Abstract
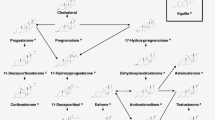
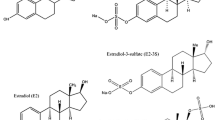
Measuring both progestagens, androgens, corticosteroids as well as estrogens with a single method makes it possible to investigate the effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) on the main pathways in the mammalian steroidogenesis. This paper presents two simple methods for the determination of the major steroid hormones in biological matrixes using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS2). A novel method was developed for the determination of 14 steroids in the H295R in vitro assay without the need for solid phase extraction (SPE) purification prior to LC-MS2 analysis. The in vitro assay was validated by exposing H295R cells to prochloraz for inhibiting steroid hormone secretion and by exposing cells to forskolin for inducing steroid hormone secretion. The developed method fulfills the recommendations for the H295R assay suggested by the OECD. Furthermore, a simple off-line SPE methodology was developed for the necessary clean-up of in vivo assays. Samples, such as gonad tissue, plasma and serum, are complex biological matrixes, and the SPE methodology was optimized to remove salts and proteins prior to elution of target analytes. At the same time, lipophilic compounds were retained on the SPE cartridge during elution. This, combined with the multi-steroid LC-MS2 method, made it possible to determine 10 steroids in male Sprague-Dawley rat gonad tissue. Furthermore, it was possible to quantify 6 steroids in the plasma. In general, the observed concentration of steroid hormones in plasma, testes, and H295R cell medium corresponded well with previous studies. The off-line SPE method was validated using spiked charcoal-stripped serum. Method recovery, accuracy, precision and robustness were all good. Instrument sensitivity was in the range of 55–530 pg/mL (LLOQ).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller WL, Auchus RJ. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:81–151.
Colborn T, Saal FS, Soto AM. Environ Impact Assess Rev. 1994;14:469–89.
Giwercman A, Carlsen E, Keiding N, Skakkebak NE. Environ Health Perspect. 1993;101:65–71.
Grün F, Blumberg B. Endocrinology. 2006;147:50–5.
Grün F, Blumberg B. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;304:19–29.
Joensen UN, Bossi R, Leffers H, Jensen AA, Skakkebaek NE, Jørgensen N. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:923–7.
Jørgensen N, Asklund C, Carlsen E, Skakkebaek NE. Int J Androl. 2006;29:54–61.
Priskorn L, Holmboe SA, Jacobsen R, Jensen TK, Lassen TH, Skakkebaek NE. Int J Androl. 2012;35:449–55.
Skakkebæk NE, Meyts ER-D, Main KM. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:972–8.
Nielsen FK, Hansen CH, Fey JA, Hansen M, Jacobsen NW, Halling-Sørensen B, et al. Toxicol in Vitro. 2012;26:343–50.
Hecker M, Newsted JL, Murphy MB, Higley EB, Jones PD, Wu R, et al. Appl Pharmacol. 2006;217:114–24.
OECD. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals http://www.oecdilibrary.org/docserver/download/9745601e.pdf?expires=1449586480&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=D5920268C409B7FC8578D7AB262A2C97. 2011.
Schloms L, Storbeck KH, Swart P, Gelderblom WCA, Swart AC. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;128:128–38.
Tonoli D, Fürstenberger C, Boccard J, Hochstrasser D, Jeanneret F, Odermatt A, et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015;28:955–66.
van der Pas R, Hofland LJ, Hofland J, Taylor AE, Arlt W, Steenbergen J, et al. J Endocrinol. 2012;215:403–12.
Xing Y, Edwards MA, Ahlem C, Kennedy M, Cohen A, Gomez-Sanches CE, et al. J Endocrinol. 2011;209:327–35.
Zhang X, Chang H, Wiseman S, He Y, Higley E, Jones P, et al. Toxicol Sci. 2011;121:320–7.
Iwaoka Y, Hashimoto R, Koizumi H, Yu J, Okabe T. Life Sci. 2010;86:894–8.
Rosenmai AK, Nielsen FK, Pedersen M, Hadrup N, Trier X, Christensen JH, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;266:132–42.
Quignot N, Arnaud M, Robidel F, Lecomte A, Tournier M, Cren-Olivé C, et al. Reprod Toxicol. 2012;33:339–52.
Matty AJ. Fish endocrinology, Matty AJ (ED.). 1985; 138-173.
Kindler PM, Philipp DP, Gross MR, Bahr JM. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1989;75:446–53.
Carvalho VM, Nakamura OH, Vieira JGH. J Chromatogr B. 2008;872:154–61.
Ceglarek U, Kortz L, Leichtle A, Fiedler GM, Kratzsch J, Thiery J. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;401:14–118.
Koren L, Ng ESM, Soma KK, Wynne-Edwards KE. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32496.
Winther CS, Nielsen FK, Hansen M, Styrishave B. Int J Toxicol. 2013;32:219–27.
Jacobsen NW, Hansen CH, Nellemann C, Styrishave B, Halling-Sørensen B. Toxicol in Vitro. 2015;29:1729–35.
Guldvang A, Hansen CH, Weisser JJ, Halling-Sørensen B, Styrishave B. Reprod Toxicol. 2015;58:174–83.
Sørensen AM, Hansen CH, Bonomo S, Olsen L, Jørgensen FS, Weisser JJ, Kretschmann AC, Styrishave B. Toxicol in Vitro. 2016;34:71–80.
Abdel-Khalik J, Björklund E, Hansen M. J Chromatogr B. 2013;935:61–9.
Yamashitaa K, Miyashirob Y, Maekubob H, Okuyamab M, Honmab S, Takahashia M, et al. Steroids. 2011;74:920–6.
Fanellia F, Belluomoa I, Lalloa VDD, Cuomoa G, Iasiob RD, Baccinia M, et al. Steroids. 2011;76:244–53.
US National Library of Medicine. ChemIDplus advanced http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/. 2010.
Hansen M, Jacobsen NW, Nielsen FK, Björklund E, Styrishave B, Halling-Sørensen B. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400:3409–17.
ICH. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Validation of Analytical Procedure: Text and Methodology Q2(R1) 1-17 http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf. 2005.
U.S. FDA, Guidance for Industry – Bioanalytical Method Validation, May 2001 http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/.%20.%20./Guidances/ucm070107.pdf.
Pouech C, Tournier M, Quignot N, Kiss A, Wiest L, Lafay F, et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402:2777–88.
Concas A, Popcu P, Sogliano C, Serra M, Purdy RH, Biggio G. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000;66:39–45.
Serra M, Pisu MG, Muggironi M, Parodo V, Papi G, Sari R, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berlin). 2001;158:48–54.
Zorrilla LM, Gibson EK, Jeffay SC, Crofton KM, Setzer WR, Cooper RL, et al. Toxicol Sci. 2009;107:56–64.
Pollard I. J Endocrinol. 1988;119:275–80.
Abdel-Khalik J, Björklund E, Hansen M. J Chromatogr B. 2013;928:58–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols for collecting plasma and testis samples from male rats were approved by the Danish Animal Experimentation Council (24th of July 2014, license holder: Anne-Marie Heegaard, case no. 2014-15-0201-00031).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 536 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weisser, J.J., Hansen, C.H., Poulsen, R. et al. Two simple cleanup methods combined with LC-MS/MS for quantification of steroid hormones in in vivo and in vitro assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 4883–4895 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9575-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9575-z