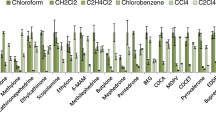
Abstract
Oral fluid is easy and safe to collect and allows the detection of drugs of abuse after local exposure by oral, smoked, and/or inhaled intake, or systemic exposure. A routine online solid-phase extraction UPLC-MS/MS method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 33 psychoactive drugs in oral fluid. The selected drugs were fourteen fentanyl analogs and nineteen other abused psychoactive compounds, including classical narcotics, which were analyzed in a run of 10 min. Limits of detection and of quantification ranged from 0.02 to 1 ng/mL and from 0.02 to 5 ng/mL depending on the analyte, respectively. Matrix effect was in the range − 17 to + 15.7% for all analytes having a deuterated analog. Accuracy ranged from 82.7 to 113.4% and precision CV was at worst of 18.6%. Carryover was below 0.8% for all analytes. Recovery from FLOQSwabs™ showed high variability between analytes with THC, D2FF, 4-ANPP, ocfentanil, and valerylfentanyl being recovered below 40%. A stability study performed over 2 weeks on collecting devices loaded with artificial oral fluid showed huge variation between analytes with morphine, BZE, and norfentanyl being the more stable. Storage at 4 °C allowed drug detection for 1 week except for THC and remifentanil. The method was successfully applied to the detection of abused psychoactive compounds in oral fluid samples from 6 patients admitted to an addiction department.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malaca S, Busardò FP, Gottardi M, Pichini S, Marchei E. Dilute and shoot ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) analysis of psychoactive drugs in oral fluid. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019;170:63–7.
Pirro V, Jarmusch AK, Vincenti M, Cooks RG. Direct drug analysis from oral fluid using medical swab touch spray mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;861:47–54.
Di Corcia D, Lisi S, Pirro V, Gerace E, Salomone A, Vincenti M. Determination of pharmaceutical and illicit drugs in oral fluid by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013;927:133–41.
Cone EJ, Huestis MA. Interpretation of oral fluid tests for drugs of abuse. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1098:51–103.
Coulter CA, Moore CM. Analysis of drugs in oral fluid using LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2019;1872:237–59.
da Cunha KF, Oliveira KD, Huestis MA, Costa JL. Screening of 104 new psychoactive substances (NPS) and other drugs of abuse in oral fluid by LC-MS-MS. J Anal Toxicol. 2020;44(7):697–707.
Fabresse N, Aouad H, Knapp A, Mayer C, Etting I, Larabi IA, et al. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous detection of 10 illicit drugs in oral fluid collected with FLOQSwabs™ and application to real samples. Drug Test Anal. 2019;11(6):824–32.
Langel K, Gunnar T, Ariniemi K, Rajamäki O, Lillsunde P. A validated method for the detection and quantitation of 50 drugs of abuse and medicinal drugs in oral fluid by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2011;879(13):859–70.
Tabarra I, Soares S, Rosado T, Gonçalves J, Luís Â, Malaca S, et al. Novel synthetic opioids - toxicological aspects and analysis. Forensic Sci Res. 2019;4(2):111–40.
Valen A, Leere Øiestad ÅM, Strand DH, Skari R, Berg T. Determination of 21 drugs in oral fluid using fully automated supported liquid extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS. Drug Test Anal. 2017;9(5):808–23.
Denia A, Esteve-Turrillas FA, Armenta S. Analysis of drugs including illicit and new psychoactive substances in oral fluids by gas chromatography-drift tube ion mobility spectrometry. Talanta. 2022;238(Pt 1):122966.
Palmquist KB, Swortwood MJ. Data-independent screening method for 14 fentanyl analogs in whole blood and oral fluid using LC-QTOF-MS. Forensic Sci Int. 2019;297:189–97.
Griswold MK, Chai PR, Krotulski AJ, Friscia M, Chapman BP, Varma N, et al. A Novel oral fluid assay (LC-QTOF-MS) for the detection of fentanyl and clandestine opioids in oral fluid after reported heroin overdose. J Med Toxicol Off J Am Coll Med Toxicol. 2017;13(4):287–92.
Fisher DS, Beyer C, van Schalkwyk G, Seedat S, Flanagan RJ. Measurement of clozapine, norclozapine, and amisulpride in plasma and in oral fluid obtained using 2 different sampling systems. Ther Drug Monit. 2017;39(2):109–17.
Concheiro M, de Castro A, Quintela O, Cruz A, López-Rivadulla M. Determination of illicit and medicinal drugs and their metabolites in oral fluid and preserved oral fluid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;391(6):2329–38.
Caglar AS. Determination of drugs by online column-switching liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr Sci. 2016;54(9):1641–7.
Jiang F, Rao Y, Wang R, Johansen SS, Ni C, Liang C, et al. Sensitive, automatic method for the determination of diazepam and its five metabolites in human oral fluid by online solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. 2016;39(10):1873–83.
Williams M, Martin J, Galettis P. A validated method for the detection of synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluid. J Anal Toxicol. 2019;43(1):10–7.
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European drug report 2021: trends and developments. [Internet]. LU: Publications Office; 2021 [cited 2021 Jul 17]. Available from: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2810/18539.
Accueil | COFRAC - Comité français d’accréditation [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jan 17]. Available from: https://tools.cofrac.fr/fr/documentation/index.php?fol_id=63.
Zhou W, Yang S, Wang PG. Matrix effects and application of matrix effect factor. Bioanalysis. 2017;9(23):1839–44.
Sergi M, Compagnone D, Curini R, D’Ascenzo G, Del Carlo M, Napoletano S, et al. Micro-solid phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of stimulants, hallucinogens, ketamine and phencyclidine in oral fluids. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;675(2):132–7.
Truver MT, Swortwood MJ. Quantitative analysis of novel synthetic opioids, morphine and buprenorphine in oral fluid by LC-MS-MS. J Anal Toxicol. 2018;42(8):554–61.
Arrêté du 13 décembre 2016 fixant les modalités du dépistage des substances témoignant de l’usage de stupéfiants, et des analyses et examens prévus par le code de la route et abrogeant l’arrêté du 5 septembre 2001 modifié fixant les modalités du dépistage des substances témoignant de l’usage de stupéfiants, et des analyses et examens prévus par le code de la route - Légifrance [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 17]. Available from: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/jorf/id/JORFTEXT000033607271.
Cocovi-Solberg DJ, Esteve-Turrillas FA, Armenta S, de la Guardia M, Miró M. Towards an automatic lab-on-valve-ion mobility spectrometric system for detection of cocaine abuse. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1512:43–50.
Kwok WH, Choi TLS, Tsoi YYK, Leung GNW, Wan TSM. Screening of over 100 drugs in horse urine using automated on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry for doping control. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1490:89–101.
Heuett NV, Ramirez CE, Fernandez A, Gardinali PR. Analysis of drugs of abuse by online SPE-LC high resolution mass spectrometry: communal assessment of consumption. Sci Total Environ. 2015;511:319–30.
Fikarová K, Horstkotte B, Machián D, Sklenářová H, Solich P. Lab-In-Syringe for automated double-stage sample preparation by coupling salting out liquid-liquid extraction with online solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatographic separation for sulfonamide antibiotics from urine. Talanta. 2021;221:121427.
Chiuminatto U, Gosetti F, Dossetto P, Mazzucco E, Zampieri D, Robotti E, et al. Automated online solid phase extraction ultra high performance liquid chromatography method coupled with tandem mass spectrometry for determination of forty-two therapeutic drugs and drugs of abuse in human urine. Anal Chem. 2010;82(13):5636–45.
Santos MG, Tavares IMC, Barbosa AF, Bettini J, Figueiredo EC. Analysis of tricyclic antidepressants in human plasma using online-restricted access molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction followed by direct mass spectrometry identification/quantification. Talanta. 2017;163:8–16.
Mulet CT, Tarifa A, DeCaprio AP. Comprehensive analysis of synthetic cannabinoids and metabolites in oral fluid by online solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(28):7937–53.
Jung J, Kolodziej A, Pape E, Bisch M, Javot L, Gibaja V, et al. Multiplex detection of 14 fentanyl analogues and U-47700 in biological samples: application to a panel of French hospitalized patients. Forensic Sci Int. 2020;317:110437.
Ransohoff JR, Petrides AK, Piscitello GJ, Flood JG, Melanson SEF. Urine is superior to oral fluid for detecting buprenorphine compliance in patients undergoing treatment for opioid addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;203:8–12.
Lee D, Milman G, Schwope DM, Barnes AJ, Gorelick DA, Huestis MA. Cannabinoid stability in authentic oral fluid after controlled cannabis smoking. Clin Chem. 2012;58(7):1101–9.
Verstraete AG. Detection times of drugs of abuse in blood, urine, and oral fluid. Ther Drug Monit. 2004;26(2):200–5.
Martini MBA, Batista TBD, Henn IW, Souza PT da R de, Vieira AR, Azevedo-Alanis LR. Whether drug detection in urine and oral fluid is similar? A systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020;50(4):348–58.
Weinmann W, Vogt S, Goerke R, Müller C, Bromberger A. Simultaneous determination of THC-COOH and THC-COOH-glucuronide in urine samples by LC/MS/MS. Forensic Sci Int. 2000;113(1–3):381–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
In accordance with local ethical standards, informed consent was obtained from each patient for sample collection and data publication. Oral fluid and urine samples were anonymized. All samples were destroyed after analysis.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercier, B., Scala-Bertola, J., Pape, E. et al. Online SPE UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of 33 psychoactive drugs from swab-collected human oral fluid samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 4203–4215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04073-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04073-9