Abstract
Purpose
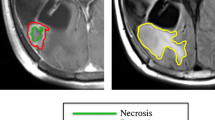
The peritumoral non-enhancing region (NER) is frequently not removed during the surgical resection of glioblastoma, with most recurrences occurring within the original treatment field. This study determined whether radiomics analysis of the NER can predict local recurrence and overall survival in patients with glioblastoma.
Methods
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans from 83 consecutive patients with glioblastoma were retrospectively reviewed and grouped into training (n = 59) and test sets (n = 24). A total of 6472 radiomic features were extracted from contrast-enhanced T1-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images and from fractional anisotropy (FA) and normalized cerebral blood volume (CBV) maps. A diagnostic model to predict 6-month progression was tested using the area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) and compared with the single parameters of FA and CBV. A survival model was tested using Harrell’s C-index and compared with clinical models that included age, sex, Karnofsky performance score, and extent of surgical resection.
Results
Four FA features and six CBV features were selected for the diagnostic model; no features were extracted from conventional MRI. Combined FA and CBV radiomics showed better predictive value for local progression (AUC, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.67–0.90) than single imaging radiomics (AUC, 0.70–0.76) or single imaging parameters (AUC, 0.51–0.54). The combined model (C-index, 0.87) improved prognostication when added to clinical models (C-index, 0.72).
Conclusion
Radiomics features using FA and CBV in the NER have the potential to improve prediction of local progression and overall survival in patients with glioblastoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oh J, Henry RG, Pirzkall A, Lu Y, Li X, Catalaa I, Chang S, Dillon WP, Nelson SJ (2004) Survival analysis in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: predictive value of choline-to-N-acetylaspartate index, apparent diffusion coefficient, and relative cerebral blood volume. J Magn Reson Imaging : JMRI 19(5):546–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20039
Parsa AT, Wachhorst S, Lamborn KR, Prados MD, McDermott MW, Berger MS, Chang SM (2005) Prognostic significance of intracranial dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme in adults. J Neurosurg 102(4):622–628
Stecco A, Pisani C, Quarta R, Brambilla M, Masini L, Beldì D, Zizzari S, Fossaceca R, Krengli M, Carriero A (2011) DTI and PWI analysis of peri-enhancing tumoral brain tissue in patients treated for glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 102(2):261–271
Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RT, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Bussink J, Monshouwer R, Haibe-Kains B, Rietveld D, Hoebers F, Rietbergen MM, Leemans CR, Dekker A, Quackenbush J, Gillies RJ, Lambin P (2014) Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 5:4006. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006
Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, Forster K, Aerts HJ, Dekker A, Fenstermacher D, Goldgof DB, Hall LO, Lambin P, Balagurunathan Y, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2012) Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1234–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010
Jain R, Poisson LM, Gutman D, Scarpace L, Hwang SN, Holder CA, Wintermark M, Rao A, Colen RR, Kirby J, Freymann J, Jaffe CC, Mikkelsen T, Flanders A (2014) Outcome prediction in patients with glioblastoma by using imaging, clinical, and genomic biomarkers: focus on the nonenhancing component of the tumor. Radiology 272(2):484–493. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14131691
Boxerman JL, Schmainda KM, Weisskoff RM (2006) Relative cerebral blood volume maps corrected for contrast agent extravasation significantly correlate with glioma tumor grade, whereas uncorrected maps do not. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(4):859–867
Mohsen L, Shi V, Jena R, Gillard J, Price S (2013) Diffusion tensor invasive phenotypes can predict progression-free survival in glioblastomas. Br J Neurosurg 27(4):436–441
Bette S, Huber T, Gempt J, Boeckh-Behrens T, Wiestler B, Kehl V, Ringel F, Meyer B, Zimmer C, Kirschke JS (2017) Local fractional anisotropy is reduced in areas with tumor recurrence in glioblastoma. Radiology 283(2):499–507. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016152832
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Zhou H, Vallieres M, Bai HX, Su C, Tang H, Oldridge D, Zhang Z, Xiao B, Liao W, Tao Y, Zhou J, Zhang P, Yang L (2017) MRI features predict survival and molecular markers in diffuse lower-grade gliomas. Neuro-oncology. 19:862–870. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now256
Kickingereder P, Burth S, Wick A, Gotz M, Eidel O, Schlemmer HP, Maier-Hein KH, Wick W, Bendszus M, Radbruch A, Bonekamp D (2016) Radiomic profiling of glioblastoma: identifying an imaging predictor of patient survival with improved performance over established clinical and radiologic risk models. Radiology 280(3):880–889. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016160845
Lee J, Jain R, Khalil K, Griffith B, Bosca R, Rao G, Rao A (2016) Texture feature ratios from relative CBV maps of perfusion MRI are associated with patient survival in glioblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4534
Kickingereder P, Neuberger U, Bonekamp D, Piechotta PL, Gotz M, Wick A, Sill M, Kratz A, Shinohara RT, Jones DTW, Radbruch A, Muschelli J, Unterberg A, Debus J, Schlemmer HP, Herold-Mende C, Pfister S, von Deimling A, Wick W, Capper D, Maier-Hein KH, Bendszus M (2018) Radiomic subtyping improves disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging characteristics in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro-oncology 20(6):848–857. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox188
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for R, Treatment of Cancer Brain T, Radiotherapy G, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials G (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28(11):1963–1972. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.3541
Nolden M, Zelzer S, Seitel A, Wald D, Muller M, Franz AM, Maleike D, Fangerau M, Baumhauer M, Maier-Hein L, Maier-Hein KH, Meinzer HP, Wolf I (2013) The Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit: challenges and advances: 10 years of open-source development. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8(4):607–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0840-8
Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Song G, Cook PA, Klein A, Gee JC (2011) A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. NeuroImage 54(3):2033–2044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.025
Shinohara RT, Sweeney EM, Goldsmith J, Shiee N, Mateen FJ, Calabresi PA, Jarso S, Pham DL, Reich DS, Crainiceanu CM, Australian Imaging Biomarkers Lifestyle Flagship Study of A, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2014) Statistical normalization techniques for magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage Clin 6:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.08.008
Weisskoff R, Boxerman J, Sorensen A, Kulke S, Campbell T, Rosen B (1994) Simultaneous blood volume and permeability mapping using a single Gd-based contrast injection. In: Proceedings of the Society of Magnetic Resonance, Second Annual Meeting, San Francisco, Calif. Berkeley, 1994. p p. 279
Collewet G, Strzelecki M, Mariette F (2004) Influence of MRI acquisition protocols and image intensity normalization methods on texture classification. Magn Reson Imaging 22(1):81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2003.09.001
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 58(1):267–288
Wu TT, Chen YF, Hastie T, Sobel E, Lange K (2009) Genome-wide association analysis by lasso penalized logistic regression. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 25(6):714–721. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp041
Hepp T, Schmid M, Gefeller O, Waldmann E, Mayr A (2016) Approaches to regularized regression - a comparison between gradient boosting and the lasso. Methods Inf Med 55(5):422–430. https://doi.org/10.3414/me16-01-0033
Gui J, Li H (2005) Penalized Cox regression analysis in the high-dimensional and low-sample size settings, with applications to microarray gene expression data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 21(13):3001–3008. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti422
Ingrisch M, Schneider MJ, Norenberg D, Negrao de Figueiredo G, Maier-Hein K, Suchorska B, Schuller U, Albert N, Bruckmann H, Reiser M, Tonn JC, Ertl-Wagner B (2017) Radiomic analysis reveals prognostic information in T1-weighted baseline magnetic resonance imaging in patients with glioblastoma. Investig Radiol 52(6):360–366. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000349
Marko NF, Weil RJ, Schroeder JL, Lang FF, Suki D, Sawaya RE (2014) Extent of resection of glioblastoma revisited: personalized survival modeling facilitates more accurate survival prediction and supports a maximum-safe-resection approach to surgery. J Clin Oncol 32(8):774–782. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.51.8886
Chamberlain MC (2011) Radiographic patterns of relapse in glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 101(2):319–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0251-4
Gebhardt BJ, Dobelbower MC, Ennis WH, Bag AK, Markert JM, Fiveash JB (2014) Patterns of failure for glioblastoma multiforme following limited-margin radiation and concurrent temozolomide. Radiat Oncol (London, England) 9:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717x-9-130
McDonald MW, Shu HK, Curran WJ Jr, Crocker IR (2011) Pattern of failure after limited margin radiotherapy and temozolomide for glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(1):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.10.048
Verma V, Simone CB 2nd, Krishnan S, Lin SH, Yang J, Hahn SM (2017) The rise of radiomics and implications for oncologic management. J Natl Cancer Inst 109(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djx055
Rios Velazquez E, Aerts HJ, Gu Y, Goldgof DB, De Ruysscher D, Dekker A, Korn R, Gillies RJ, Lambin P (2012) A semiautomatic CT-based ensemble segmentation of lung tumors: comparison with oncologists' delineations and with the surgical specimen. Radiother Oncol 105(2):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2012.09.023
van Dam IE, van Sornsen de Koste JR, Hanna GG, Muirhead R, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2010) Improving target delineation on 4-dimensional CT scans in stage I NSCLC using a deformable registration tool. Radiother Oncol 96(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.05.003
Park JE, Kim HS, Goh MJ, Kim SJ, Kim JH (2015) Pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma: assessment by using volume-weighted voxel-based multiparametric clustering of MR imaging data in an independent test set. Radiology 275(3):792–802. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14141414
Verma R, Zacharaki EI, Ou Y, Cai H, Chawla S, Lee SK, Melhem ER, Wolf R, Davatzikos C (2008) Multiparametric tissue characterization of brain neoplasms and their recurrence using pattern classification of MR images. Acad Radiol 15(8):966–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2008.01.029
Kim JY, Park JE, Jo Y, Shim WH, Nam SJ, Kim JH, Yoo R-E, Choi SH, Kim HS (2018) Incorporating diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI into a radiomics model improves diagnostic performance for pseudoprogression in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology 21:noy133-noy133. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy133
Materka A, Strzelecki M Texture analysis methods–a review
Kickingereder P, Gotz M, Muschelli J, Wick A, Neuberger U, Shinohara RT, Sill M, Nowosielski M, Schlemmer HP, Radbruch A, Wick W, Bendszus M, Maier-Hein KH, Bonekamp D (2016) Large-scale radiomic profiling of recurrent glioblastoma identifies an imaging predictor for stratifying anti-angiogenic treatment response. Clin Cancer Res 22(23):5765–5771. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0702
Law M, Yang S, Babb JS, Knopp EA, Golfinos JG, Zagzag D, Johnson G (2004) Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(5):746–755
Sadeghi N, D'Haene N, Decaestecker C, Levivier M, Metens T, Maris C, Wikler D, Baleriaux D, Salmon I, Goldman S (2008) Apparent diffusion coefficient and cerebral blood volume in brain gliomas: relation to tumor cell density and tumor microvessel density based on stereotactic biopsies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(3):476–482. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0851
Brem S, Cotran R, Folkman J (1972) Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst 48(2):347–356
Hirai T, Murakami R, Nakamura H, Kitajima M, Fukuoka H, Sasao A, Akter M, Hayashida Y, Toya R, Oya N, Awai K, Iyama K, Kuratsu JI, Yamashita Y (2008) Prognostic value of perfusion MR imaging of high-grade astrocytomas: long-term follow-up study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(8):1505–1510. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1121
Jain R, Poisson L, Narang J, Gutman D, Scarpace L, Hwang SN, Holder C, Wintermark M, Colen RR, Kirby J, Freymann J, Brat DJ, Jaffe C, Mikkelsen T (2013) Genomic mapping and survival prediction in glioblastoma: molecular subclassification strengthened by hemodynamic imaging biomarkers. Radiology 267(1):212–220. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120846
Kickingereder P, Wiestler B, Burth S, Wick A, Nowosielski M, Heiland S, Schlemmer HP, Wick W, Bendszus M, Radbruch A (2015) Relative cerebral blood volume is a potential predictive imaging biomarker of bevacizumab efficacy in recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro-oncology. 17:1139–1147. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov028
Ballman KV, Buckner JC, Brown PD, Giannini C, Flynn PJ, LaPlant BR, Jaeckle KA (2007) The relationship between six-month progression-free survival and 12-month overall survival end points for phase II trials in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro-oncology 9(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2006-025
Darefsky AS, King JT Jr, Dubrow R (2012) Adult glioblastoma multiforme survival in the temozolomide era: a population-based analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries. Cancer 118(8):2163–2172. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26494
Johnson DR, O’Neill BPJJoN-O (2012) Glioblastoma survival in the United States before and during the temozolomide era. 107 (2):359–364. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0749-4
O'Connor JPB, Aboagye EO, Adams JE, Aerts HJWL, Barrington SF, Beer AJ, Boellaard R, Bohndiek SE, Brady M, Brown G, Buckley DL, Chenevert TL, Clarke LP, Collette S, Cook GJ, Desouza NM, Dickson JC, Dive C, Evelhoch JL, Faivre-Finn C, Gallagher FA, Gilbert FJ, Gillies RJ, Goh V, Griffiths JR, Groves AM, Halligan S, Harris AL, Hawkes DJ, Hoekstra OS, Huang EP, Hutton BF, Jackson EF, Jayson GC, Jones A, Koh DM, Lacombe D, Lambin P, Lassau N, Leach MO, Lee TY, Leen EL, Lewis JS, Liu Y, Lythgoe MF, Manoharan P, Maxwell RJ, Miles KA, Morgan B, Morris S, Ng T, Padhani AR, Parker GJM, Partridge M, Pathak AP, Peet AC, Punwani S, Reynolds AR, Robinson SP, Shankar LK, Sharma RA, Soloviev D, Stroobants S, Sullivan DC, Taylor SA, Tofts PS, Tozer GM, van Herk M, Walker-Samuel S, Wason J, Williams KJ, Workman P, Yankeelov TE, Brindle KM, McShane LM, Jackson A, Waterton JC (2017) Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(3):169–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.162
Levine D, Bankier AA, Halpern EF (2009) Submissions to radiology: our top 10 list of statistical errors. Radiology 253(2):288–290. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2532090759
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (Grant no. NRF-2017R1C1B2007258) and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (1720030). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (Reference no. 2018-0003) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
The requirement for informed patient consent was waived for this retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 97 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.Y., Yoon, M.J., Park, J.E. et al. Radiomics in peritumoral non-enhancing regions: fractional anisotropy and cerebral blood volume improve prediction of local progression and overall survival in patients with glioblastoma. Neuroradiology 61, 1261–1272 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02255-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02255-4