Abstract
Introduction
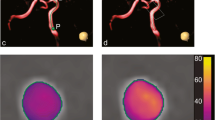
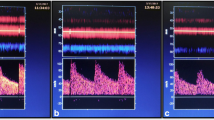
The purpose of the present study was to investigate normal ranges and test-retest reproducibility of phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI)-measured flow and velocity parameters in intracranial arteries.
Methods
Highest flow (HF), lowest flow (LF), peak systolic velocity (PSV), and end diastolic velocity (EDV) were measured at two dates in the anterior (ACA), middle (MCA), and posterior (PCA) cerebral arteries of 30 healthy volunteers using two-dimensional PC-MRI at 3 T. Least detectable difference (LDD) was calculated.
Results
In the left ACA, HF was (mean (range, LDD)) 126 ml/min (36–312, 59 %), LF 61 ml/min (0–156, 101 %), PSV 64 cm/s (32–141, 67 %), and EDV 35 cm/s (18–55, 42 %); in the right ACA, HF was 154 ml/min (42–246, 49 %), LF 77 ml/min (0–156, 131 %), PSV 75 cm/s (26–161, 82 %), and EDV 39 cm/s (7–59, 67 %). In the left MCA, HF was 235 ml/min (126–372, 35 %), LF 116 ml/min (42–186, 48 %), PSV 90 cm/s (55–183, 39 %), and EDV 46 cm/s (20–66, 28 %); in the right MCA, HF was 238 ml/min (162–342, 44 %), LF 120 ml/min (72–216, 48 %), PSV 88 cm/s (55–141, 35 %), and EDV 45 cm/s (26–67, 23 %). In the left PCA, HF was 108 ml/min (42–168, 54 %), LF 53 ml/min (18–108, 64 %), PSV 50 cm/s (24–77, 63 %), and EDV 28 cm/s (14–40, 45 %); in the right PCA, HF was 98 ml/min (30–162, 49 %), LF 49 ml/min (12–84, 55 %), PSV 47 cm/s (27–88, 59 %), and EDV 27 cm/s (16–41, 45 %).
Conclusion
PC-MRI-measured flow and velocity parameters in the main intracranial arteries have large normal ranges. Reproducibility is highest in MCA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsumoto K, Urano M, Hirai M, Masaki H, Tenjin H, Mineura K (2000) Haemodynamic evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations by quantification of transit time using high speed digital subtraction angiography: basic considerations. J Clin Neurosc : Off J Neurosurg Soc Australas 7(Suppl 1):39–41. doi:10.1054/jocn.2000.0709
Pereira VM, Ouared R, Brina O, Bonnefous O, Satwiaski J, Aerts H, Ruijters D, van Nijnatten F, Perren F, Bijlenga P, Schaller K, Lovblad KO (2014) Quantification of internal carotid artery flow with digital subtraction angiography: validation of an optical flow approach with Doppler ultrasound. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(1):156–163. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3662
Kaufmann TJ, Huston J 3rd, Mandrekar JN, Schleck CD, Thielen KR, Kallmes DF (2007) Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography: evaluation of 19,826 consecutive patients. Radiology 243(3):812–819. doi:10.1148/radiol.2433060536
Aaslid R, Markwalder TM, Nornes H (1982) Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 57(6):769–774. doi:10.3171/jns.1982.57.6.0769
Baumgartner RW (1999) Transcranial color-coded duplex sonography. J Neurol 246(8):637–647
Carr HY, Purcell EM (1954) Effects of diffusion on free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Phys Rev 94(3):630–638
Nayler GL, Firmin DN, Longmore DB (1986) Blood flow imaging by cine magnetic resonance. J Comput Assist Tomogr 10(5):715–722
Zhao M, Amin-Hanjani S, Ruland S, Curcio AP, Ostergren L, Charbel FT (2007) Regional cerebral blood flow using quantitative MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(8):1470–1473. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0582
Enzmann DR, Ross MR, Marks MP, Pelc NJ (1994) Blood flow in major cerebral arteries measured by phase-contrast cine MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15(1):123–129
Wahlin A, Ambarki K, Birgander R, Wieben O, Johnson KM, Malm J, Eklund A (2013) Measuring pulsatile flow in cerebral arteries using 4D phase-contrast MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34(9):1740–1745. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3442
Stock KW, Wetzel SG, Lyrer PA, Radu EW (2000) Quantification of blood flow in the middle cerebral artery with phase-contrast MR imaging. Eur Radiol 10(11):1795–1800
Baledent O, Fin L, Khuoy L, Ambarki K, Gauvin AC, Gondry-Jouet C, Meyer ME (2006) Brain hydrodynamics study by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial color doppler. J Magn Reson Imaging : JMRI 24(5):995–1004. doi:10.1002/jmri.20722
Meckel S, Leitner L, Bonati LH, Santini F, Schubert T, Stalder AF, Lyrer P, Markl M, Wetzel SG (2013) Intracranial artery velocity measurement using 4D PC MRI at 3 T: comparison with transcranial ultrasound techniques and 2D PC MRI. Neuroradiology 55(4):389–398. doi:10.1007/s00234-012-1103-z
Seitz J, Strotzer M, Schlaier J, Nitz WR, Volk M, Feuerbach S (2001) Comparison between magnetic resonance phase contrast imaging and transcranial Doppler ultrasound with regard to blood flow velocity in intracranial arteries: work in progress. J Neuroimaging : Off J Am Soc Neuroimaging 11(2):121–128
Chang W, Landgraf B, Johnson KM, Kecskemeti S, Wu Y, Velikina J, Rowley H, Wieben O, Mistretta C, Turski P (2011) Velocity measurements in the middle cerebral arteries of healthy volunteers using 3D radial phase-contrast HYPRFlow: comparison with transcranial Doppler sonography and 2D phase-contrast MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32(1):54–59. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2240
Bammer R, Hope TA, Aksoy M, Alley MT (2007) Time-resolved 3D quantitative flow MRI of the major intracranial vessels: initial experience and comparative evaluation at 1.5T and 3.0T in combination with parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med : Off J Soc Magn Reson Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 57(1):127–140. doi:10.1002/mrm.21109
Wetzel S, Meckel S, Frydrychowicz A, Bonati L, Radue EW, Scheffler K, Hennig J, Markl M (2007) In vivo assessment and visualization of intracranial arterial hemodynamics with flow-sensitized 4D MR imaging at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(3):433–438
Yamashita S, Isoda H, Hirano M, Takeda H, Inagawa S, Takehara Y, Alley MT, Markl M, Pelc NJ, Sakahara H (2007) Visualization of hemodynamics in intracranial arteries using time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging : JMRI 25(3):473–478. doi:10.1002/jmri.20828
van Ooij P, Zwanenburg JJ, Visser F, Majoie CB, vanBavel E, Hendrikse J, Nederveen AJ (2013) Quantification and visualization of flow in the Circle of Willis: time-resolved three-dimensional phase contrast MRI at 7 T compared with 3 T. Magn Reson Med : Off J Soc Magn Reson Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 69(3):868–876. doi:10.1002/mrm.24317
Sekine T, Amano Y, Takagi R, Matsumura Y, Murai Y, Kumita S (2014) Feasibility of 4D flow MR imaging of the brain with either Cartesian y-z radial sampling or k-t SENSE: comparison with 4D Flow MR imaging using SENSE. Magn Reson Med Sci : MRMS : Off J Jpn Soc Magn Reson Med 13(1):15–24
MacDonald ME, Frayne R (2015) Phase contrast MR imaging measurements of blood flow in healthy human cerebral vessel segments. Physiol Meas 36(7):1517–1527. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/36/7/1517
Ring BA, Waddington MM (1967) Intraluminal diameters of the intracranial arteries. Vasc Surg 1(3):137–151
Tang C, Blatter DD, Parker DL (1993) Accuracy of phase-contrast flow measurements in the presence of partial-volume effects. J Magn Reson Imaging : JMRI 3(2):377–385
Gunnal SA, Farooqui MS, Wabale RN (2014) Anatomical variations of the circulus arteriosus in cadaveric human brains. Neurol Res Int 2014:687281. doi:10.1155/2014/687281
Lotz J, Doker R, Noeske R, Schuttert M, Felix R, Galanski M, Gutberlet M, Meyer GP (2005) In vitro validation of phase-contrast flow measurements at 3 T in comparison to 1.5 T: precision, accuracy, and signal-to-noise ratios. J Magn Reson Imaging : JMRI 21(5):604–610. doi:10.1002/jmri.20275
Baumgartner RW, Mathis J, Sturzenegger M, Mattle HP (1994) A validation study on the intraobserver reproducibility of transcranial color-coded duplex sonography velocity measurements. Ultrasound Med Biol 20(3):233–237
Hsieh K, Stein K, Mono ML, Kellner-Weldon F, Verma RK, Weisstanner C, Andereggen L, Reinert M, Gralla J, Schroth G, El-Koussy M (2015) In-vivo phase contrast magnetic resonance angiography of the cerebrovascular system: a comparative study with duplex sonography. Swiss Med Wkly 145:w14155. doi:10.4414/smw.2015.14155
Tegeler CH, Crutchfield K, Katsnelson M, Kim J, Tang R, Passmore Griffin L, Rundek T, Evans G (2013) Transcranial Doppler velocities in a large, healthy population. J Neuroimaging : Off J Am Soc Neuroimaging 23(3):466–472. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2012.00711.x
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants from the Swedish Stroke Foundation, Uppsala County Council and Philips Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Institutional Review Board and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correia de Verdier, M., Wikström, J. Normal ranges and test-retest reproducibility of flow and velocity parameters in intracranial arteries measured with phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroradiology 58, 521–531 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1661-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1661-6