Abstract
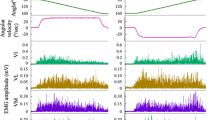
The quadriceps femoris (QF) muscle group plays an essential role in human movement, such as standing, walking and running. The ability to maintain a steady force during physical activity of the human lower limb is important for mobility, postural control and balance. Although prolonged mechanical vibration of the muscle–tendon unit can moderate the efficacy of synaptic input from Ia afferent onto the α-motor neuron pathway, the effect of prolonged tendon vibration on fluctuations of knee extensor force has received little attention. The purpose of the present study was to examine the effects of prolonged patellar tendon vibration on the force steadiness of the QF muscle. Nine healthy men performed a submaximal force-matching task involving isometric knee extension before and after patellar tendon vibration or quiet seated rest (n = 7, control condition) for 30 min. The target force was 2.5, 10 and 30 % of maximal voluntary contraction (MVC). Surface electromyography (EMG) of the four QF synergists was recorded and normalized to EMG amplitude during the MVC. The knee extension force and the EMG amplitude of vastus medialis during the MVC were significantly reduced after the vibration, but did not significantly decrease in the control condition. Fluctuations of force and normalized EMG of individual QF muscles at each submaximal force level did not significantly change after the vibration. We conclude that prolonged patellar tendon vibration does not influence the force steadiness of the QF muscle during an isometric force-matching task.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akima H, Saito A, Watanabe K, Kouzaki M (2012) Alternate muscle activity patterns among synergists of the quadriceps femoris including the vastus intermedius during low-level sustained contraction in men. Muscle Nerve 46:86–95. doi:10.1002/mus.23268
Ando R, Saito A, Umemura Y, Akima H (2015) Local architecture of the vastus intermedius is a better predictor of knee extension force than that of the other quadriceps femoris muscle heads. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 35:376–382. doi:10.1111/cpf.12173
Baker SN, Chiu M, Fetz EE (2006) Afferent encoding of central oscillations in the monkey arm. J Neurophysiol 95:3904–3910. doi:10.1152/jn.01106.2005
Banks RW (2006) An allometric analysis of the number of muscle spindles in mammalian skeletal muscles. J Anat 208:753–768. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00558.x
Blazevich AJ, Gill ND, Zhou S (2006) Intra- and intermuscular variation in human quadriceps femoris architecture assessed in vivo. J Anat 209:289–310. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00619.x
Bongiovanni LG, Hagbarth KE, Stjernberg L (1990) Prolonged muscle vibration reducing motor output in maximal voluntary contractions in man. J Physiol 423:15–26
Burnett RA, Laidlaw DH, Enoka RM (2000) Coactivation of the antagonist muscle does not covary with steadiness in old adults. J Appl Physiol 89:61–71
Clark BC, Pierce JR, Manini TM, Ploutz-Snyder LL (2007) Effect of prolonged unweighting of human skeletal muscle on neuromotor force control. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:53–62. doi:10.1007/s00421-007-0399-6
Durbaba R, Cassidy A, Budini F, Macaluso A (2013) The effects of isometric resistance training on stretch reflex induced tremor in the knee extensor muscles. J Appl Physiol 114:1647–1656. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00917.2011
Elble RJ, Randall JE (1976) Motor-unit activity responsible for 8- to 12-Hz component of human physiological finger tremor. J Neurophysiol 39:370–383
Enoka RM, Burnett RA, Graves AE, Kornatz KW, Laidlaw DH (1999) Task- and age-dependent variations in steadiness. Prog Brain Res 123:389–395
Folland JP, Wakamatsu T, Fimland MS (2008) The influence of maximal isometric activity on twitch and H-reflex potentiation, and quadriceps femoris performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:739–748. doi:10.1007/s00421-008-0823-6
Freund HJ (1983) Motor unit and muscle activity in voluntary motor control. Physiol Rev 63:387–436
Fry A, Folland JP (2014) Prolonged infrapatellar tendon vibration does not influence quadriceps maximal or explosive isometric force production in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 114:1757–1766. doi:10.1007/s00421-014-2904-z
Hagbarth KE, Kunesch EJ, Nordin M, Schmidt R, Wallin EU (1986) Gamma loop contributing to maximal voluntary contractions in man. J Physiol 380:575–591
Harwood B, Cornett KM, Edwards DL, Brown RE, Jakobi JM (2014) The effect of tendon vibration on motor unit activity, intermuscular coherence and force steadiness in the elbow flexors of males and females. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 211:597–608. doi:10.1111/apha.12319
Kakuda N, Vallbo AB, Wessberg J (1996) Fusimotor and skeletomotor activities are increased with precision finger movement in man. J Physiol 492:921–929
Kim MS, Masakado Y, Tomita Y, Chino N, Pae YS, Lee KE (2001) Synchronization of single motor units during voluntary contractions in the upper and lower extremities. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1243–1249
Kouzaki M, Shinohara M (2010) Steadiness in plantar flexor muscles and its relation to postural sway in young and elderly adults. Muscle Nerve 42:78–87. doi:10.1002/mus.21599
Kouzaki M, Shinohara M, Fukunaga T (2000) Decrease in maximal voluntary contraction by tonic vibration applied to a single synergist muscle in humans. J Appl Physiol 89:1420–1424
Kouzaki M, Shinohara M, Masani K, Fukunaga T (2004) Force fluctuations are modulated by alternate muscle activity of knee extensor synergists during low-level sustained contraction. J Appl Physiol 97:2121–2131. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00418.2004
Krishnan C, Allen EJ, Williams GN (2011) Effect of knee position on quadriceps muscle force steadiness and activation strategies. Muscle Nerve 43:563–573. doi:10.1002/mus.21981
Marchetti C, Beato M, Nistri A (2001) Alternating rhythmic activity induced by dorsal root stimulation in the neonatal rat spinal cord in vitro. J Physiol 530:105–112
Moritz CT, Barry BK, Pascoe MA, Enoka RM (2005) Discharge rate variability influences the variation in force fluctuations across the working range of a hand muscle. J Neurophysiol 93:2449–2459. doi:10.1152/jn.01122.2004
O’Brien TD, Reeves ND, Baltzopoulos V, Jones DA, Maganaris CN (2010) Muscle-tendon structure and dimensions in adults and children. J Anat 216:631–642. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01218.x
Orr R (2010) Contribution of muscle weakness to postural instability in the elderly. A systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 46:183–220
Rainoldi A, Melchiorri G, Caruso I (2004) A method for positioning electrodes during surface EMG recordings in lower limb muscles. J Neurosci Methods 134:37–43. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.014
Roll JP, Vedel JP, Ribot E (1989) Alteration of proprioceptive messages induced by tendon vibration in man: a microneurographic study. Exp Brain Res 76:213–222
Saito A, Akima H (2013) Knee joint angle affects EMG-force relationship in the vastus intermedius muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23:1406–1412. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2013.08.009
Saito A, Watanabe K, Akima H (2013) The highest antagonistic coactivation of the vastus intermedius muscle among quadriceps femoris muscles during isometric knee flexion. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23:831–837. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2013.02.005
Shinohara M (2005) Effects of prolonged vibration on motor unit activity and motor performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:2120–2125
Shinohara M, Yoshitake Y, Kouzaki M, Fukuoka H, Fukunaga T (2003) Strength training counteracts motor performance losses during bed rest. J Appl Physiol 95:1485–1492. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01173.2002
Shinohara M, Yoshitake Y, Kouzaki M (2009) Alterations in synergistic muscle activation impact fluctuations in net force. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:191–197. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318183c0d9
Taylor AM, Christou EA, Enoka RM (2003) Multiple features of motor-unit activity influence force fluctuations during isometric contractions. J Neurophysiol 90:1350–1361. doi:10.1152/jn.00056.2003
Tracy BL, Enoka RM (2002) Older adults are less steady during submaximal isometric contractions with the knee extensor muscles. J Appl Physiol 92:1004–1012. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00954.2001
Tracy BL, Dinenno DV, Jorgensen B, Welsh SJ (2007) Aging, visuomotor correction, and force fluctuations in large muscles. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:469–479. doi:10.1249/mss.0b013e31802d3ad3
Ushiyama J, Masani K, Kouzaki M, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2005) Difference in aftereffects following prolonged Achilles tendon vibration on muscle activity during maximal voluntary contraction among plantar flexor synergists. J Appl Physiol 98:1427–1433. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00613.2004
Ushiyama J, Takahashi Y, Ushiba J (2010) Muscle dependency of corticomuscular coherence in upper and lower limb muscles and training-related alterations in ballet dancers and weightlifters. J Appl Physiol 109:1086–1095. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00869.2009
Ushiyama J, Katsu M, Masakado Y, Kimura A, Liu M, Ushiba J (2011) Muscle fatigue-induced enhancement of corticomuscular coherence following sustained submaximal isometric contraction of the tibialis anterior muscle. J Appl Physiol 110:1233–1240. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01194.2010
Vaillancourt DE, Newell KM (2003) Aging and the time and frequency structure of force output variability. J Appl Physiol 94:903–912. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00166.2002
Vaillancourt DE, Larsson L, Newell KM (2003) Effects of aging on force variability, single motor unit discharge patterns, and the structure of 10, 20, and 40 Hz EMG activity. Neurobiol Aging 24:25–35
Watanabe K, Akima H (2009a) Cross-talk from adjacent muscle has a negligible effect on surface electromyographic activity of vastus intermedius muscle during isometric contraction. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 19:e280–e289. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2008.06.002
Watanabe K, Akima H (2009b) Normalized EMG to normalized torque relationship of vastus intermedius muscle during isometric knee extension. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:665–673. doi:10.1007/s00421-009-1064-z
Watanabe K, Akima H (2010) Neuromuscular activation of vastus intermedius muscle during fatiguing exercise. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 20:661–666. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2010.01.003
Watanabe K, Akima H (2011) Effect of knee joint angle on neuromuscular activation of the vastus intermedius muscle during isometric contraction. Scand J Med Sci Sports 21:e412–e420. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2011.01347.x
Yoshitake Y, Shinohara M, Kouzaki M, Fukunaga T (2004) Fluctuations in plantar flexion force are reduced after prolonged tendon vibration. J Appl Physiol 97:2090–2097. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00560.2004
Yoshitake Y, Kouzaki M, Fukuoka H, Fukunaga T, Shinohara M (2007) Modulation of muscle activity and force fluctuations in the plantarflexors after bedrest depends on knee position. Muscle Nerve 35:745–755. doi:10.1002/mus.20764
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (#25-860) to AS, and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Grant (#23300239) to HA. We appreciate the assistance of Dr. Toshiaki Wasaka from Nagoya Institute of Technology for instruction of vibration technique. We also thank Dr. Junichi Ushiyama from Keio University for valuable comments regarding the draft version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, A., Ando, R. & Akima, H. Effects of prolonged patellar tendon vibration on force steadiness in quadriceps femoris during force-matching task. Exp Brain Res 234, 209–217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4447-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4447-x