Abstract
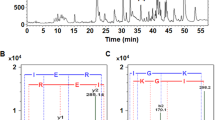
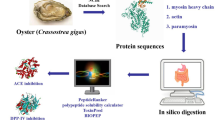
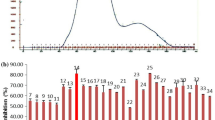
This study aimed to specifically prepare angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides rich in C-terminal proline from oyster proteins using chymotrypsin and proline-specific endopeptidases (PSEases). The hydrolysates were purified with Sephadex G25, Superdex™ 30 Increase 10/300 GL gel filtration chromatography and reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). The ACE inhibitory IC50 of purified fraction (G1E1C1) was 0.032 ± 0.003 mg/mL. According to ESI–MS and ESI–MS/MS analyses, there were three novel ACE inhibitory peptides in G1E1C1 fraction. Their sequences were Ser-Ala-Pro, Ala-Met-Pro and Thr-Ser-Gly-Pro. Molecular docking of peptides to ACE was studied. Metal–acceptor interactions and conventional hydrogen bonds greatly promoted the stability of peptides to ACE interaction. Pyrrole ring of proline may lead to higher inhibitory activity of peptides. It easily formed a Pi–alkyl interaction with aromatic ring residues (His353, His387, His513, and Phe512). Pi interactions may promote the effect of peptides on ACE. Also, C atom adjacent to the N atom of the pyrrole ring easily formed a carbon hydrogen bond with Ala354. The research discovered three novel ACE inhibitory peptides and provided a method to obtain ACE inhibitory peptides with specific structure X-Pro. The research result played an important role in revealing the structure–activity relationship of ACE inhibitory peptides and designing novel peptides with enhanced biological activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akabori S, Ohno K, Narita K (1952) On the hydrazinolysis of proteins and peptides: a method for the characterisation of carboxyl-terminal amino acids in proteins. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 25:214
Byun HG, Kim SK (2001) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin. Process Biochem 36(12):1155–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(00)00297-1
Cao W, Zhang C, Hong P, Ji H, Hao J (2010) Purification and identification of an ACE inhibitory peptide from the peptic hydrolysate of Acetes chinensis and its antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Food Sci Technol 45(5):959–965. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02219.x
Cushman DW, Cheung HS (1971) Spectrophotometic assay andproperties of the angiotensin- converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol 20:1637–1648. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9
Dai YG, Nan XP, Li TZ, Yang Z (2010) Separation and purification of ACE inhibitory peptides from casein. China Dairy Ind 55(3):254–257. https://doi.org/10.1159/000185971
Du L, Fang M, Wu H, Xie J, Wu Y, Li P, Zhang D, Huang Z, Xia Y, Zhou L, Wei D (2013) A novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Phascolosoma esculenta water-soluble protein hydrolysate. J Funct Foods 5(1):475–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2012.12.003
Espejo-Carpio FJ, Pérez-Gálvez R, Almécija Mdel C, Guadix A, Guadix EM (2014) Production of goat milk protein hydrolysate enriched in ACE-inhibitory peptides by ultrafiltration. J Dairy Res 81(04):385–393. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022029914000284
Guo Y, Pan D, Tanokura M (2009) Optimisation of hydrolysis conditions for the production of the angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from whey protein using response surface methodology. Food Chem 114(1):328–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.041
Huang G, Zhang R, Luo Y, Zeng W, Wu W (2014) Studies on the QSAR of ACE inhibitory tripeptides with proline as C-terminal and determination inhibitory activities. Chin J Struct Chem 33(12):1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-0395
Je JY, Park JY, Jung WK, Park PJ, Kim SK (2005) Isolation of angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor from fermented oyster sauce, Crassostrea gigas. Food Chem 90(4):809–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.05.028
Jiang Z, Tian B, Brodkorb A, Huo G (2010) Production, analysis and in vivo evaluation of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from bovine casein. Food Chem 123(3):779–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.026
Jimsheena VK, Lalitha RG (2010) Arachin derived peptides as selective angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: structure-activity relationship. Peptides 31(6):1165–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.02.022
Jimsheena VK, Lalitha RG (2011) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from arachin by simulated gastric digestion. Food Chem 125(2):561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.048
Kasai KI, Yokoyama S, Ishii SI (1971) Determination of C-terminal amino acid residues of bovine fibrinogen by hydrazinolysis. FEBS Lett 11(4):298–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(70)80553-1
Lahogue V, Réhel K, Taupin L, Haras D, Allaume P (2010) A HPLC-UV method for the determination of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity. Food Chem 118:870–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.080
Lau CC, Abdullah N, Shuib AS, Aminudin N (2014) Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (J.E. Lange) Imbach identified by LC–MS/MS. Food Chem 148:396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.053
Mehanna AS, Dowling M (1999) Liquid chromatographic determination of hippuric acid for the evaluation of ethacrynic acid as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. J Pharm Biomed Anal 19:967–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0731-7085(98)00122-8
Mizuno S, Nishimura S, Matsuura K, Gotou T, Yamamoto N (2004) Release of short and proline- rich antihypertensive peptides from casein hydrolysate with an Aspergillus oryzae protease. J Dairy Sci 87(10):3183–3188. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(04)73453
Miyoshi S, Ishikawa H, Kaneko T, Fukui F, Tanaka H, Maruyama S (1991) Structures and activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in an alpha-zein hydrolysate. Agric Biol Chem 55:1313–1318. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb1961.55.1313
Miyatake N, Satake K, Kamo M, Tsugita A (1994) Specific chemical cleavage of asparaginyl and glycyl-glycine bonds in peptides and proteins by anhydrous hydrazine vapor. J Biochem 115(2):208. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02215997
Memarpoor-Yazdi M, Asoodeh A, Chamani JK (2012) Structure and ACE-inhibitory activity of peptides derived from hen egg white lysozyme. Int J Pept Res Ther 18(4):353–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-012-9311-2
Nejati F, Rizzello CG, Cagno RD, Cagno RD, Sheikh-Zeinoddin M, Diviccaro A, Minervini F, Gobbetti M (2013) Manufacture of a functional fermented milk enriched of angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides and γ-amino butyric acid (GABA). LWT Food Sci Technol 51(1):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.09.017
Norris R, O’Keeffe MB, Poyarkov A, FitzGerald RJ (2015) Peptide identification and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity in prolyl endoproteinase digests of bovine αs-casein. Food Chem 188:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.04.130
Pan D, Guo Y (2010) Optimization of sour milk fermentation for the production of ACE-inhibitory peptides and purification of a novel peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Int Dairy J 20(7):472–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.01.007
Pan D, Cao J, Guo H, Zhao B (2012) Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 130(1):121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.011
Qi C, Lin G, Zhang R, Wu W (2017) Studies on the bioactivities of ACE-inhibitory peptides with phenylalanine C-terminus using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and in vitro evaluation. Mol Inform. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201600157
Rawendra RDS, Aisha, Chang C, Aulanni’am, Chen H, Huang T, Hsu J (2013) A novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from proteolytic digest of Chinese soft-shelled turtle egg white proteins. J Proteom 94:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2013.10.006
Samarakoon KW, Onam K, Ko JY, Lee JH, Kang MC, Kim D, Lee JB, Lee JS, Jeon YJ (2013) Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cultured marine microalgae (Nannochloropsis oculata) protein hydrolysate. J Appl Phycol 25(5):1595–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-9994-6
Wang C, Song W, Jiang LZ, Ming D (2014) Purification and identification of an ACE-inhibitory peptide from walnut protein hydrolysate. Eur Food Res Technol 239(2):333–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2227-7
Wu S, Feng X, Lan X, Xu Y, Liao D (2015) Purification and identification of angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) hydrolysate. J Funct Foods 13:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.12.051
Wu J, Aluko RE, Nakai S (2006) Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: quantitative structure-activity relationship study of di- and tripeptides. J Agric Food Chem 54:732–738. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf051263l
Wu J, Ding X (2013) Hypotensive and physiological effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from soy protein on spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Agric Food Chem 49(1):501–506. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000695n
Wu S, Sun J, Tong Z, Lan X, Shu B, Liu Y, Liao D (2012) Rapid and simple colorimetric assay for screening angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Pharm Biol 50(10):1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2012.674534
Wang J, Hu J, Cui J, Bai X, Du Y, Miyaguchi Y, Lin B (2008) Purification and identification of a ACE inhibitory peptide from oyster proteins hydrolysate and the antihypertensive effect of hydrolysate in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 111(2):302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.059
Xie CL, Kim JS, Ha JM, Choung SY, Choi YJ (2014) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor derived from cross-linked oyster protein. Biomed Res Int 379234:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/379234
Yao GL, Chai Y, Chen J, Wu Y (2017) Separation and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from cashew nut (Anacardium occidentale Linnaeus) protein. Int J Food Prop 20(23):S981–S991. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1325902
Yi L, Liang MA, Yuhao Z (2014) Influence of pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of collagen and release of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Food Sci 35(21):21–25. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201421005
Yust MM, Pedroche J, Girón-Calle J, Alaiz M, Millán F, Vioque J (2003) Production of ace inhibitory peptides by digestion of chickpea legumin with alcalase. Food Chem 81(3):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-8146(02)00431-4
Zhao Y, Li B, Liu Z, Dong S, Zhao X, Zeng M (2007) Antihypertensive effect and purification of an ACE inhibitory peptide from sea cucumber gelatin hydrolysate. Process Biochem 42(12):1586–1591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.08.011
Zhao X, Fong Z (1995) A study on the determination of the degree of hydrolysis in soy protein hydrolysates. J Northeast Agric Univ 2:178–181
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFC1600703), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 201864002), and the Key Research and Development Project Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2017YYSP003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Li, M., Fu, X. et al. Purification and charicterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides with specific structure X-Pro. Eur Food Res Technol 245, 1743–1753 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03290-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03290-4