Abstract
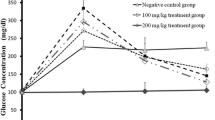
This study investigated the possible role of glutathione (GSH) in diabetic complications and its biochemical safety in experimental diabetic rats. Serum biochemical parameters and the histology of the pancreas were investigated. Seven rats were separated as controls. To create the diabetes in rats, 45 mg/kg single-dose streptozotocin (STZ) was administered i.p. The treatment was continued for 1 month. STZ was administered to the diabetes + GSH group, then reduced GSH, dissolved in isotonic salt solution (200 mg/kg), was applied i.p. two times a week. The GSH group received i.p. GSH. Serum biochemical parameters were determined by autoanalyzer. Immunohistochemical procedures were used to determine the percentage of the insulin-immunoreactive β-cell area in the islets of Langerhans. The biochemical parameters changed to different degrees or did not change. Pancreatic cells of the control and GSH groups were healthy, but in the diabetic and GSH-treated diabetic groups we found damage in different numbers. The results from these analyses show that GSH supplementation can exert beneficial effects on pancreatic cells in STZ-induced diabetic rats and can safely be used for therapy in and protection from diabetes and complications of diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Salem OM, El-Edel RH, Harisa GE, El-Halawany N, Ghonaim MM (2009) Experimental diabetic nephropathy can be prevented by propolis: effect on metabolic disturbances and renal oxidative parameters. Pak J Pharm Sci 22(2):205–210
Abou-Seif MA, Youssef A (2004) Evaluation of some biochemical changes in diabetic patients. Clin Chim Acta 346(2):161–170
ADA (American Diabetes Association) (2011) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 1):62–69
Aw TY, Wierzbicka G, Jones DP (1991) Oral glutathione increases tissue glutathione in vivo. Chem Biol Interact 80(1):89–97
Borodaco A (2007) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Terapia 15:6–11
Bourdon E, Loreau N, Blache D (1999) Glucose and free radicals impair the antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FASEB J 13:233–244
Bravenboer B, Kappelle AC, Hamers FPT, van Buren T, Erkelens DW, Gispen WH (1992) Potential use of glutathione for the prevention and treatment of diabetic neuropathy in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Diabetologia 35:813–817
Cameron NE, Cotter MA (1999) Effects of antioxidants on nerve and vascular dysfunction in experimental diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 45(2–3):137–146
Chen TS, Richie JP, Nagasawa HT, Lang CA (2000) Glutathione monoethyl ester protects against glutathione deficiencies due to aging and acetaminophen in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 120(1–3):127–139
Damasceno DC, Volpato GT, de Mattos Paranhos Calderon I, Cunha Rudge MV (2002) Oxidative stress and diabetes in pregnant rats. Anim Reprod Sci 72(3–4):235–244
De Mattia G, Bravi MC, Laurenti O, Cassone-Faldetta M, Armiento A, Ferri C, Balsano F (1998) Influence of reduced glutathione infusion on glucose metabolism in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 47(8):993–997
Eidi A, Eidi M, Esmaeili E (2006) Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 13(9–10):624–629
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, El-Naga NI (2005) Biochemical study on the hypoglycemic effects of onion and garlic in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 43(1):57–63
Fadillioglu E, Kurcer Z, Parlakpinar H, Iraz M, Gursu C (2008) Melatonin treatment against remote organ injury induced by renal ischemia reperfusion injury in diabetes mellitus. Arch Pharm Res 31(6):705–712
Fernandes AA, Novelli EL, Okoshi K, Okoshi MP, Di Muzio BP, Guimarães JF, Fernandes JA (2010) Influence of rutin treatment on biochemical alterations in experimental diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother 64(3):214–219
Franco R, Schoneveld OJ, Pappa A, Panayiotidis MI (2007) The central role of glutathione in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Arch Physiol Biochem 113(4–5):234–258
He FJ, MacGregor GA (2008) Beneficial effects of potassium on human health. Physiol Plant 133(4):725–735
Hu ML (1994) Measurement of protein thiol groups and glutathione in plasma. Methods Enzymol 233:381–385
Kanter M, Uysal H, Karaca T, Ozdemir-Sagmanligil H (2006) Depression of glucose levels and partial restoration of pancreatic β-cell damage by melatonin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Arch Toxicol 80:362–369
Karaca T, Yörük M, Yörük İH, Uslu S (2010) Effects of extract of green tea and ginseng on pancreatic beta cells and levels of serum glucose, insulin, cholesterol and triglycerides in rats with experimentally streptozotocin-induced diabetes: a histochemical and immunohistochemical study. J Anim Vet Adv 9(1):102–107
Karasu Ç (1999) Increased activity of H2O2 in aorta isolated from chronically streptozotocin diabetic rats: effects of antioxidant enzymes and enzyme inhibitors. Free Radic Biol Med 27:16–27
Lim J, Sanders RA, Snyder AC, Eells JT, Henshel DS, Watkins JB 3rd (2010) Effects of low-level light therapy on streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney. J Photochem Photobiol B 99(2):105–110
Liu Z, Li J, Zeng Z, Liu M, Wang M (2008) The antidiabetic effects of cysteinyl metformin, a newly synthesized agent, in alloxan- and streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact 173(1):68–75
Loven D, Schedl H, Wilson H, Daabees TT, Stegink LD, Diekus M, Oberley L (1986) Effect of insulin and oral glutathione on glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase activities in organs of rats with streptozocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes 35(5):503–507
Lu SC (2008) Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30(1–2):42–59
Memisoğullari R, Taysi S, Bakan E, Capoglu I (2003) Antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in type II diabetes mellitus. Cell Biochem Funct 21(3):291–296
Molitch ME (1990) Diabetes mellitus. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW (eds) Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations, 3rd edn. Butterworths, Boston
Nascimento NR, Costa-e-Forti A, Peter AA, Fonteles MC (2003) Free radical scavengers improve the impaired endothelium-dependent responses in aorta and kidneys of diabetic rabbits. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 61(3):145–153
Paolisso G, Di Maro G, Pizza G, D’Amore A, Sgambato S, Tesauro P, Varricchio M, D’Onofrio F (1992) Plasma GSH/GSSG affects glucose homeostasis in healthy subjects and non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 263(3 Pt 1):E435–E440
Quiros JA, Marcin JP, Kuppermann N, Nasrollahzadeh F, Rewers A, Di Carlo J, Neely EK, Glaser N (2008) Elevated serum amylase and lipase in pediatric diabetic ketoacidosis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 9(4):418–422
Ramakrishna V, Jailkhani R (2008) Oxidative stress in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients. Acta Diabetol 45(1):41–46
Ramires PR, Ji LL (2001) Glutathione supplementation and training increases myocardial resistance to ischemia–reperfusion in vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H679–H688
Rizvi AA (2003) Amylase and lipase in diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care 26(11):3193–3194
Shabeer J, Srivastava RS, Kumar Singh S (2009) Antidiabetic and antioxidant effect of various fractions of Phyllanthus simplex in alloxan diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 124(1):34–38
Sheng XQ, Huang KX, Xu HB (2005) Influence of alloxan-induced diabetes and selenite treatment on blood glucose and glutathione levels in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18(3):261–267
Stoppa GR, Cesquini M, Roman EA, Ogo SH, Torsoni MA (2006) Aminoguanidine prevented impairment of blood antioxidant system in insulin-dependent diabetic rats. Life Sci 78(12):1352–1361
Takagi S, Tanabe A, Tsuiki M, Naruse M, Takano K (2009) Age, HbA1c, and prevalence of diabetes mellitus were positively correlated and serum potassium levels were negatively correlated with the severity of cardiac dysfunction. Endocr J 56(8):1009–1018
Thorp ML (2005) Diabetic nephropathy: common questions. Am Fam Physician 72(1):96–99
Trachtenbarg DE (2005) Diabetic ketoacidosis. Am Fam Physician 71(9):1705–1714
Van Konynenburg RA (2004) Is glutathione depletion an important part of the pathogenesis of chronic fatigue syndrome? Presented at the AACFS Seventh International Conference Madison, Wisconsin, 8–10 Oct 2004. http://www.aboutmecfs.org/Rsrch/GluAACFS04.aspx
Veno Y, Kizaki M, Nakagiri R, Kamiya T, Sumi H, Osawa T (2002) Dietary glutathione protects rats from diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy. J Nutr 132(5):897–900
Vincent AM, Russel SW, Low P, Feldman EL (2004) Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropaths. Endocr Rev 25(4):612–628
Winiarska K, Szymanski K, Gorniak P, Dudziak M, Bryla J (2009) Hypoglycaemic, antioxidative and nephroprotective effects of taurine in alloxan diabetic rabbits. Biochimie 91(2):261–270
Yüksek V (2012) The electrophoretical determination of serum protein fraction of lycopene treated experimental diabetic rats. MSc thesis, Yüzüncü Yıl University, Van
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yur, F., Dede, S., Karaca, T. et al. The Effect of Glutathione Treatment on the Biochemical and Immunohistochemical Profile in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J Membrane Biol 246, 427–433 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9541-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9541-z