Abstract
A rapid, simple, and sensitive technique for the quantitative detection of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in biological fluids was developed based on the combination of field-amplified sample stacking (FASS)–related capillary electrophoresis (CE) with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (UA-DLLME). The extraction efficiency of UA-DLLME was strongly related to extraction time, salt concentration, type of extraction and dispersion solvents, and volume of extraction and dispersion solvents. The extracted fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in a mixture of 50% methanol and 50% deionized water were efficiently stacked using FASS and then separated using cyclodextrin-modified CE. Under optimal conditions of FASS (chiral selector, 3 mM trimethyl-β-cyclodextrin; and background electrolyte, 100 mM phosphate buffer) and UA-DLLME (extraction solvent, 200 μL of acetone; and dispersed solvent, 50 μL of C2H2Cl4 in 1 mL of the sample solution), the obtained enrichment factors of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers reached approximately 2000. The linear ranges for the quantification of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers were 0.3–150 and 0.6–150 nM, respectively. The relative standard deviations in peak areas and migration time for four analytes were less than 3.3% and 6.3%, respectively. The proposed system provided limits of detection (signal-to-noise ratio of 3) for four analytes corresponding to 0.1 nM. The precision and accuracy for urine and serum samples were less than 6.8 and 8.3%, respectively. These findings suggested that the proposed system exhibited a high potential for the reliable determination of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in clinical samples.

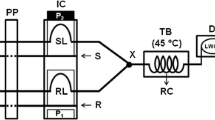
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DLLME:
-
Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
- FASS:
-
Field-amplified sample stacking
- Flx:
-
Fluoxetine
- Nflx:
-
Norfluoxetine
References
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Engleman EA. Prozac (fluoxetine, lilly 110140), the first selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and an antidepressant drug: twenty years since its first publication. Life Sci. 1995;57(5):411–41.
Barclay VKH, Tyrefors NL, Johansson IM, Pettersson CE. Trace analysis of fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine. Part I: development of a chiral liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for wastewater samples. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(33):5587–96.
Hiemke C, Härtter S. Pharmacokinetics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;85(1):11–28.
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Reid LR, Mayle DA, Krushinski JH, Robertson DW. Norfluoxetine enantiomers as inhibitors of serotonin uptake in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1993;8:337.
Stokes PE, Holtz A. Fluoxetine tenth anniversary update: the progress continues. Clin Ther. 1997;19(5):1135–250.
Fuller RW, Snoddy HD, Krushinski JH, Robertson DW. Comparison of norfluoxetine enantiomers as serotonin uptake inhibitors in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 1992;31(10):997–1000.
Ribeiro AR, Maia AS, Moreira IS, Afonso CM, Castro PML, Tiritan ME. Enantioselective quantification of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine by HPLC in wastewater effluents. Chemosphere. 2014;95:589–96.
Alvim-Jr J, Lopes BR, Cass QB. Simultaneous enantioselective quantification of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in human milk by direct sample injection using 2-dimensional liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1451:120–6.
Mifsud J, Sghendo LJ. A novel chiral GC/MS method for the analysis of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in biological fluids. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012;4(3):236–45.
Weiß JA, Mohr S, Schmid MG. Indirect chiral separation of new recreational drugs by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using trifluoroacetyl-L-prolyl chloride as chiral derivatization reagent. Chirality. 2015;27(3):211–5.
Tabani H, Mahyari M, Sahragard A, Fakhari AR, Shaabani A. Evaluation of sulfated maltodextrin as a novel anionic chiral selector for the enantioseparation of basic chiral drugs by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2015;36(2):305–11.
Asensi-Bernardi L, Martin-Biosca Y, Villanueva-Camañas RM, Medina-Hernández MJ, Sagrado Vives S. Evaluation of enantioselective binding of fluoxetine to human serum albumin by ultrafiltration and CE – experimental design and quality considerations. Electrophoresis. 2010;31(19):3268–80.
D'Hulst A, Verbeke N. Chiral analysis of basic drugs by oligosaccharide-mediated capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 1996;735(1):283–93.
Cârcu-Dobrin M, Budău M, Hancu G, Gagyi L, Rusu A, Kelemen H. Enantioselective analysis of fluoxetine in pharmaceutical formulations by capillary zone electrophoresis. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(3):397–403.
Hancu G, Budău M, Muntean DL, Gagyi L, Rusu A. Capillary electrophoresis in the enantioseparation of modern antidepressants: an overview. Biomed Chromatogr. 2018;32(11):e4335.
Rudaz S, Calleri E, Geiser L, Cherkaoui S, Prat J, Veuthey J-L. Infinite enantiomeric resolution of basic compounds using highly sulfated cyclodextrin as chiral selector in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2003;24(15):2633–41.
Catai APF, Carrilho E, Lanças FM, Queiroz MEC. Fast separation of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors antidepressants in plasma sample by nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216(30):5779–82.
Shen Z, Wang S, Bakhtiar R. Enantiomeric separation and quantification of fluoxetine (Prozac®) in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry using liquid-liquid extraction in 96-well plate format. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002;16(5):332–8.
Sánchez de la Torre C, Martínez MA, Almarza E. Determination of several psychiatric drugs in whole blood using capillary gas–liquid chromatography with nitrogen phosphorus detection: comparison of two solid phase extraction procedures. Forensic Sci Int. 2005;155(2):193–204.
Zare F, Ghaedi M, Daneshfar A. Solid phase extraction of antidepressant drugs amitriptyline and nortriptyline from plasma samples using core-shell nanoparticles of the type Fe3O4@ZrO2@N- cetylpyridinium, and their subsequent determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta. 2015;182(11):1893–902.
Silva BJG, Lanças FM, Queiroz MEC. Determination of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in human plasma by polypyrrole-coated capillary in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216(49):8590–7.
Zhou X, He M, Chen B, Hu B. Hollow fiber based liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction combined with sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography for the sensitive determination of second-generation antidepressants in human fluids. Analyst. 2015;140(5):1662–71.
Abolhasani J, Jafariyan HR, Mahdi khataei M, Hosseinzadeh-khanmiri R, Ghorbani-kalhor E, Hassanpour A. Hollow fiber supported liquid-phase microextraction combined with maltodextrin-modified capillary electrophoresis for the determination of citalopram enantiomers in urine samples. Anal Methods. 2015;7(5):2012–9.
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Milani Hosseini M-R, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1116(1):1–9.
Tu Y-Y, Hsieh M-M, Chang SY. Sensitive detection of piperazinyl phenothiazine drugs by field-amplified sample stacking in capillary electrophoresis with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Electrophoresis. 2015;36(21–22):2828–36.
Wen J, Zhang W-T, Cao W-Q, Li J, Gao F-Y, Yang N, et al. Enantioselective separation of mirtazapine and its metabolites by capillary electrophoresis with acetonitrile field-amplified sample stacking and its application. Molecules. 2014;19(4):4907.
Su H-L, Hsieh Y-Z. Using cation-selective exhaustive injection and sweeping micellar electrokinetic chromatography to determine selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1209(1):253–9.
Ho Y-H, Wang C-C, Hsiao Y-T, Ko W-K, Wu S-M. Analysis of ten abused drugs in urine by large volume sample stacking–sweeping capillary electrophoresis with an experimental design strategy. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1295:136–41.
Wang M, Cai Z, Xu L. Coupling of acetonitrile deproteinization and salting-out extraction with acetonitrile stacking in chiral capillary electrophoresis for the determination of warfarin enantiomers. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(26):4045–51.
Lin E-P, Chiu T-C, Hsieh M-M. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with acetonitrile stacking through capillary electrophoresis for the determination of three selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor drugs in body fluids. J Sep Sci. 2016;39(24):4841–50.
Kitagawa F, Otsuka K. Recent applications of on-line sample preconcentration techniques in capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1335:43–60.
Meng P, Wang Y, Meng L. pH-mediated stacking in capillary electrophoresis for analysis of opiates in saliva. Anal Methods. 2012;4(11):3695–700.
Lin E-P, Lin K-C, Chang C-W, Hsieh M-M. On-line sample preconcentration by sweeping and poly(ethylene oxide)-mediated stacking for simultaneous analysis of nine pairs of amino acid enantiomers in capillary electrophoresis. Talanta. 2013;114:297–303.
Hsieh M-M, Lin E-P, Huang S-W. On-line concentration and separation of cationic and anionic neurochemicals by capillary electrophoresis with UV absorption detection. Talanta. 2012;88:638–45.
Soisungnoen P, Burakham R, Srijaranai S. Determination of organophosphorus pesticides using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with reversed electrode polarity stacking mode—micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Talanta. 2012;98:62–8.
Zhao Y, Yu G, Chen S, Zhang S, Wang B, Huang J, et al. Ozonation of antidepressant fluoxetine and its metabolite product norfluoxetine: kinetics, intermediates and toxicity. Chem Eng J. 2017;316:951–63.
Lian D-S, Zhao S-J, Li J, Li B-L. Progress in stacking techniques based on field amplification of capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(25):6129–50.
Desiderio C, Rudaz S, Raggi MA, Fanali S. Enantiomeric separation of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in plasma and serum samples with high detection sensitivity capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1999;20(17):3432–8.
Bavili Tabrizi A, Rezazadeh A. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique for the extraction and spectrofluorimetric determination of fluoxetine in pharmaceutical formulations and human urine. Adv Pharm Bull. 2012;2(2):157–64.
Maham M, Kiarostami V, Waqif-Husain S, Abroomand-Azar P, Tehrani MS, Khoeini Sharifabadi M, et al. Extraction and determination of cyproheptadine in human urine by DLLME-HPLC method. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013;12(2):311–8.
Chen X, Zheng S, Le J, Qian Z, Zhang R, Hong Z, et al. Ultrasound-assisted low-density solvent dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the simultaneous determination of 12 new antidepressants and 2 antipsychotics in whole blood by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017;142:19–27.
Ni X-J, Wang Z-Z, Shang D-W, Lu H-Y, Zhang M, Wen Y-G. Simultaneous analysis of olanzapine, fluoxetine, and norfluoxetine in human plasma using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B. 2018;1092:506–14.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under contract number MOST 108-2113-M-017-003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, as reflected in a priori approval by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Human Research Ethics Committee at National Cheng University (NCKU HREC-F-107-044-2). The urine and serum samples in this work were collected from three healthy volunteers. Written, informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Euroanalysis XX with guest editor Sibel A. Ozkan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 444 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z.R., Hsieh, M.M. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with field-amplified capillary electrophoresis for sensitive and quantitative determination of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine enantiomers in biological fluids. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 5113–5123 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02441-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02441-x