Abstract
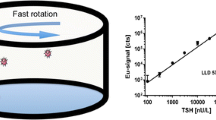
Concurrent measurement of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) hormones profoundly help clinicians diagnose hyper- and hypothyroidism. This work demonstrates the development of a sandwich-type electrochemical immunoassay using Janus and magnetic nanoparticles for one-pot detection of thyroxine (T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The signaling probe was developed by preparing Janus cadmium (CdO) and zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs decorated by T4/TSH-specific molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPT4-CdO and MIPTSH-ZnO). The capture probe was obtained by coating magnetic Fe3O4 NPs with 1,3-Bis(3-carboxy propyl) tetramethyl disiloxane and activating using N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC), and finally conjugating with T4/TSH-specific antibodies. To analyze T4 and TSH in actual samples, MIPT4-CdO and MIPTSH-ZnO were added to the sample solutions, and after incubation, capture probes (Fe3O4-AbTSH and Fe3O4-AbT4) were added. An external magnetic field was used to separate the sandwiched nanosystem, followed by adding a dilute solution of nitric acid (HNO3) to dissolve CdO and ZnO NPs and free Cd(II) and Zn(II) cations. The concentration of these cations was determined using constant-current potentiometric stripping analysis (cc-PSA) on screen-printed electrodes (SPE) modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT). The obtained signals for Cd(II) and Zn(II) were proportional to T4 and TSH concentrations. Limits of detection (LOD) for T4 and TSH analyses were respectively 0.02 ng.dL−1 and 0.0002 µU.mL−1 with a linear range of 0.05–50 ng.dL−1 and 0.001–100 µU.mL−1. The proposed nanosystem’s main advantage is the simultaneous detection of T4 and TSH in clinical samples with high sensitivity, selectivity, and stability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Higa S, Maesato A, Ishigaki S, Suenari K, Chen Y-J, Chen S-A. Diabetes and endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism) as risk factors for atrial fibrillation. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2021;13(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccep.2020.11.005.
Saravanan P, Siddique H, Simmons DJ, Greenwood R, Dayan CM. Twenty-four hour hormone profiles of TSH, Free T3 and free T4 in hypothyroid patients on combined T3/T4 therapy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2007;115(04):261–7.
Dimachkieh AL, Kazahaya K, Chelius DC. Assessment and management of thyroid disease in children. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019;52(5):957–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2019.06.009.
Ramsay N, Carizey R, Popa D. Coronavirus disease 2019-induced thyroiditis. J Emerg Med. 2021;61(4):420–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.01.012.
Schumm MA, Lechner MG, Shu ML, Ochoa JE, Kim J, Tseng C-H, Leung AM, Yeh MW. Frequency of thyroid hormone replacement after lobectomy for differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr Pract. 2021;27(7):691–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2021.01.004.
Evron JM, Papaleontiou M. Decision making in subclinical thyroid disease. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105(6):1033–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2021.05.014.
Shamsadini S, Darvish MS, Abdollahi H, Fekri AR. Ebrahimi HA (2006) Creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and thyroid hormone levels before and after haemodialysis. EMHJ-East Mediterr Health J. 2006;12(1–2):231–5.
Zhou Y, Xia X, Xu Y, Ke W, Yang W, Li Q. Application of europium (III) chelates-bonded silica nanoparticle in time-resolved immunofluorometric detection assay for human thyroid stimulating hormone. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;722:95–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.01.065.
Parra MD, Bernal LJ, Ceron JJ. Cortisol and free thyroxine determination by time-resolved fluorometry in canine serum. Can J Vet Res. 2004;68(2):98.
Choi S, Hwang J, Lee S, Lim DW, Joo H, Choo J. Quantitative analysis of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) using SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2017;240:358–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.178.
Park SY, Kim J, Yim G, Jang H, Lee Y, Kim SM, Park C, Lee M-H, Lee T. Fabrication of electrochemical biosensor composed of multi-functional DNA/rhodium nanoplate heterolayer for thyroxine detection in clinical sample. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2020;195:111240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111240.
Wang H, Wu X, Dong P, Wang C, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen J. Electrochemical biosensor based on interdigitated electrodes for determination of thyroid stimulating hormone. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2014;9(1):12.
Kashefi-Kheyrabadi L, Koyappayil A, Kim T, Cheon Y-P, Lee M-H. A MoS2@Ti3C2Tx MXene hybrid-based electrochemical aptasensor (MEA) for sensitive and rapid detection of thyroxine. Bioelectrochemistry 2021;137:107674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107674.
Zhao Y-Y, Luo H, Ge Q, Liu M, Tao Z, Cong H. An ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical sensor with layer-by-layer assembly of chiral multifarene[3,2,1] and g-C3N4 quantum dots for enantiorecognition towards thyroxine. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2021;336:129750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129750.
Waseem A, Yaqoob M, Nabi A, Greenway GM. Determination of thyroxine using Tris (2, 2′-bipyridyl) ruthenium (III)-NADH enhanced electrochemiluminescence detection. Anal Lett. 2007;40(6):1071–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710701298495
Gurgel MHC, Ponte CMM, Fontes R, Rocha ÍV, Batista LAA, Sousa T, Montenegro Junior RM. Establishment of reference interval for thyroid-stimulating hormone using electrochemiluminescence assay in a healthy adult population from Fortaleza, Brazil. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020;64:362–8.
Zhang Q, Shen Y, Gong L, Shen L, Xiao H, Cao L, Wei S, Hu F, Zhao F, Chen Z. A new thyroxine-labeled alkaline phosphatase chemiluminescence immunoassay for detection of thyroxine hormone. Sci Adv Mater. 2022;14(2):257–62. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2022.4199.
Couto RAS, Gonçalves LM, Góes MS, Rodrigues CMP, Quinaz MB, Rodrigues JA. SAM-based immunosensor for the analysis of thyroxine (T4). J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164(4):B103–6. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0561704jes.
Mradula, Raj R, Mishra S. Voltammetric immunosensor for selective thyroxine detection using Cu-MOF@PANI composite. Electrochem Sci Adv 2021;e2100051. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsa.202100051.
Ozcan HM, Aydin UD. A simple immunosensor for thyroid stimulating hormone. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2021;49(1):61–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2020.1867153.
Rana Kausar SN, Sultana I. Performance evaluation of thyroid hormones and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) assays by conventional and modular electro-chemi luminescence (ECL) systems. World J Med Sci. 2014;11(3):315–9.
Wu F-B, Han S-Q, Xu T, He Y-F. Sensitive time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for simultaneous detection of serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and total thyroxin with Eu and Sm as labels. Anal Biochem. 2003;314(1):87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(02)00624-3.
Koç Y, Moralı U, Erol S, Avci H. Electrochemical investigation of gold based screen printed electrodes: an application for a seafood toxin detection. Electroanalysis. 2021;33(4):1033–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060433.
Koç Y, Morali U, Erol S, Avci H. Investigation of electrochemical behavior of potassium ferricyanide/ferrocyanide redox probes on screen printed carbon electrode through cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Turk J Chem. 2021;45(6):1895–915. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-2105-55.
Li X, Chen L, Cui D, Jiang W, Han L, Niu N. Preparation and application of Janus nanoparticles: recent development and prospects. Coord Chem Rev. 2022;454:214318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214318.
Sánchez A, Díez P, Martínez-Ruíz P, Villalonga R, Pingarrón JM. Janus Au-mesoporous silica nanoparticles as electrochemical biorecognition-signaling system. Electrochem Commun. 2013;30:51–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2013.02.008.
Musarurwa H, Tavengwa NT. Stimuli-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers as adsorbents of analytes in complex matrices. Microchem J. 2022;181:107750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107750.
Karadurmus L, Ozcelikay G, Armutcu C, Ozkan SA. Electrochemical chiral sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of (1S,2S)-pseudoephedrine in dosage forms and biological sample. Microchem J. 2022;107820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107820.
Majidi MR, Omidi Y, Karami P, Johari-Ahar M. Reusable potentiometric screen-printed sensor and label-free aptasensor with pseudo-reference electrode for determination of tryptophan in the presence of tyrosine. Talanta. 2016;150:425–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.064
Lister AS. 7 - Validation of HPLC methods in pharmaceutical analysis. In: Ahuja S, Dong MW, editors. Separation Science and Technology, vol 6. Academic Press; 2005. p. 191–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-6395(05)80051-0.
Han J, Zhuo Y, Chai Y, Yu Y, Liao N, Yuan R. Electrochemical immunoassay for thyroxine detection using cascade catalysis as signal amplified enhancer and multi-functionalized magnetic graphene sphere as signal tag. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;790:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.06.025.
Bhatia A, Nandhakumar P, Kim G, Lee N-S, Yoon YH, Yang H. Simple and fast Ag deposition method using a redox enzyme label and quinone substrate for the sensitive electrochemical detection of thyroid-stimulating hormone. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;197:113773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113773.
Kashefi-Kheyrabadi L, Koyappayil A, Kim T, Cheon Y-P, Lee M-H. A MoS2@ Ti3C2Tx MXene hybrid-based electrochemical aptasensor (MEA) for sensitive and rapid detection of thyroxine. Bioelectrochemistry. 2021;137: 107674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107674
Couto RAS, Goncalves LM, Goes MS, Rodrigues CMP, Quinaz MB, Rodrigues JA. SAM-based immunosensor for the analysis of thyroxine (T4). J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164(4):B103.
Stefan van Staden R-I, Frederick van Staden J, Aboul-Enein Y, H, Balcu I,. Simultaneous determination of L-and D-T4 using a sequential injection analysis/sensors system. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2010;13(6):497–501.
Stefan R-I, van Staden JF, Aboul-Enein HY. Simultaneous determination of l-thyroxine (l-T4), d-thyroxine (d-T4), and l-triiodothyronine (l-T3) using a sensors/sequential injection analysis system. Talanta. 2004;64(1):151–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.01.024
Wani TA, Zargar S, Wakil SM, Darwish IA. New analytical application of antibody-based biosensor in estimation of thyroid-stimulating hormone in serum. Bioanalysis. 2016;8(7):625–32. https://doi.org/10.4155/bio-2015-0034
Bikkarolla SK, McNamee SE, Vance P, McLaughlin J. High-sensitive detection and quantitative analysis of thyroid-stimulating hormone using gold-nanoshell-based lateral flow immunoassay device. Biosensors. 2022;12(3):182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113773.
Smaniotto A, Mezalira DZ, Zapp E, Gallardo H, Vieira IC. Electrochemical immunosensor based on an azo compound for thyroid-stimulating hormone detection. Microchem J. 2017;133:510–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.04.010
Yang B, Liu D, Zhu L, Liu Y, Wang X, Qiao L, Zhang W, Liu B. Sensitive detection of thyroid stimulating hormone by inkjet printed microchip with a double signal amplification strategy. Chin Chem Lett. 2018;29(12):1879–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2018.01.042
Beitollahi H, Ivari SG, Torkzadeh-Mahani M. Application of antibody–nanogold–ionic liquid–carbon paste electrode for sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of thyroid-stimulating hormone. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;110:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.003.
Liu Y, Zhang Q, Wang H, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R. An electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for thyroid stimulating hormone based on polyamidoamine-norfloxacin functionalized Pd–Au core–shell hexoctahedrons as signal enhancers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;71:164–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.04.022
Helin M, Väre L, Håkansson M, Canty P, Hedman HP, Heikkilä L, Ala-Kleme T, Kankare J, Kulmala S. Electrochemiluminoimmunoassay of hTSH at disposable oxide-coated n-silicon electrodes. J Electroanal Chem. 2002;524:176–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(02)00638-1.
Funding
The Biosensor Sciences and Technologies Research Center, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran, financially supported the current study (Grant No.:1002756).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Johari-Ahar: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Pari Karami: methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—review, and editing.
Danial Gholamin: investigation and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The protocols for this study have been approved by the ethics committee of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran (Approval No: IR.ARUMS.REC.1398.614).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karami, P., Gholamin, D. & Johari-Ahar, M. Electrochemical immunoassay for one-pot detection of thyroxin (T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) using magnetic and Janus nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 4741–4751 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04767-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04767-8