Abstract
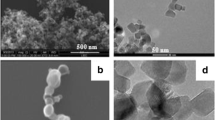
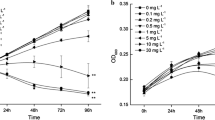
A series of experiments was undertaken on three different marine microalgae to compare the effect of two metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) on different physiological responses to stress: zinc oxide (ZnO), a known toxic compound for microalgae, and the never before tested yttrium oxide (Y2O3). The effect of these potential pollutants was estimated for different physiological variables and temporal scales: Growth, carbon content, carbon-to-nitrogen (C:N) ratio, and chlorophyll fluorescence were evaluated in long-term assays, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was evaluated in a short-term assay. Population growth was the most susceptible variable to the acute toxic effects of both NPs as measured in terms of number of cells and of biomass. Although Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Alexandrium minutum were negatively affected by ZnO NPs, this effect was not detected in Tetraselmis suecica, in which cell growth was significantly decreased by Y2O3 NPs. Biomass per cell was negatively affected in the most toxic treatments in T. suecica but was positively affected in A. minutum. ZnO treatments induced a sharper decrease in chlorophyll fluorescence and higher ROS than did Y2O3 treatments. The pronounced differences observed in the responses between the species and the physiological variables tested highlight the importance of analyzing diverse groups of microalgae and various physiological levels to determine the potential effects of environmental pollutants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahner BA, Morel FMM (1995) Phytochelatin production in marine algae. 2. Induction by various metals. Limnol Oceanogr 40:658–665
Ahner BA, Wei L, Oleson JR, Ogura N (2002) Glutathione and other low molecular weight thiols in marine phytoplankton under metal stress. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 232:93–103
Aruoja V, Dubourguier HC, Kasemets K, Kahru A (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci Total Environ 407:1461–1468
Bour G, Reinholdt A, Stepanov A, Keutgen C, Kreibig U (2001) Optical and electrical properties of hydrogenated yttrium nanoparticles. Eur Phys J D 16:219–223
Brand LE, Sunda WG, Guillard RRL (1986) Reduction of marine phytoplankton reproduction rates by copper and cadmium. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 96:225–250
Croot PL, Moffett JW, Brand LE (2000) Production of extracellular Cu complexing ligands by eucaryotic phytoplankton in response to Cu stress. Limnol Oceanogr 45:619–627
Cross SE, Innes B, Roberts MS, Tsuzuki T, Robertson TA, McCormick P (2007) Human skin penetration of sunscreen nanoparticles: in-vitro assessment of a novel micronized zinc oxide formulation. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 20:148–154
Díaz B, Sánchez-Espinel C, Arruebo M, Faro J, de Miguel E, Magadán S et al (2008) Assessing methods for blood cell cytotoxic responses to inorganic nanoparticles and nanoparticle aggregates. Small 4:2025–2034
Dietz KJ, Krämer U, Baier M (1999) Free radicals and reactive oxygen species as mediators of heavy metal toxicity. In: Prasad MNV, Hagemeyer J (eds) Heavy metal stress in plants: from molecules to ecosystem. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 73–97
Domingues N, Matos AR, da Silva JM, Cartaxana P (2012) Response of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum to photooxidative stress resulting from high light exposure. PLoS ONE 7:e38162
Ebenezer V, Nancharaiah YV, Venugopalan VP (2012) Chlorination-induced cellular damage and recovery in marine microalga, Chlorella salina. Chemosphere 89:1042–1047
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41:8484–8490
Gélabert A, Pokrovsky OS, Viers J, Schott J, Boudou A, Feurtet-Mazel A (2006) Interaction between zinc and freshwater and marine diatom species: surface complexation and Zn isotope fractionation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:839–857
Guillard RRL, Hargraves PE (1993) Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 32:234–236
Hiltunen TJ, Barreiro A, Hairston NG Jr (2012) Mixotrophy and the toxicity of Ochromonas in a pelagic food web. Freshw Biol 57:2262–2271
Hotze EM, Phenrat T, Lowry GV (2010) Nanoparticle aggregation: challenges to understanding transport and reactivity in the environment. J Environ Qual 39:1909–1924
Hund-Rinke K, Simon M (2006) Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 13:225–232
Hutchinson TC, Stokes PM (1975) Heavy metal toxicity and algal bioassays. Water Qual Parameter 573:320–343
Kawakami SK, Gledhill M, Achterberg EP (2006) Production of phytochelatins and glutathione by marine phytoplankton in response to metal stress. J Phycol 42:975–998
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY et al (2009) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1825–1851
Kottuparambil S, Shin W, Brown MT, Han T (2012) UV-B affects photosynthesis, ROS production and motility of the freshwater flagellate, Euglena agilis Carter. Aquat Toxicol 122:206–213
Leonardos N, Geider RJ (2005) Elemental and biochemical composition of Rhinomonas reticulate (Cryptophyta) in relation to light and nitrate-to-phosphate supply ratios. J Phycol 41:567–576
Liu S, Xu L, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2010) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by nanosized titanium dioxide in PC12 cells. Toxicology 267:172–177
Liufu S, Xiao H, Li Y (2004) Investigation of PEG adsorption on the surface of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Powder Technol 145:20–24
Lozano T, Rey M, Rojas E, Moya S, Fleddermann J, Estrela-Lopis I et al (2011) Cytotoxicity effects of metal oxide nanoparticles in human tumor cell lines. J Phys Conf Ser 304:012046
Macfie SM, Tarmohamed Y, Welbourn PM (1994) Effects of cadmium, cobalt, copper, and nickel on growth of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: the influences of the cell wall and pH. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27:454–458
Maeda S, Mizoguchi M, Ohki A, Takeshita T (1990) Bioaccumulation of zinc and cadmium in freshwater alga, Chlorella vulgaris. Part I. Toxicity and accumulation. Chemosphere 21:953–963
Miao AJ, Zhang XY, Luo Z, Chen CS, Chin WC, Santschi PH et al (2010a) Zinc oxide-engineered nanoparticles: dissolution and toxicity to marine phytoplankton. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2814–2822
Miao AJ, Luo Z, Chen CS, Chin WC, Santschi PH, Quigg A (2010b) Intracellular uptake: a possible mechanism for silver engineered nanoparticle toxicity to a freshwater alga Ochromonas danica. PLoS ONE 5:e15196
Miller RJ, Lenihan HS, Muller EB, Tseng N, Hanna SK, Keller AA (2010) Impacts of metal oxide nanoparticles on marine phytoplankton. Environ Sci Technol 44:7329–7334
Moore MN (2006) Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ Int 32:967–976
Mu L, Sprando RL (2010) Application of nanotechnology in cosmetics. Pharmacol Res 27:1746–1749
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao AJ et al (2008a) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N et al (2008b) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964
Neal AL (2008) What can be inferred from bacterium-nanoparticle interactions about the potential consequences of environmental exposure to nanoparticles? Ecotoxicology 17:362–371
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Özkoc HB, Taylan ZS (2010) Assessment of various parameters of metal biology in marine microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Fresenius Environ Bull 19(12):2981–2986
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1712–1720
Pérez-Rama M, Abalde Alonso J, Herrero López C, Torres Vaamonde E (2002) Cadmium removal by living cells of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica. Bioresource Technol 84:265–270
Rijstenbil JW, Derksen JWM, Gerringa LJA, Poortvliet TCW, Sandee A, Berg M et al (1994) Oxidative stress induced by copper: defense and damage in the marine planktonic diatom Ditylum brightwellii grown in continuous cultures with high and low zinc levels. Mar Biol 119:583–590
Rodriguez-Moya M, Li D, Alvarez PJJ (2007) Inactivation of virus in water by nanoparticles under UV irradiation. In: Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, Utah
Schubert D, Dargusch R, Raitano J, Chan SW (2006) Cerium and yttrium oxide nanoparticles are neuroprotective. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:86–91
Srinivasan R, Yogamalar R, Bose AC (2010) Structural and optical studies of yttrium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater Res Bull 45:1165–1170
Sunda WG, Huntsman SA (1996) Antagonisms between cadmium and zinc toxicity and manganese limitation in a coastal diatom. Limnol Oceanogr 41:373–387
Sunda W, Kieber DJ, Kiene RP, Huntsman S (2002) An antioxidant function for DMSP and DMS in marine algae. Nature 418:317–320
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2006) Physiological behavior of Scenedesmus sp. during exposure to elevated levels of Cu and Zn and after withdrawal of metal stress. Protoplasma 229:1–9
Volk T, Hoffert MI (1985) Ocean carbon pumps: Analysis of relative strengths and efficiencies in ocean-driven atmospheric CO2 changes. In: Sundquist ET, Broecker WS (eds) The carbon cycle and atmospheric CO2: natural variations archean to present. Geophysical Monograph Series, vol 32. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 99–110
Wang ZL (2004) Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J Phys Condens Matter 16:R829–R858
Weckx JEJ, Clijsters HMM (1997) Zn phytotoxicity induces oxidative stress in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:405–410
Wigginton NS, Haus KL, Hochella MF Jr (2007) Aquatic environmental nanoparticles. J Environ Monit 9:1306–1316
Wong SWY, Leung PT, Djurišić AB, Leung KM (2010) Toxicities of nano zinc oxide to five marine organisms: influences of aggregate size and ion solubility. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:609–618
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Maëdler L, Gilbert B, Shi H et al (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2:2121–2134
Xia T, Li N, Nel AE (2009) Potential health impact of nanoparticles. Annu Rev Public Health 30:137–150
Yang L, Watts DJ (2005) Particle surface characteristics may play an important role in phytotoxicity of alumina nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 158:122–132
Acknowledgments
We thank Tamara Lozano and Mercedes Peleteiro for advice on flow cytometry. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7-NMP-SMALL-2) and (FP7/REGPOT-2012-2013.1) under grant agreements HINAMOX-228825 and BIOCAPS-316265, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro-Bugallo, A., González-Fernández, Á., Guisande, C. et al. Comparative Responses to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Marine Phytoplankton. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67, 483–493 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0044-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0044-4