Abstract
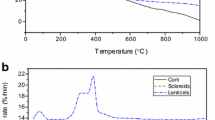
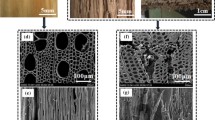
The crystalline characteristics, chemical composition, and thermal decomposition of elements in Quercus variabilis (Qv) virgin cork were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric methods, respectively, and compared with those of elements in Quercus suber (Qs) reproduction cork. Samples of cork elements, including pure cork, lenticular filling tissue (LFT), dark-brown zone (DBZ), and sclereids, were prepared. The X-ray diffractograms of pure cork from both species showed an amorphous pattern, whereas those of LFT, DBZ, and sclereid showed a crystalline cellulose I pattern. The relative crystallinity of DBZ was significantly lower than that of Qv LFT and the sclereid. In the FTIR spectra, Qv pure cork tended to show weaker band intensities for the suberin, lignin, and carbohydrate compounds than Qs pure cork. The pure corks of both species showed stronger suberin bands than LFT, DBZ, and the sclereid. In the thermogravimetric analyses, the peaks of hemicellulose and cellulose decomposition in both pure corks were weaker than those in LFT, DBZ, and sclereid, whereas the peaks of suberin decomposition in both pure corks were the highest among all elements.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abenojar J, de Armentia SL, Barbosa AQ, Martinez MA, Velasco F, da Silva LFM, del Real Romero JC (2020) Coating cork particles with iron oxide: effect on magnetic properties. Wood Sci Technol 54:869–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-020-01191-4
Alexander LE (1969) X-ray diffraction in polymer science. Wiley-Intersciene, Amsterdam
Anjos O, Pereira H, Rosa ME (2011) Tensile properties of cork in axial stress and influence of porosity, density, quality and radial position in the plank. Eur J Wood Prod 69:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-009-0407-0
Aronson J, Pereira JS, Pausas JG (2009) Cork oak woodlands on edge: ecology, adaptive management, and restoration. Island Press Publication, Washington
Chen D, Zhang X, Kang H, Sun X, Yin S, Du H, Yamanaka N, Gapare W, Wu HX, Liu C (2012) Phylogeography of Quercus variabilis based on chloroplast DNA sequence in East Asia: multiple glacial refugia and mainland-migrated island populations. PLoS ONE 7(10):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047268
Conti C, Casati M, Colombo C, Possenti E, Realini M, Gatta GD, Merlini M, Brambilla L, Zerbi G (2015) Synthesis of calcium oxalate trihydrate: new data by vibrational spectroscopy and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 150:721–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.06.009
Costa PA, Barreiros MA, Mouquinho AI, e Silva PO, Paradela F, Oliveira FAC (2022) Slow pyrolysis of cork granules under nitrogen atmosphere: by-products characterization and their potential valorization. Biofuel Res J 33:1562–1572. https://doi.org/10.18331/BRJ2022.9.1.3
Faix O (1991) Classification of lignins from different botanical origins by FT-IR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 45:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1515/hfsg.1991.45.s1.21
Ferreira R, Garcia H, Sousa AF, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Rebelo LPN, Pereira CS (2013) Isolation of suberin from birch outer bark and cork using ionic liquids: a new source of macromonomers. Ind Crops Prod 44:520–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.10.002
Ferreira J, Miranda I, Şen U, Pereira H (2016) Chemical and cellular features of virgin and reproduction cork from Quercus variabilis. Ind Crops Prod 94:638–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.038
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Gibson LJ, Easterling KE, Ashby MF (1981) The structure and mechanics of cork. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. 377(1769):99–117. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1981.0117
Hidayat W, Kim YK, Jeon WS, Lee JA, Kim AR, Park SH, Maail RS, Kim NH (2017) Qualitative and quantitative anatomical characteristics of four tropical wood species from Moluccas Indonesia. J Korean Wood Sci Technol 45(4):21–222. https://doi.org/10.5658/WOOD.2017.45.4.369
Hon DNS, Shiraishi N (2001) Wood and cellulosic chemistry, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Hourlier D (2019) Thermal decomposition of calcium oxalate: beyond appearances. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:2221–2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7888-1
Kang HY, Kim SW (2004) Air-klin drying the boards and disks of Quercus variabilis. J Korean Wood Sci Technol 32(1):52–58
Kim NH, Hanna RB (2006) Morphological characteristics of Quercus variabilis charcoal prepared at different temperatures. Wood Sci Technol 40(2006):392–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-005-0062-5
Kim BR, Mishiro A, Sugitama J, Okano T (1990) The physical properties of virgin and reproduction corks of Quercus variabilis Blume. Bull Tokyo Univ for 82:199–217
Knapic S, Oliveira V, Machado JS, Pereira H (2016) Cork as a building material: a review. Eur J Wood Prod 74:775–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-016-1076-4
Kwon SM, Kim NH, Cha DS (2009) An investigation on the transition characteristics of the wood cell walls during carbonization. Wood Sci Technol 43:487–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0245-6
Lacerda PSS, Gama N, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Barros-Timmons A (2020) Grafting Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) from cork via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) towards higher quality of three-dimensional (3D) printed PMMA/cork-g-PMMA materials. Polymers 12(9):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091867
Li J, Bi J, Song X, Qu W, Liu D (2019) Surface and dynamic viscoelastic properties of cork from Quercus variabilis. BioResources 14(1):607–618
Marques AV, Pereira H, Meier D, Faix O (1996) Isolation and characterization of a guaiacyl lignin from saponified cork of Quercus suber L. Holzforschung 50:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1515/hfsg.1996.50.5.393
Miranda I, Gominho J, Pereira H (2013) Cellular structure and chemical composition of cork from the Chinese cork oak (Quercus variabilis). J Wood Sci 59:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-012-1300-8
Navi P, Sandberg D (2012) Thermo-hydro-mechanical processing of wood. EPFL Press, New York
Neto CP, Rocha J, Gil A, Cordeiro N, Esculcas AP, Rocha S, Delgadillo I, de Jesus JDP, Correia AJF (1995) 13C solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and fourier transform infrared studies of the thermal decomposition of cork. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 4:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-2040(94)00039-F
Nobre C, Şen A, Durão L, Miranda I, Pereira H, Gonçalves M (2021) Low-temperature pyrolysis products of waste cork and lignocellulosic biomass: product characterization. Biomass Conv Biorefinery 13:2267–2277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01300-8
Özgenç Ö, Durmaz S, Kuştaş S (2017) Chemical analysis of tree barks using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and conventional techniques. BioResources 12(4):9143–9151
Pandey KK (1999) A study of chemical structure of soft and hardwood and wood polymers by FTIR spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci 71:1969–1975. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19990321)71:12%3c1969::AID-APP6%3e3.0.CO;2-D
Pereira H (2007) Cork: biology, production, and uses. Elsevier Publications, Amsterdam
Pereira H (2015) The Rationale behind cork properties: a review of structure and chemistry. BioResources 10(3):6207–6229
Pereira H, Rosa ME, Fortes MA (1987) The cellular structure of cork from Quercus suber. IAWA Bull 8(3):213–218. https://doi.org/10.1163/22941932-90001048
Prasetia D, Purusatama BD, Kim J-H, Yang G-U, Jang J-H, Park S-Y, Lee S-H, Kim N-H (2022a) Quantitative anatomical characteristics of virgin cork in Quercus variabilis grown in Korea. Forests 13(10):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13101711
Prasetia D, Purusatama BD, Kim J-H, Yang G-U, Jang J-H, Park S-Y, Kim N-H (2022) Qualitative anatomical characteristics of the virgin cork in Quercus variabilis grown in Korea. Bioresources 18(1):884–898. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.18.1.884-898
Purusatama BD, Choi JK, Lee SH, Kim NH (2019) Microfbril angle, crystalline characteristics, and chemical compounds of reaction wood in stem wood of Pinus densifora. Wood Sci Technol 54:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-019-01140-w
Ribeiro AM, Ramalho E, Neto MP, Pilão RM (2022) Thermogravimetric analysis of high-density cork granules using isoconversional methods. Energy Rep 8(3):442–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.100
Rosa ME, Fortes MA (1988) Thermogravimetric analysis of cork. J Mater Sci Lett 7:1064–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00720828
Schwanninger M, Rodrigues JC, Pereira H, Hinterstoisser B (2004) Effects of short-time vibratory ball milling on the shape of FT-IR spectra of wood and cellulose. Vib Spectrosc 36(1):23–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2004.02.003
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Şen A, Marques AV, Gominho J, Pereira H (2012) Study of thermochemical treatments of the cork in the 150–400 °C range using colour analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. Ind Crops Prod 38:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.01.018
Şen A, Van den Bulcke J, Defoirdt N, Van Acker J, Pereira H (2014) Thermal behavior of cork and cork components. Thermochim Acta 582:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2014.03.007
Shangguan W, Chen Z, Zhao J, Song X (2018) Thermogravimetric analysis of cork and cork components from Quercus variabilis. Wood Sci Technol 52:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-017-0959-9
Shiqian W, Xiaozhou S, Yafang L, Mingqiang Z (2018) Characterizations and properties of torrefied Quercus variabilis cork. Wood Research 63(6):947–958
Silva SP, Sabino MA, Fernandes EM, Correlo VM, Boesel LF, Reis RL (2005) Cork: properties, capabilities and applications. Int Mater Rev 50(6):345–365. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328005X41168
Sousa VB, Leal S, Quilhó T, Pereira H (2009) Characterization of cork oak (Quercus suber) wood anatomy. IAWA J 30(2):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1163/22941932-90000210
Sun X-Y, Zhang C-Y, Bhadja P, Ouyang J-M (2018) Preparation, properties, formation mechanisms, and cytotoxicity of calcium oxalate monohydrate with various morphologies. CrystEngComm 20(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE01912B
Suri IF, Purusatama BD, Lee SH, Hidayat W, Ma’ruf SD, Febrianto F, Kim NH (2021) Characteristic features of the oil-heat treated woods from tropical fast growing wood species. Wood Res 66(3):365–378. https://doi.org/10.37763/wr.1336-4561/66.3.365378
Xu WJ, Qiu DP, Liu S-Q, Li M, Yang R (2019) Preparation of cork-derived porous activated carbon for high performance supercapacitors. J Inorg Mater 34(6):625–632. https://doi.org/10.15541/jim20180426
Yang GU, Purusatama BD, Kim JH, Suri IF, Prasetia D, Hidayat W, Febrianto F, Lee SH, Kim NH (2022) Physical and chemical characteristics of the bamboo culm and wood carbonized at low temperature. BioResources 17(3):4837–4855
Zhao JF, Feng DJ, Lei YF, Zhang WH, Zhang YJ (2013) Cell structure and chemical components of sclereids and lenticels from Quercus variabilis cork. J Northwest A&F Univ (Natural Science Edition) 41(7):119–124. https://doi.org/10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2013.07.005
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Support Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (No. 2022R1A2C1006470); the Basic Science Research Program through the NRF, funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2018R1A6A1A03025582); and the R&D Program for Forest Science Technology (Project No. 2021350C10-2323-AC03), funded by the Korea Forest Service (Korea Forestry Promotion Institute).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: DP and NHK; Methodology: DP, BDP, J-HK, J-HJ, S-YP, S-HL, and NHK; Formal analysis and investigation: DP; Writing—original draft preparation: DP; Writing—review and editing: DP, BDP, S-HL, and NHK; Funding acquisition: J-HJ, S-HL, and NHK; Resources: NHK; Supervision: NHK. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prasetia, D., Purusatama, B.D., Kim, JH. et al. X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermal decomposition analyses of virgin cork elements in Quercus variabilis grown in Korea. Wood Sci Technol 58, 313–332 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01520-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01520-3