Abstract
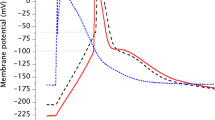
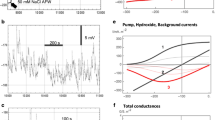
Salt sensitive Characeae Chara australis responds to 50 mM NaCl by a prompt appearance of noise in the trans-membrane potential difference (PD). The noise diminishes with time in saline and PD depolarization, leading to altered current–voltage characteristics that could be modeled with H+/OH− channels. Beilby and Al Khazaaly (JMB 230:21–34, 2009) suggested that the noise might arise from cooperative transient opening of H+/OH− channels. Presoaking cells in 10 μM melatonin over 24 h abolished the noise in some cells, postponed its appearance in others or changed its characteristics. As melatonin is a very effective antioxidant, we postulated opening of H+/OH− channels by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Measurement of ROS using dihydrodichlorofluorescein diacetate confirmed substantial reduction in ROS production in melatonin-treated cells in saline and sorbitol media. However, ROS concentration decreased as a function of time in saline medium. Possible schemes for activation of H+/OH− channels under salinity stress are considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Khazaaly S (2011) Modelling electrophysiological responses of Characeae to salt and osmotic stress. Ph. D. thesis, School of Physics, The University of NSW, Sydney, Australia
Al Khazaaly S, Beilby MJ (2012) Zinc ion blocks H+/OH− channels in Chara australis. Plant Cell Environ 35:1380–1392
Al Khazaaly S, Walker NA, Beilby MJ, Shepherd VA (2009) Membrane potential fluctuations in Chara australis: a characteristic signature of high external sodium. Eur Biophys J 39:167–174
Amirjani MR (2010) Effect of NaCl on some physiological parameters of rice. Eur J Biol Sci 3:6–16
Beilby MJ, Al Khazaaly S (2009) The role of H+/OH− channels in salt stress response of Chara australis. J Membr Biol 230:21–34
Beilby MJ, Bisson MA (2012) pH banding in charophyte algae. In: Volkov A (ed) Plant electrophysiology: methods and cell electrophysiology. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 247–271
Beilby MJ, Casanova MT (2013) The physiology of Characean cells. Springer, New York
Bisson MA (1984) Calcium effects on electrogenic pump and passive permeability of the plasma membrane of C. corallina. J Membr Biol 81:59–67
Bisson MA, Walker NA (1980) The Chara plasmalemma at high pH. electrical measurements show rapid specific passive uniport of H+ or OH−. J Membr Biol 56:1–7
Bisson MA, Walker NA (1981) The hyperpolarisation of the Chara membrane at high pH: effects of external potassium, internal pH, and DCCD. J Exp Bot 32:951–971
Boccalandro HE, Gonzalez CV, Wunderlin DA, Silva MF (2011) Melatonin levels, determined by LC-ESI-MS/MS, fluctuate during the day/night cycle in Vitis vinifera cv Malbec: evidence of its antioxidant role in fruits. J Pineal Res 51:226–232
Brown PN, Turi CE, Shipley PR, Murch SJ (2012) Phytochemical discovery in large cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait.) and small cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccus L. and Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.) in British Columbia. Planta Med 78:1–11
Brzezinski A (1997) Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med 336:186–195
Dubbels R, Reiter RJ, Klenke E, Goebel A, Schnakenberg E, Ehlers C, Schiwara HW, Schloot W (1995) Melatonin in edible plants identified by radioimmunoassay and high-performance liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometry. J Pineal Res 18:28–31
Eremin A, Bulychev A, Hauser MJB (2013) Cyclosis-mediated transfer of H2O2 elicited by localized illumination of Chara cells and its relevance to the formation of pH bands. Protoplasma 250:1339–1349
Feijo J, Sainhas J, Hackett GR, Kunkel JG, Hepler PK (1999) Growing pollen tubes possess a constitutive alkaline band in the clear zone and a growth-dependent acidic tip. J Cell Biol 144:483–496
Hattori A, Migitaka H, Masayake I, Itoh M, Yamamoto K, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Hara M, Suzuki T, Reiter RJ (1995) Identification of melatonin in plant seed, its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 35:627–634
Hope AB, Walker NA (1975) The physiology of giant algal cells. Cambridge university press, London
Lazar D, Murch SJ, Beilby MJ, Al Khazaaly S (2013) Exogenous melatonin affects photosynthesis in Characeae Chara australis. Plant Signal Behav 8(3):23279
Li J-Y, Jiang A-L, Zhang W (2007) Salt stress-induced programmed cell death in rice root tip cells. J Integr Plant Biol 49:481–486
McCourt RM, Delwiche CF, Karol KG (2004) Charophyte algae and land plant origins. Trends Ecol Evol 19:661–666
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467
Murch SJ, Saxena PK (2002) Melatonin: a potential regulator of plant growth and development. Dev Biol 38:531–536
Murch SJ, Simmons CB, Saxena PK (1997) Melatonin in feverfew and other medicinal plants. Lancet 350:1598–1599
Murch SJ, Krishnara JS, Saxena PK (2000) Tryptophan is a precursor for melatonin and serotonin biosynthesis in vitro regenerated St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L. cv. Anthos) plants. Plant Cell Rep 19:698–704
Murch SJ, Campbell SSB, Saxena PK (2001) The role of serotonin and melatonin in plant morphogenesis: regulation of auxin- induced root organogenesis in in vitro cultured explants of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 37:786–793
Murch SJ, Ali AR, Cao J, Saxena PK (2009) Melatonin and serotonin in flowers and fruits of Datura metel L. J Pineal Res 47:277–283
Murch SJ, Hall BA, Le CH, Saxena PK (2010) Changes in the levels of indoleamine phytochemicals in véraison and ripening of wine grapes. J Pineal Res 49:95–100
Pelagio-Flores R, Munoz-Parra E, Ortiz-Castro R, Lopez-Bucio J (2012) Melatonin regulates Arabidopsis root system architecture likely acting independently of auxin signaling. J Pineal Res 53:279–288
Poggeler B, Balzer I, Hardeland R, Lerchl A (2001) Pineal hormone melatonin oscillates also in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra. Naturwissenschaften 78:268–269
Posmyk M, Janas K (2009) Melatonin in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 31:1–11
Prins HBA, Snel JFH, Helder RJ, Zanstra PE (1980) Photosynthetic HCO3 - utilization and OH- excretion in aquatic angiosperms. Plant Physiol 66:818–822
Raven JA (1991) Terrestrial rhizophytes and H+ currents circulating over at least a millimeter: an obligate relationship? New Phytol 117:177–185
Shepherd VA, Beilby MJ, Al Khazaaly S, Shimmen T (2008) Mechano-perception in Chara cells: the influence of salinity and calcium on touch-activated receptor potentials, action potentials and ion transport. Plant Cell Environ 31:1575–1591
Shimmen T (2007) The sliding theory of cytoplasmic streaming: fifty years of progress. J Plant Res 120:31–43
Tan D-X, Manchester LC, Di Mascio P, Martinez GR, Prado FM, Reiter RJ (2007a) Novel rhythms of N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine and its precursor melatonin in water hyacinth: importance for phytoremediation. FASEB J 21:1724–1729
Tan D-X, Manchester LC, Terron MP, Flores LJ, Reiter RJ (2007b) One molecule, many derivatives: a never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? J Pineal Res 42:28–42
Tan D-X, Hardeland R, Manchester LC, Korkmaz A, Ma S, Rosales-Corral SA, Reichle RA (2012) Functional roles of melatonin in plants, and perspectives in nutritional and agricultural science. J Exp Bot 63:577–597
Tan D-X, Manchester LC, Rosales-Corral SA, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Reiter RJ (2013) Mitochondria and chloroplasts as the original sites of melatonin synthesis: a hypothesis related to melatonin’s primary function and evolution in eukaryotes. J Pineal Res 54:127–138
Timme RE, Bachvaroff TR, Delwiche ChF (2012) Broad phylogenomic sampling and the sister lineage of land plants. PloS ONE 7:29696
Tyerman S, Beilby MJ, Whittington J, Juswono U, Newman I, Shabala S (2001) Oscillations in proton transport revealed from simultaneous measurements of net current and net proton fluxes from isolated root protoplasts: MIFE meets patch-clamp. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:591–604
Tyerman S, Skerrett M, Garrill A, Findlay GP, Leigh RA (1997) Pathways for the permeation of Na+, and Cl- into protoplasts derived from the cortex of wheat roots. J Exp Bot 48:459–480
Van Tassel DL, Roberts N, Lewy A, O’Neil SD (2001) Melatonin in plant organs. J Pineal Res 31:8–15
Wang P, Yin L, Liang D, Li Ch, Ma F, Yue Z (2012) Delayed senescence of apple leaves by exogenous melatonin treatment: toward regulating the ascorbate–glutathione. J Pineal Res 53:11–20
Wodniok S, Brinkmann H, Glockner G, Heidel AJ, Philippe H, Melkonian M, Becker B (2011) Origin of land plants: do conjugating green algae hold the key? BMC Evol Biol 11:104–114
Wolf K, Kolar J, Witters E, van Dongen W, van Onckelen H, Machackova I (2001) Daily profile of melatonin levels in Chenopodium rubrum L. depends on photoperiod. J Plant Physiol 158:1491–1493
Wu L -J (2014) Voltage-gated proton channel HV1 in microglia. The Neuroscientist online first http://nro.sagepub.com/content/early/2014/01/23/1073858413519864
Zhang N, Zhao B, Zhang H-J, Weeda S, Yang C, Yang Z-C, Ren S, Guo Y-D (2013) Melatonin promotes water-stress tolerance, lateral root formation, and seed germination in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Pineal Res 54:15–23
Acknowledgments
We thank P. Ranganathan and G. Craigie for assistance with the ROS experiments.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beilby, M.J., Al Khazaaly, S. & Bisson, M.A. Salinity-Induced Noise in Membrane Potential of Characeae Chara australis: Effect of Exogenous Melatonin. J Membrane Biol 248, 93–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9746-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9746-9