Abstract
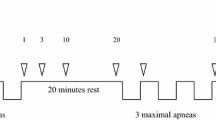
Swimming and diving are popular recreational activities, representing an effective option in maintaining and improving cardiovascular fitness in healthy people. To date, only little is known about the cardiovascular adaption to submersion in children. This study was conducted to improve an understanding thereof. We used a stepwise apnea protocol with apnea at rest, apnea with facial immersion, and at last apnea during whole body submersion. Continuous measurement of heart rate, oxygen saturation, and peripheral resistance index was done. Physiologic data and analysis of influencing factors on heart rate, oxygen saturation, and peripheral vascular tone response are reported. The current study presents the first data of physiologic diving response in children. Data showed that facial or whole body submersion leads to a major drop in heart rate, and increase of peripheral resistance, while the oxygen saturation seems to be unaffected by static apnea in most children, with apnea times of up to 75 s without change in oxygen saturation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein M (1978) Renal effects of head-out water immersion in man: implications for an understanding of volume homeostasis. Physiol Rev 58:529. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1978.58.3.529
Lehmann M, Samek L (1990) Recreational swimming in CHD patients and healthy control subjects in relation to left heart function. Clin Cardiol 13:547–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.4960130808
Lotshaw AM, Thompson M, Sadowsky HS et al (2007) Quality of life and physical performance in land- and water-based pulmonary rehabilitation. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 27:247–251. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.HCR.0000281772.28394.30
Lin YC (1984) Circulatory functions during immersion and breath-hold dives in humans. Undersea Biomed Res 11:123–138
Arborelius M, JR, Ballidin UI, Lilja B, et al (1972) Hemodynamic changes in man during immersion with the head above water. Aerosp Med 43:592–598
Park KS, Choi JK, Park YS (1999) Cardiovascular regulation during water immersion. Appl Human Sci 18:233–241. https://doi.org/10.2114/jpa.18.233
Schagatay E, Andersson J (1998) Diving response and apneic time in humans. Undersea Hyperb Med 25:13–19
Foster GE, Sheel AW (2005) The human diving response, its function, and its control. Scand J Med Sci Sports 15:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0838.2005.00440.x
Pelliccia A, Sharma S, Gati S et al (2021) 2020 ESC Guidelines on sports cardiology and exercise in patients with cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 42:17–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa605
Paech C, Gebauer RA, Weidenbach M et al (2021) The Fontan and the sea: first-in-man data on swimming and diving physiology in Fontan patients. Pediatr Cardiol 42:1614–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-021-02649-3
Paech C, Gebauer RA, Weidenbach M et al (2023) Into the Blue: first in man data on diving physiology in Fontan patients. Pediatr Cardiol 44:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-02966-1
de Felice C, Goldstein MR, Parrini S et al (2006) Early dynamic changes in pulse oximetry signals in preterm newborns with histologic chorioamnionitis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 7:138–142. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PCC.0000201002.50708.62
Schena F, Picciolli I, Agosti M et al (2017) Perfusion index and pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart defects. J Pediatr 183:74-79.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.12.076
Lima A, Bakker J (2005) Noninvasive monitoring of peripheral perfusion. Intensive Care Med 31:1316–1326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-005-2790-2
Coutrot M, Dudoignon E, Joachim J et al (2021) Perfusion index: physical principles, physiological meanings and clinical implications in anaesthesia and critical care. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med 40:100964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accpm.2021.100964
Andersson JPA, Linér MH, Rünow E et al (1985) (2002) Diving response and arterial oxygen saturation during apnea and exercise in breath-hold divers. J Appl Physiol 93:882–886. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00863.2001
Scholander PF (1963) The master switch of life. Sci Am 209(92):106. https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican1263-92
Butler PJ, Woakes AJ (1987) Heart rate in humans during underwater swimming with and without breath-hold. Respir Physiol 69:387–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-5687(87)90091-0
Shattock MJ, Tipton MJ (2012) “Autonomic conflict”: a different way to die during cold water immersion? J Physiol 590:3219–3230. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.229864
Mulder E, Schagatay E, Sieber A (2021) Using underwater pulse oximetry in freediving to extreme depths to study risk of hypoxic blackout and diving response phases. Front Physiol 12:651128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.651128
Andersson JPA, Linér MH, Fredsted A et al (1985) (2004) Cardiovascular and respiratory responses to apneas with and without face immersion in exercising humans. J Appl Physiol 96:1005–1010. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01057.2002
Funding
The current study was funded by the Deutsche Stiftung für Herzforschung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR, CP, and ES wrote the main manuscript text. CP, MR, DM, and MP conducted the measurements during diving protocol. JW performed the statistical analysis. FM and AM provided Figs. 1, 2, and 6. JW, RAG, and AS prepared Table 1 and Figs. 3, 4, and 5. MW and ID supervised the study and helped in developing the study protocol. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and / or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study received ethical approval by the ethics committee University of Leipzig and is listed under the reference 549/19-ek.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study as well as from their legal guardians.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rixen, M., Weickmann, J., Gebauer, R.A. et al. First Real-Life Data on the Diving Response in Healthy Children. Pediatr Cardiol 45, 314–322 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-023-03370-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-023-03370-z