Abstract
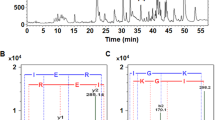
We studied angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory effect of the protein hydrolysates prepared from commercially available nori products that contain Pyropia pseudolinearis as the main ingredient. The water extract of the nori product consisted mainly of phycobiliproteins and RubisCO. The proteins in the aqueous extracts were sequentially hydrolyzed with pepsin and trypsin, and the peptides in the pepsin–trypsin digests were fractionated by reversed-phase HPLC. As a result, 12 ACE inhibitory peptides containing ten novel peptides were identified. These peptides are suggested to have originated from the α- and β-subunits of phycobiliproteins and the large subunits of RubisCO of P. pseudolinearis. The interactions of eight peptides (ALR, FAR, FSR, FDR, EVYR, AYR, GRP, and MVT) with ACE were then simulated using the flexible docking tool Auto Dock Vina. The results showed that all peptides interacted with the active center of ACE, and their docking scores ranged from − 6.8 to − 10.2 kcal/mol. In addition, we synthesized four peptides (AYR, FAR, EVYR, and GRP) and measured the IC50 values of these peptides for ACE. Consequently, FAR and GRP showed considerably low IC50 values (0.29 μmol and 0.45 μmol, respectively) in addition to other ACE inhibitory peptides. Moreover, FAR, which is specific to the nori product, was predicted to bind to the S1, S1′, and S2′ subsites of the catalytic center of ACE. Therefore, it can be expected that daily intake of "nori products" may have a positive effect on the prevention of hypertension.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2021) Newsroom/Fact sheets/Detail/ Hypertension. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension. Accessed 25 Aug 2021
Daskaya-Dikmen C, Yucetepe A, Karbancioglu-Guler F, Daskaya H, Ozcelik B (2017) Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from plants. Nutrients 9:316
Skeggs LT, Kahn JR, Shumway NP (1956) The preparation and function of the hypertensin-converting enzyme. J Exp Med 103:295–299
Messerli FH (1999) Outcome studies are all antihypertensive drugs created equal? J Am Coll Cardiol 34:1652–1653
Bicket DP (2002) Using ACE inhibitors appropriately. Am Fam Physician 66:461–468
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, Horio T, Hoshide S, Ikeda S, Ishimitsu T et al (2019) The Japanese society of hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res 42:1235–1481
Peighambardoust SH, Karami Z, Pateiro M, Lorenzo JM (2021) A review on health-promoting, biological, and functional aspects of bioactive peptides in food applications. Biomolecules 11:631
Xue L, Yin R, Howell K, Zhang P (2021) Activity and bioavailability of food protein-derived angiotensin-I-converting enzyme–inhibitory peptides. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 20:1150–1187
Sato M, Hosokawa T, Yamaguchi T, Nakano T, Muramoto K, Kahara T, Funayama K, Kobayashi A, Nakano T (2002) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and their antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Agric Food Chem 50:6245–6252
Cha SH, Lee KW, Jeon YJ (2006) Screening of extracts from red algae in Jeju for potentials marine angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity. Algae 21:343–348
Holdt LS, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compound in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J Appl Phycol 23:543–597
Cermeno M, Kleelayai T, Amigo-Benavent M, Harnedy-Rothwell P, FitzGerald RJ (2020) Current knowledge on the extraction, purification, identification, and validation of bioactive peptides from seaweed. Electrophoresis 41:1694–1717
Furuta T, Miyabe Y, Yasui H, Kinoshita Y, Kishimura H (2016) Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from phycobiliproteins of dulse Palmaria palmata. Mar Drugs 14:32
Miyabe Y, Furuta T, Takeda T, Kanno G, Shimizu T, Tanaka Y, Gai Z, Yasui H, Kishimura H (2017) Structural properties of phycoerythrin from dulse Palmaria palmata. J Food Biochem 41:e12301
Kitade Y, Miyabe Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeda H, Shimizu T, Yasui H, Kishimura H (2018) Structural characteristics of phycobiliproteins from red alga Mazzaella japonica. J Food Biochem 42:e12436
Kumagai Y, Kitade Y, Kobayashi M, Watanabe K, Kurita H, Takeda H, Yasui H, Kishimura H (2020) Identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from red alga Mazzaella japonica. Eur Food Res Technol 246:2225–2231
Sumikawa K, Takei K, Kumagai Y, Shimizu T, Yasui H, Kishimura H (2020) In silico analysis of ACE inhibitory peptides from chloroplast proteins of red alga Grateloupia asiatica. Mar Biotechnol 22:391–402
Tsurunaga Y, Takahashi T, Matsumoto S, Nagata Y, Yoshino K (2017) Color, texture, mineral, volatile components, and shape of naturally occurring Uppurui nori (Porphyra pseudolinearis). Food Preserv Sci 43:63–70
Kumagai Y, Toji K, Katsukura S, Morikawa R, Uji T, Yasui H, Shimizu T, Kishimura H (2021) Characterization of ACE inhibitory peptides prepared from Pyropia pseudolinearis protein. Mar Drugs 19:200
Bellgrove A, Nakaya F, Serisawa Y, Tatsuyama-Serisawa K, Kagami Y, Jones PM, Suzuki H, Kawano S, Aoki MN (2020) Maintenance of complex life cycles via cryptic differences in the ecophysiology of haploid and diploid spores of an isomorphic red alga. J Phycol 56:159–169
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Minkiewicz P, Iwaniak A, Darewicz M (2019) BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: current opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 20:5978
Laskowski RA, Swindells MB (2011) LigPlot+: multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model 51:2778–2786
Xhang J, Ma J, Liu D, Qin S, Sun S, Zhao J, Sui SF (2017) Structure of phycobilisome from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica. Nature 551:58–63
Lundell DJ, Glazer AN, Delange RJ, Brown DM (1984) Bilin attachment sites in the α- and β-subunits of B-phycoerythrin: amino acid sequence studies. J Biol Chem 259:5472–5480
Ficner R, Lobeck K, Schmidt G, Huber R (1992) Isolation, crystallization, structure analysis and refinement of B-phycoerythrin from the red alga Porphyridium sordidum at 2.2 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 228:935–950
Apt KE, Collier JL, Grossman AR (1995) Evolution of the phycobiliproteins. J Mol Biol 248:79–96
Fan H, Liao W, Wu J (2018) Molecular interactions, bioavailability, and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J Food Biochem 43:e12572
Lopez-Fandino R, Otte J, van Camp J (2006) Physiological, chemical and technological aspects of milk-protein-derived peptides with antihypertensive and ACE-inhibitory activity. Int Dairy J 16:1277–1293
Guang C, Phillips RD (2009) Plant food-derived angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J Agric Food Chem 57:5113–5120
FitzGerald RJ, Meisel H (2000) Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Br J Nutr 84:S33–S37
Murray BA, FitzGerald RJ (2007) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins: biochemistry, bioactivity and production. Curr Pharm Des 13:773–791
Natesh R, Schwager SLU, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR (2003) Crystal structure of the human enzyme-lisinopril complex. Nature 421:1427–1429
Lin K, Zhang L, Han X, Meng Z, Zhang J, Wu Y, Cheng D (2018) Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling coupled with molecular docking analysis in screening of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Qula casein hydrolysates obtained by two-enzyme combination hydrolysis. J Agric Food Chem 66:3221–3228
Gu Y, Wu J (2013) LC-MS/MS coupled with QSAR modeling in characterising of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from soybean proteins. Food Chem 141:2682–2690
Natesh R, Schwager SLU, Edward D, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR (2003) Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme-lisinopril complex. Nature 421(30):551–554
Masuyer G, Schwager SLU, Sturrock ED, Isaac RE, Acharya KR (2012) Molecular recognition and regulation of human angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) activity by natural inhibitory peptides. Sci Rep 2:717
Matsufuji H, Matsui T, Seki E, Osajima K, Nakashima M, Osajima Y (1994) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in an alkaline proteinase hydrolysate derived from sardine muscle. Biosci Biotech Biochem 58:2244–2245
Sturrock ED, Natesh R, van Rooyen JM, Acharya KR (2004) Structure of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2677–2686
Corradi HR, Schwager SLU, Nchinda AT, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR (2006) Crystal structure of the N domain of human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme provides a structural basis for domain-specific inhibitor design. J Mol Biol 357:964–974
Papakyriakou A, Spyroulias GA, Sturrock ED, Manessi-Zoupa E, Cordopatis P (2007) Simulated interactions between angiotensin-converting enzyme and substrate gonadotropin-releasing hormone: novel insights into domain selectivity. Biochemistry 46:8753–8765
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Toshiki Uji for providing useful information on red algae species.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article dose not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morikawa, R., Toji, K., Kumagai, Y. et al. ACE inhibitory effect of the protein hydrolysates prepared from commercially available nori product by pepsin–trypsin digestion. Eur Food Res Technol 248, 243–251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-021-03876-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-021-03876-x