Abstract
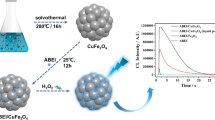
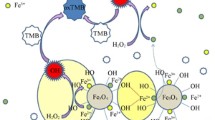
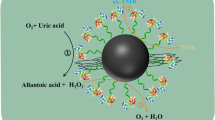
The convenience of colorimetric sensors is useful for practical applications. In this work, we constructed a novel colorimetric sensor with magnetic separation ability that can be operated in nearly neutral conditions and achieve one-step detection of metabolites. Magnetic Cu doped Fe3O4@FeOOH magnetic nanocomposite (Cu/Fe3O4@FeOOH) with an oxygen vacancy was prepared by a one-step self-assembly hydrothermal method, and fully characterized by different methods. The oxygen vacancy generated by the incorporation of Cu2+ cations into the Fe3O4@FeOOH structure was confirmed to be a vital reactive site for enhancing the catalytic activity, which opens up a new way of designing highly efficient enzyme mimics. Benefiting from its inherent horseradish-peroxidase-like activity, a simple and selective enzyme-based colorimetric sensor was developed for one-step detection of H2O2 and cholesterol, and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine was catalyzed by H2O2 to generate a colored product of oxidized 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine for signaling. H2O2 and cholesterol can be linearly detected in the same range from 0.01 to 0.4 mmol L-1 with detection limits of 0.0075 mmol L-1 and 0.0082 mmol L-1, respectively. The proposed colorimetric sensor has satisfactory reusability, accuracy, and practicability in human serum samples, indicating its potential application for the detection of different metabolites in the fields of life science and analytical science.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma Y, Cen Y, Sohail M, Xu G, Wei F, Shi M, et al. A Ratiometric fluorescence universal platform based on N, Cu codoped carbon dots to detect metabolites participating in H2O2-generation reactions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:33011–9.
Pang P, Zhang Y, Ge S, Cai Q, Yao S, Grimes CA. Determination of glucose using bienzyme layered assembly magnetoelastic sensing device. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2009;136:310–4.
Sun H, Zhou Y, Ren J, Qu X. Carbon nanozymes: enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57:9224–37.
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:577–83.
Wei H, Wang E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:6060–93.
Wang Q, Wei H, Zhang Z, Wang E, Dong S. Nanozyme: an emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. Trends Anal Chem. 2018;105:218–24.
Ding N, Yan N, Ren C, Chen X. Colorimetric determination of melamine in dairy products by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles-H2O2-ABTS detection system. Anal Chem. 2010;82:5897–9.
Wei H, Wang E. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics and their applications in H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal Chem. 2008;80:2250–4.
Ding Y, Yang B, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zheng X, et al. FePt-Au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;259:775–83.
Liu H, Ma H, Xu H, Wen J, Huang Z, Qiu Y, et al. Hollow and porous nickel sulfide nanocubes prepared from a metal-organic framework as an efficient enzyme mimic for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:129–37.
Nirala NR, Abraham S, Kumar V, Bansal A, Srivastava A, Saxena PS. Colorimetric detection of cholesterol based on highly efficient peroxidase mimetic activity of graphene quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;218:42–50.
Wang Y-M, Liu J-W, Jiang J-H, Zhong W. Cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflakes with intrinsic peroxidase catalytic activity and their application to serum glucose detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:4225–32.
Chen M, Ding Y, Gao Y, Zhu X, Wang P, Shi Z, et al. N,N′-Di-caboxy methyl perylene diimide (PDI) functionalized CuO nanocomposites with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their application in visual biosensing of H2O2 and glucose. RSC Adv. 2017;7:25220–8.
Lin T, Qin Y, Huang Y, Yang R, Hou L, Ye F, et al. A label-free fluorescence assay for hydrogen peroxide and glucose based on the bifunctional MIL-53(Fe) nanozyme. Chem Commun. 2018;54:1762–5.
Tao Y, Ju E, Ren J, Qu X. Bifunctionalized mesoporous silica-supported gold nanoparticles: intrinsic oxidase and peroxidase catalytic activities for antibacterial applications. Adv Mater. 2015;27:1097–104.
Han L, Li C, Zhang T, Lang Q, Liu A. Au@Ag heterogeneous nanorods as nanozyme interfaces with peroxidase-like activity and their application for one-pot analysis of glucose at nearly neutral pH. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:14463–70.
Hu Y, Cheng H, Zhao X, Wu J, Muhammad F, Lin S, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering active gold nanoparticles with enzyme-mimicking activities for measuring glucose and lactate in living tissues. ACS Nano. 2017;11:5558–66.
Li N, Than A, Wang X, Xu S, Sun L, Duan H, et al. Ultrasensitive profiling of metabolites using tyramine-functionalized graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano. 2016;10:3622–9.
Valekar AH, Batule BS, Kim MI, Choa K-H, Hong D-Y, Lee U-H, et al. Novel amine-functionalized iron trimesates with enhanced peroxidase-like activity and their applications for the fluorescent assay of choline and acetylcholine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;100:161–8.
Lin T, Zhong L, Chen H, Li Z, Song Z, Guo L, et al. A sensitive colorimetric assay for cholesterol based on the peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanosheets. Microchim Acta. 2017;184:1233–7.
Gao L, Fan K, Yan X. Iron oxide nanozyme: a multifunctional enzyme mimetic for biomedical applications. Theranostics. 2017;7:3207–27.
Jin H, Tian X, Nie Y, Zhou Z, Yang C, Li Y, et al. Oxygen vacancy promoted heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of ofloxacin at pH 3.2-9.0 by Cu substituted magnetic Fe3O4@FeOOH nanocomposite. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51:12699–706.
Chang HC, Ho JA. Gold nanocluster-assisted fluorescent detection for hydrogen peroxide and cholesterol based on the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2015;87:10362–7.
Huang Y, Tan J, Cui L, Zhou Z, Zhou S, Zhang Z, et al. Graphene and Au NPs co-mediated enzymatic silver deposition for the ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of cholesterol. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:560–7.
Wang C, Li Q, Wang F, Xia G, Liu R, Li D, et al. Morphology-dependent performance of CuO anodes via facile and controllable synthesis for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:1243–50.
Liang M, Fan K, Pan Y, Jiang H, Wang F, Yang D, et al. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle peroxidase mimetic-based colorimetric assay for the rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticide and nerve agent. Anal Chem. 2013;85:308–12.
Ou P, Xu G, Ren Z, Hou X, Han G. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of uniform α-FeOOH nanowires in high yield. Mater Lett. 2008;62:914–7.
Wang S, Xu D, Ma L, Qiu J, Wang X, Dong Q, et al. Ultrathin ZIF-67 nanosheets as a colorimetric biosensing platform for peroxidase-like catalysis. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410:7145–52.
Liu H, Ding Y-N, Yang B, Liu Z, Zhang X, Liu Q. Iron doped CuSn(OH)6 microspheres as a peroxidase-mimicking artificial enzyme for H2O2 colorimetric detection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018;6:14383–93.
O'Neill L, Johnston C, Grant PS. Enhancing the supercapacitor behaviour of novel Fe3O4/FeOOH nanowire hybrid electrodes in aqueous electrolytes. J Power Sources. 2015;274:907–15.
Galtayries A, Bonnelle J-P. XPS and ISS studies on the interaction of H2S with polycrystalline Cu, Cu2Oand CuO surfaces. Surf Interface Anal. 1995;23:171–9.
Mesquita AM, Guimarães IR, de Castro GMM, Gonçalves MA, Ramalho TC, Guerreiro MC. Boron as a promoter in the goethite (α-FeOOH) phase: organic compound degradation by Fenton reaction. Appl Catal B Environ. 2016;192:286–95.
Tian X, Jin H, Nie Y, Zhou Z, Yang C, Li Y, et al. Heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of ofloxacin over a wide pH range of 3.6–10.0 over modified mesoporous iron oxide. Chem Eng J. 2017;328:397–405.
Zhuang L, Jia Y, He T, Du A, Yan X, Ge L, et al. Tuning oxygen vacancies in two-dimensional iron-cobalt oxide nanosheets through hydrogenation for enhanced oxygen evolution activity. Nano Res. 2018;11:3509–18.
Xu L, Jiang Q, Xiao Z, Li X, Huo J, Wang S, et al. Plasma-engraved Co3O4 nanosheets with oxygen vacancies and high surface area for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55:5277–81.
Li D, Li K, Xu R, Wang H, Tian D, Wei Y, et al. Ce1-xFexO2-δ catalysts for catalytic methane combustion: role of oxygen vacancy and structural dependence. Catal Today. 2018;318:73–85.
Zhang JW, Zhang HT, Du ZY, Wang X, Yu SH, Jiang HL. Water-stable metal-organic frameworks with intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity as a colorimetric biosensing platform. Chem Commun. 2014;50:1092–4.
Li L, Li P, Wang Y, Lin L, Shah AH, He T. Modulation of oxygen vacancy in hydrangea-like ceria via Zr doping for CO2 photoreduction. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;452:498–506.
Sun M, Li W, Zhang B, Cheng G, Lan B, Ye F, et al. Enhanced catalytic performance by oxygen vacancy and active interface originated from facile reduction of OMS-2. Chem Eng J. 2018;331:626–35.
Arciga-Duran E, Meas Y, Pérez-Bueno JJ, Ballesteros JC, Trejo G. Effect of oxygen vacancies in electrodeposited NiO towards the oxygen evolution reaction: role of Ni-glycine complexes. Electrochim Acta. 2018;268:49–58.
Ding Y, Zhu L, Wang N, Tang H. Sulfate radicals induced degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate. Appl Catal B Environ. 2013;129:153–62.
Buxton GV, Greenstock CL, Helman WP, Ross AB. Review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (•OH/•O−) in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Ref Data. 1988;17:513–886.
Zhou Y, Ding J, Liang T, Abdel-Halim ES, Jiang L, Zhu JJ. FITC doped rattle-type silica colloidal particle-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for biosensing and imaging of superoxide anion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:6423–30.
Lu N, Zhang M, Ding L, et al. Yolk-shell nanostructured Fe3O4@C magnetic nanoparticles with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for label-free colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. Nanoscale. 2017;9:4508–15.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21765002), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2017GXNSFDA198044), the State Key Laboratory for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources (Guangxi Normal University) (CMEMR2017-A10, CMEMR2018-C11), the Key Project of Guangxi Normal University (2017ZD003), and the BAGUI Scholar Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangxi Normal University and was performed in accordance with its ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants before the testing of serum samples obtained from Guilin Hospital of Chinese Traditional and Western Medicine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 3.63 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Liang, G., Lin, T. et al. Magnetic Cu/Fe3O4@FeOOH with intrinsic HRP-like activity at nearly neutral pH for one-step biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 3801–3810 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01841-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01841-y