Abstract
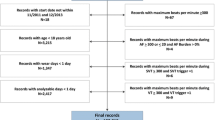
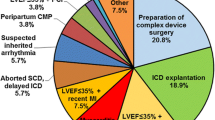
Ambulatory electrocardiogram monitoring devices can be used for 24–72 h to detect arrhythmias. A new device, the ZIO® XT Patch has cardiac monitoring capabilities that can be utilized for up to 14 days. The purpose of this study is to describe duration of ZIO use by age, and to compare its time to arrhythmia detection with the Holter monitor in a pediatric population. A single-center, retrospective review of patients < 18 years of age who underwent clinical investigation with ZIO from October 2014 to February 2016 was performed. An age-matched cohort was utilized to compare ZIO to Holter monitor results. Demographic and diagnostic data, time to first arrhythmia, and arrhythmia burden were analyzed. A total of 406 ZIO were prescribed; median age 12.7 years and 50% male subjects. Median duration of ZIO monitoring significantly increased with age (p < 0.001). 499 Holter monitors were prescribed on a statistically different age group. Arrhythmia detection rates were similar between groups, 10% (n = 42) by ZIO and 9% (n = 45) by Holter (p = NS). The majority of arrhythmias (57%) detected by ZIO were after 24 h (p < 0.0001). All arrhythmias detected by Holter monitor occurred within 24 h (p < 0.0001), mean duration of wear was 24.1 h, range 0.5–48 h. The ZIO® XT Patch may be considered as an ambulatory ECG monitor to diagnose arrhythmia in pediatric patients of all ages. Increasing patient age resulted in increasing duration of ZIO monitoring. Majority of arrhythmias detected with ZIO were identified after 24 h, which would have been missed by other short-term monitors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locati ET, Vecchi AM, Vargiu S, Cattafi G et al (2013) Role of extended external loop recorders for the diagnosis of unexplained syncope, pre-syncope, and sustained palpitations. Europace 16(6):914–922
Sreeram N, Gass M, Apitz C et al (2007) The diagnostic yield from implantable loop recorders in children and young adults. Clin Res Cardiol 97(5):327–333
Fung E, Järvelin M-R, Doshi RN et al (2015) Electrocardiographic patch devices and contemporary wireless cardiac monitoring. Front Physiol 6:149
Zimetbaum P, Goldman A (2010) Ambulatory arrhythmia monitoring: choosing the right device. Circulation 122(16):1629–1636
Rees AH, Solinger R, Elbl F (1985) Holter monitoring in the management of cardiac arrhythmias in children. Compr Ther 11(3):11–16
Hegazy RA, Lotfy WN (2007) The value of Holter monitoring in the assessment of Pediatric patients. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 7(4):204–214
Begic Z, Begic E, Mesihovic-Dinarevic S, Masic I et al (2016) The use of continuous electrocardiographic Holter monitoring in pediatric cardiology. Acta Inform Med 24(4):253–256
Turakhia MP, Hoang DD, Zimetbaum P, Miller JD et al (2013) Diagnostic utility of a novel leadless arrhythmia monitoring device. Am J Cardiology 112(4):520–524
Schreiber D, Sattar A, Drigalla D, Higgins S (2014) Ambulatory cardiac monitoring for discharged emergency department patients with possible cardiac arrhythmias. West J Emerg Med 15(2):194–198
Cheung CC, Kerr CR, Krahn AD (2014) Comparing 14-day adhesive patch with 24-h Holter monitoring. Future Cardiol 10(3):319–322
Barrett PM, Komatireddy R, Haaser S, Topol S (2014) Comparison of 24-hour Holter monitoring with 14-day novel adhesive patch electrocardiographic monitoring. Am J Med 127(1):95.e11–95.e17
Bolourchi M, Batra AS (2015) Diagnostic yield of patch ambulatory electrocardiogram monitoring in children (from a national registry). Am J Cardiol 115(5):630–634
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SP: data review, writing. JAR: study design, data collection, writing. JKS: study design, paper final review. CSS: study design, data review, writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pradhan, S., Robinson, J.A., Shivapour, J.K. et al. Ambulatory Arrhythmia Detection with ZIO® XT Patch in Pediatric Patients: A Comparison of Devices. Pediatr Cardiol 40, 921–924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-019-02089-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-019-02089-0