Abstract
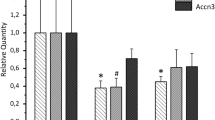
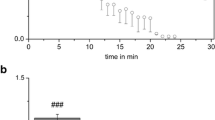
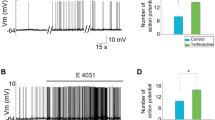
Major voltage-activated ionic channels of stellate cells in the ventral part of cochlear nucleus (CN) were largely characterized previously. However, it is not known if these cells are equipped with other ion channels apart from the voltage-sensitive ones. In the current study, it was aimed to study subunit composition and function of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) in stellate cells of the ventral cochlear nucleus. Subunits of KATP channels, Kir6.1, Kir6.2, SUR1, and SUR2, were expressed at the mRNA level and at the protein level in the mouse VCN tissue. The specific and clearly visible bands for all subunits but that for Kir6.1 were seen in Western blot. Using immunohistochemical staining technique, stellate cells were strongly labeled with SUR1 and Kir6.2 antibodies and moderately labeled with SUR2 antibody, whereas the labeling signals for Kir6.1 were too weak. In patch clamp recordings, KATP agonists including cromakalim (50 µM), diazoxide (0.2 mM), 3-Amino-1,2,4-triazole (ATZ) (1 mM), 2,2-Dithiobis (5-nitro pyridine) (DTNP) (330 µM), 6-Chloro-3-isopropylamino- 4H-thieno[3,2-e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide (NNC 55-0118) (1 µM), 6-chloro-3-(methylcyclopropyl)amino-4H-thieno[3,2-e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide (NN414) (1 µM), and H2O2 (0.88 mM) induced marked responses in stellate cells, characterized by membrane hyperpolarization which were blocked by KATP antagonists. Blockers of KATP channels, glibenclamide (0.2 mM), tolbutamide (0.1 mM) as well as 5-hydroxydecanoic acid (1 mM), and catalase (500 IU/ml) caused depolarization of stellate cells, increasing spontaneous action potential firing. In conclusion, KATP channels seemed to be composed dominantly of Kir 6.2 subunit and SUR1 and SUR2 and activation or inhibition of KATP channels regulates firing properties of stellate cells by means of influencing resting membrane potential and input resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC, Warr WB (1976) Origins of axons in the cat’s acoustic striae determined by injection of horseradish peroxidase into severed tracts. Comp Neurol 170:107–121
Aguilar-Bryan L, Clement JP, Gonzalez G, Kunjilwar K, Babenko A, Bryan J (1998) Toward understanding the assembly and structure of KATP channels. Physiol Rev 78:227–245
Allen TG, Brown DA (2004) Modulation of the excitability of cholinergic basal forebrain neurones by KATP channels. J Physiol 554:353–370
Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM (1998) Correlating structure and function in ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Neurosci 21:288–294
Ashcroft SJ, Ashcroft FM (1990a) Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal 2:197–214
Ashcroft SJ, Ashcroft FM (1990b) Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal 2:197–214
Ashford ML, Boden PR, Treherne JM (1990a) Glucose-induced excitation of hypothalamic neurones is mediated by ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pflugers Arch 415:479–483
Ashford ML, Boden PR, Treherne JM (1990b) Tolbutamide excites rat glucoreceptive ventromedial hypothalamic neurones by indirect inhibition of ATP-K+ channels. Br J Pharmacol 101:531–540
Avshalumov MV, Chen BT, Koos T, Tepper JM, Rice ME (2005) Endogenous hydrogen peroxide regulates the excitability of midbrain dopamine neurons via ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Neurosci 25:4222–4231
Babenko AP, Gonzalez G, Bryan J (2000) Pharmaco-topology of sulfonylurea receptors. Separate domains of the regulatory subunits of K(ATP) channel isoforms are required for selective interaction with K(+) channel openers. J Biol Chem 275:717–720
Bal R, Baydas G (2009) Electrophysiological properties of octopus neurons of the cat cochlear nucleus: an in vitro study. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 10:281–293
Bal R, Baydas G, Naziroglu M (2009) Electrophysiological properties of ventral cochlear nucleus neurons of the dog. Hear Res 256:93–103
Bal R, Oertel D (2000) Hyperpolarization-activated, mixed-cation current (I(h)) in octopus cells of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 84:806–817
Bal R, Oertel D (2001) Potassium currents in octopus cells of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 86:2299–2311
Bal R, Oertel D (2007) Voltage-activated calcium currents in octopus cells of the mouse cochlear nucleus. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 8:509–521
Balfour RH, Hansen AM, Trapp S (2006) Neuronal responses to transient hypoglycaemia in the dorsal vagal complex of the rat brainstem. J Physiol 570:469–484
Bao L, Taskin E, Foster M, Ray B, Rosario R, Ananthakrishnan R, Howlett SE, Schmidt AM, Ramasamy R, Coetzee WA (2013) Alterations in ventricular K(ATP) channel properties during aging. Aging Cell 12:167–176
Baukrowitz T, Schulte U, Oliver D, Herlitze S, Krauter T, Tucker SJ, Ruppersberg JP, Fakler B (1998) PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science 282:1141–1144
Brawer JR, Morest DK (1975) Relations between auditory nerve endings and cell types in the cat’s anteroventral cochlear nucleus seen with the Golgi method and Nomarski optics. J Comp Neurol 160:491–506
Bustamante JO (2006) Current concepts in nuclear pore electrophysiology. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 84:347–365
Calabrese V, Cornelius C, Maiolino L, Luca M, Chiaramonte R, Toscano MA, Serra A (2010) Oxidative stress, redox homeostasis and cellular stress response in Meniere’s disease: role of vitagenes. Neurochem Res 35:2208–2217
Cao XJ, Shatadal S, Oertel D (2007) Voltage-sensitive conductances of bushy cells of the Mammalian ventral cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 97:3961–3975
Capaccio P, Pignataro L, Gaini LM, Sigismund PE, Novembrino C, De Giuseppe R, Uva V, Tripodi A, Bamonti F (2011) Unbalanced oxidative status in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:449–453
Carr RD, Brand CL, Bodvarsdottir TB, Hansen JB, Sturis J (2003) NN414, a SUR1/Kir6.2-selective potassium channel opener, reduces blood glucose and improves glucose tolerance in the VDF Zucker rat. Diabetes 52:2513–2518
Clark R, Proks P (2010) ATP-sensitive potassium channels in health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 654:165–192
Cohen G (1994) Enzymatic/nonenzymatic sources of oxyradicals and regulation of antioxidant defenses. Ann N Y Acad Sci 738:8–14
Dabrowski M, Larsen T, Ashcroft FM, Bondo Hansen J, Wahl P (2003) Potent and selective activation of the pancreatic beta-cell type K(ATP) channel by two novel diazoxide analogues. Diabetologia 46:1375–1382
Dunn-Meynell AA, Rawson NE, Levin BE (1998) Distribution and phenotype of neurons containing the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rat brain. Brain Res 814:41–54
Fechter LD (2005) Oxidative stress: a potential basis for potentiation of noise-induced hearing loss. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19:543–546
Fellows LK, Boutelle MG, Fillenz M (1993) ATP-sensitive potassium channels and local energy demands in the rat hippocampus: an in vivo study. J Neurochem 61:949–954
Ferragamo MJ, Golding NL, Oertel D (1998) Synaptic inputs to stellate cells in the ventral cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 79:51–63
Fridovich I (1995) Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem 64:97–112
Golding NL, Ferragamo MJ, Oertel D (1999) Role of intrinsic conductances underlying responses to transients in octopus cells of the cochlear nucleus. J Neurosci 19:2897–2905
Golding NL, Robertson D, Oertel D (1995) Recordings from slices indicate that octopus cells of the cochlear nucleus detect coincident firing of auditory nerve fibers with temporal precision. J Neurosci 15:3138–3153
Gribble FM, Ashcroft FM (2000) Sulfonylurea sensitivity of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels from beta cells and extrapancreatic tissues. Metabolism 49:3–6
Harrison JM, Irving R (1966) The organization of the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 126:391–401
Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement JP, Wang CZ, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J, Seino S (1996) A family of sulfonylurea receptors determines the pharmacological properties of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Neuron 16:1011–1017
Inagaki N, Tsuura Y, Namba N, Masuda K, Gonoi T, Horie M, Seino Y, Mizuta M, Seino S (1995) Cloning and functional characterization of a novel ATP-sensitive potassium channel ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues, including pancreatic islets, pituitary, skeletal muscle, and heart. J Biol Chem 270:5691–5694
Karschin A, Brockhaus J, Ballanyi K (1998) KATP channel formation by the sulphonylurea receptors SUR1 with Kir6.2 subunits in rat dorsal vagal neurons in situ. J Physiol 509(Pt 2):339–346
Karschin C, Ecke C, Ashcroft FM, Karschin A (1997) Overlapping distribution of K(ATP) channel-forming Kir6.2 subunit and the sulfonylurea receptor SUR1 in rodent brain. FEBS Lett 401:59–64
Kossl M, Vater M (1989) Noradrenaline enhances temporal auditory contrast and neuronal timing precision in the cochlear nucleus of the mustached bat. J Neurosci 9:4169–4178
Lamm K, Arnold W (1996) Noise-induced cochlear hypoxia is intensity dependent, correlates with hearing loss and precedes reduction of cochlear blood flow. Audiol Neurootol 1:148–160
Lee K, Brownhill V, Richardson PJ (1997) Antidiabetic sulphonylureas stimulate acetylcholine release from striatal cholinergic interneurones through inhibition of K(ATP) channel activity. J Neurochem 69:1774–1776
Lee K, Dixon AK, Freeman TC, Richardson PJ (1998) Identification of an ATP-sensitive potassium channel current in rat striatal cholinergic interneurones. J Physiol 510(Pt 2):441–453
Lee K, Dixon AK, Richardson PJ, Pinnock RD (1999) Glucose-receptive neurones in the rat ventromedial hypothalamus express KATP channels composed of Kir6.1 and SUR1 subunits. J Physiol 515(Pt 2):439–452
Liss B, Roeper J (2001) Molecular physiology of neuronal K-ATP channels (review). Mol Membr Biol 18:117–127
Liu M, Seino S, Kirchgessner AL (1999) Identification and characterization of glucoresponsive neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Neurosci 19:10305–10317
Matsumoto N, Komiyama S, Akaike N (2002) Pre- and postsynaptic ATP-sensitive potassium channels during metabolic inhibition of rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Physiol 541:511–520
Mattson MP, Duan W, Pedersen WA, Culmsee C (2001) Neurodegenerative disorders and ischemic brain diseases. Apoptosis 6:69–81
Miki T, Liss B, Minami K, Shiuchi T, Saraya A, Kashima Y, Horiuchi M, Ashcroft F, Minokoshi Y, Roeper J, Seino S (2001) ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 4:507–512
Needham K, Paolini AG (2003) Fast inhibition underlies the transmission of auditory information between cochlear nuclei. J Neurosci 23:6357–6361
Nichols CG (2006) KATP channels as molecular sensors of cellular metabolism. Nature 440:470–476
Nielsen FE, Bodvarsdottir TB, Worsaae A, MacKay P, Stidsen CE, Boonen HC, Pridal L, Arkhammar PO, Wahl P, Ynddal L, Junager F, Dragsted N, Tagmose TM, Mogensen JP, Koch A, Treppendahl SP, Hansen JB (2002) 6-Chloro-3-alkylamino-4H-thieno[3,2-e]-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide derivatives potently and selectively activate ATP sensitive potassium channels of pancreatic beta-cells. J Med Chem 45:4171–4187
Noma A (1983) ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature 305:147–148
Oertel D (1991) The role of intrinsic neuronal properties in the encoding of auditory information in the cochlear nuclei. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1:221–228
Oertel D, Bal R, Gardner SM, Smith PH, Joris PX (2000) Detection of synchrony in the activity of auditory nerve fibers by octopus cells of the mammalian cochlear nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11773–11779
Oertel D, Wu SH, Garb MW, Dizack C (1990) Morphology and physiology of cells in slice preparations of the posteroventral cochlear nucleus of mice. J Comp Neurol 295:136–154
Osen KK (1970) Course and termination of the primary afferents in the cochlear nuclei of the cat. An experimental anatomical study. Arch italiennes deBiol 108:21–51
Osen KK (1972) Projection of the cochlear nuclei on the inferior colliculus in the cat. J Comp Neurol 144:355–372
Pierrefiche O, Bischoff AM, Richter DW (1996) ATP-sensitive K+ channels are functional in expiratory neurones of normoxic cats. J Physiol 494(Pt 2):399–409
Rodrigues AR, Oertel D (2006) Hyperpolarization-activated currents regulate excitability in stellate cells of the mammalian ventral cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol 95:76–87
Smith PH, Rhode WS (1989) Structural and functional properties distinguish two types of multipolar cells in the ventral cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 282:595–616
Stanford IM, Lacey MG (1995) Regulation of a potassium conductance in rat midbrain dopamine neurons by intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the sulfonylureas tolbutamide and glibenclamide. J Neurosci 15:4651–4657
Thomzig A, Wenzel M, Karschin C, Eaton MJ, Skatchkov SN, Karschin A, Veh RW (2001) Kir6.1 is the principal pore-forming subunit of astrocyte but not neuronal plasma membrane K-ATP channels. Mol Cell Neurosci 18:671–690
Tokube K, Kiyosue T, Arita M (1998) Effects of hydroxyl radicals on KATP channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch 437:155–157
Trapp S, Ballanyi K, Richter DW (1994) Spontaneous activation of KATP current in rat dorsal vagal neurones. Neuroreport 5:1285–1288
Yamane H, Nakai Y, Takayama M, Iguchi H, Nakagawa T, Kojima A (1995) Appearance of free radicals in the guinea pig inner ear after noise-induced acoustic trauma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 252:504–508
Zawar C, Plant TD, Schirra C, Konnerth A, Neumcke B (1999) Cell-type specific expression of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 514(Pt 2):327–341
Zhou M, Tanaka O, Sekiguchi M, Sakabe K, Anzai M, Izumida I, Inoue T, Kawahara K, Abe H (1999) Localization of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit (Kir6. 1/uK(ATP)-1) in rat brain. Mol Brain Res 74:15–25
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from TUBITAK, 109S516 and 110S397 (Turkey). We thank Novo Nordisk A/S (Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) for providing NNC 55-0118 and NN414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, R., Ozturk, G., Etem, E.O. et al. Modulation of Excitability of Stellate Neurons in the Ventral Cochlear Nucleus of Mice by ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels. J Membrane Biol 251, 163–178 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-017-0011-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-017-0011-x