography in a large single-center cohort. Pediatr Radiol 52, 1061–1074 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-021-05278-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-021-05278-3