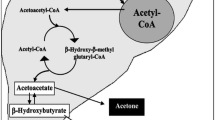
Abstract
The detection of cancer at an early stage is often significant in the successful treatment of the disease. Tumor cells have been reported to generate unique cancer volatile organic compound (VOC) profiles which can reflect the disease conditions. The detection and analysis of VOC biomarkers from exhaled breath has been recognized as a new frontier in cancer diagnostics and health inspections owing to its potential in developing rapid, noninvasive, and inexpensive cancer screening tools. To detect specific VOCs of low concentrations from exhaled breath, and to enhance the accuracy of early diagnosis, many breath collection and analysis approaches have been developed. This paper will summarize and critically review the exhaled-breath VOC-related sampling, collection, detection, and analytical methods, especially the recent development in VOC sensors. VOC sensors are commonly inexpensive, portable, programmable, easy to use, and can obtain data in real time with high sensitivities. Therefore, many sensor-based VOC detection techniques have huge potential in clinical point-of-care use.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shirasu M, Touhara K (2011) The scent of disease: volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J Biochem 150(3):257–266. doi:10.1093/Jb/Mvr090
Todd J, McGrath EE (2011) Chest X-ray mass in a patient with lung cancer! Qjm-Int J Med 104(10):903–904. doi:10.1093/Qjmed/Hcq159
Singeap AM, Trifan A, Cojocariu C, Stanciu C (2012) Colon capsule endoscopy compared to colonoscopy for colorectal neoplasms diagnosis: an initial experience and a brief review of the literature. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 116(1):145–149
Apantaku LM (2000) Breast cancer diagnosis and screening. Am Fam Physician 62(3):596–602
Brandman S, Ko JP (2011) Pulmonary nodule detection, characterization, and management with multidetector computed tomography. J Thorac Imaging 26(2):90–105. doi:10.1097/RTI.0b013e31821639a9
Truong MT, Viswanathan C, Erasmus JJ (2011) Positron emission tomography/computed tomography in lung cancer staging, prognosis, and assessment of therapeutic response. J Thorac Imaging 26(2):132–146. doi:10.1097/RTI.0b013e3182128704
Hochhegger B, Marchiori E, Sedlaczek O, Irion K, Heussel CP, Ley S, Ley-Zaporozhan J, Soares Souza A Jr, Kauczor HU (2011) MRI in lung cancer: a pictorial essay. Br J Radiol 84(1003):661–668. doi:10.1259/bjr/24661484
Haick H, Broza YY, Mochalski P, Ruzsanyi V, Amann A (2014) Assessment, origin, and implementation of breath volatile cancer markers. Chem Soc Rev 43(5):1423–1449. doi:10.1039/C3cs60329f
Roberts HC, Patsios D, Paul NS, McGregor M, Weisbrod G, Chung T, Herman S, Boerner S, Waddell T, Keshavjee S, Darling G, Pereira A, Kale A, Bayanati H, Sitartchouk I, Tsao M, Shepherd FA (2007) Lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography: Canadian experience. Can Assoc Radiol J 58(4):225–235
Amann A, Corradi M, Mazzone P, Mutti A (2011) Lung cancer biomarkers in exhaled breath. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11(2):207–217. doi:10.1586/erm.10.112
Wu CC, Maher MM, Shepard JAO (2011) CT-guided percutaneous needle biopsy of the chest: preprocedural evaluation and technique. Am J Roentgenol 196(5):W511–W514. doi:10.2214/Ajr.10.4657
Rossi ED, Mule A, Maggiore C, Miraglia A, Lauriola L, Vecchio FM, Fadda G (2004) Cytologic diagnosis of pulmonary lesions. Rays 29(4):357–361
Hakim M, Broza YY, Barash O, Peled N, Phillips M, Amann A, Haick H (2012) Volatile organic compounds of lung cancer and possible biochemical pathways. Chem Rev 112(11):5949–5966. doi:10.1021/Cr300174a
Boots AW, van Berkel JJBN, Dallinga JW, Smolinska A, Wouters EF, van Schooten FJ (2012) The versatile use of exhaled volatile organic compounds in human health and disease. J Breath Res 6(2). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/6/2/027108
Tisch U, Haick H (2010) Arrays of chemisensitive monolayer-capped metallic nanoparticles for diagnostic breath testing. Rev Chem Eng 26(5–6):171–179. doi:10.1515/Revce.2010.009
Park J, Itoh T, Shin W, Sato K, Sakumura Y, Horio Y, Hida T (2013) Analysis of exhaled breath for screening of lung cancer patients. J Thorac Oncol 8:S1275–S1276
Turner APF, Magan N (2004) Electronic noses and disease diagnostics. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):161–166. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro823
Guernion N, Ratcliffe NM, Spencer-Phillips PTN, Howe RA (2001) Identifying bacteria in human urine: current practice and the potential for rapid, near-patient diagnosis by sensing volatile organic compounds. Clin Chem Lab Med 39(10):893–906. doi:10.1515/Cclm.2001.146
Dummer J, Storer M, Swanney M, McEwan M, Scott-Thomas A, Bhandari S, Chambers S, Dweik R, Epton M (2011) Analysis of biogenic volatile organic compounds in human health and disease. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 30(7):960–967. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2011.03.011
Cicolella A (2008) Volatile organic compounds (VOC): definition, classification and properties. Rev Mal Respir 25(2):155–163. doi:10.1016/S0761-8425(08)71513-4
Garner CE, Smith S, Costello BD, White P, Spencer R, Probert CSJ, Ratcliffe NM (2007) Volatile organic compounds from feces and their potential for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease. FASEB J 21(8):1675–1688. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6927com
Schantz MM, Benner BA, Heckert NA, Sander LC, Sharpless KE, Vander Pol SS, Vasquez Y, Villegas M, Wise SA, Alwis KU, Blount BC, Calafat AM, Li Z, Silva MJ, Ye X, Gaudreau E, Patterson DG, Sjodin A (2015) Development of urine standard reference materials for metabolites of organic chemicals including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, phthalates, phenols, parabens, and volatile organic compounds. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(11):2945–2954
Phillips M (1992) Breath tests in medicine. Sci Am 267(1):74–79
Miekisch W, Schubert JK, Noeldge-Schomburg GFE (2004) Diagnostic potential of breath analysis–focus on volatile organic compounds. Clin Chim Acta 347(1–2):25–39. doi:10.1016/j.cccm.2004.04.023
Cao WQ, Duan YX (2006) Breath analysis: potential for clinical diagnosis and exposure assessment. Clin Chem 52(5):800–811. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.063545
Smith D, Spanel P (2007) The challenge of breath analysis for clinical diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Analyst 132(5):390–396. doi:10.1039/B700542n
Buszewski B, Kesy M, Ligor T, Amann A (2007) Human exhaled air analytics: biomarkers of diseases. Biomed Chromatogr 21(6):553–566. doi:10.1002/Bmc.835
Sethi S, Nanda R, Chakraborty T (2013) Clinical application of volatile organic compound analysis for detecting infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev 26(3):462–475. doi:10.1128/Cmr.00020-13
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Cheema T, Greenberg J (2004) Increased breath biomarkers of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 344(1–2):189–194. doi:10.1016/j.cccn.2004.02.025
Galassetti PR, Novak B, Nemet D, Rose-Gottron C, Cooper DM, Meinardi S, Newcomb R, Zaldivar F, Blake DR (2005) Breath ethanol and acetone as indicators of serum glucose levels: an initial report. Diabetes Technol Ther 7(1):115–123. doi:10.1089/dia.2005.7.115
Novak BJ, Blake DR, Meinardi S, Rowland FS, Pontello A, Cooper DM, Galassetti PR (2007) Exhaled methyl nitrate as a noninvasive marker of hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(40):15613–15618. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706533104
Manolis A (1983) The diagnostic potential of breath analysis. Clin Chem 29(1):5–15
Phillips M, Herrera J, Krishnan S, Zain M, Greenberg J, Cataneo RN (1999) Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J Chromatogr B 729(1–2):75–88. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(99)00127-9
Ambrosone CB (2000) Oxidants and antioxidants in breast cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 2(4):903–917
Tayek JA (1992) A review of cancer cachexia and abnormal glucose metabolism in humans with cancer. J Am Coll Nutr 11(4):445–456
Kroemer G (2006) Mitochondria in cancer. Oncogene 25(34):4630–4632
Bayley JP, Devilee P (2010) Warburg tumours and the mechanisms of mitochondrial tumour suppressor genes. Barking up the right tree? Curr Opin Genet Dev 20(3):324–329. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2010.02.008
Vousden KH, Ryan KM (2009) p53 and metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 9(10):691–700
Amann A, Mochalski P, Ruzsanyi V, Broza YY, Haick H (2014) Assessment of the exhalation kinetics of volatile cancer biomarkers based on their physicochemical properties. J Breath Res 8(1):016003. doi:10.1088/1752-7155/8/1/016003
Nakhleh MK, Broza YY, Haick H (2014) Monolayer-capped gold nanoparticles for disease detection from breath. Nanomedicine (Lond) 9(13):1991–2002. doi:10.2217/Nnm.14.121
Anderson JC, Babb AL, Hlastala MP (2003) Modeling soluble gas exchange in the airways and alveoli. Ann Biomed Eng 31(11):1402–1422
Broza YY, Haick H (2013) Nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of disease by volatile organic compounds. Nanomedicine (Lond) 8(5):785–806. doi:10.2217/Nnm.13.64
Van den Velde S, Nevens F, Van Hee P, van Steenberghe D, Quirynen M (2008) GC–MS analysis of breath odor compounds in liver patients. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 875(2):344–348. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.08.031
Konvalina G, Haick H (2014) Sensors for breath testing: from nanomaterials to comprehensive disease detection. Acc Chem Res 47(1):66–76. doi:10.1021/ar400070m
Vereb H, Dietrich AM, Alfeeli B, Agah M (2011) The possibilities will take your breath away: breath analysis for assessing environmental exposure. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8167–8175. doi:10.1021/es202041j
Righettoni M, Amann A, Pratsinis SE (2015) Breath analysis by nanostructured metal oxides as chemo-resistive gas sensors. Mater Today 18(3):163–171. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2014.08.017
Risby TH, Solga SF (2006) Current status of clinical breath analysis. Appl Phys B 85(2–3):421–426
Phillips M (1997) Method for the collection and assay of volatile organic compounds in breath. Anal Biochem 247(2):272–278
Rattray NJW, Hamrang Z, Trivedi DK, Goodacre R, Fowler SJ (2014) Taking your breath away: metabolomics breathes life in to personalized medicine. Trends Biotechnol 32(10):538–548. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.08.003
Robroeks CM, van Berkel JJ, Jobsis Q, van Schooten FJ, Dallinga JW, Wouters EF, Dompeling E (2013) Exhaled volatile organic compounds predict exacerbations of childhood asthma in a 1-year prospective study. Eur Respir J 42(1):98–106
Riess U, Tegtbur U, Fauck C, Fuhrmann F, Markewitz D, Salthammer T (2010) Experimental setup and analytical methods for the non-invasive determination of volatile organic compounds, formaldehyde and NOx in exhaled human breath. Anal Chim Acta 669(1–2):53–62. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.04.049
Poli D, Carbognani P, Corradi M, Goldoni M, Acampa O, Balbi B, Bianchi L, Rusca M, Mutti A (2005) Exhaled volatile organic compounds in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: cross sectional and nested short-term follow-up study. Resp Res 6. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-6-71
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Cummin ARC, Gagliardi AJ, Gleeson K, Greenberg J, Maxfield RA, Rom WN (2003) Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 123(6):2115–2123. doi:10.1378/chest.123.6.2115
Kim YH, Kim KH (2015) Test on the reliability of gastight syringes as transfer/storage media for gaseous VOC analysis: the extent of VOC sorption between the inner needle and a glass wall surface. Anal Chem 87(5):3056–3063. doi:10.1021/Ac504713y
Ma HY, Li X, Chen JM, Wang HJ, Cheng TT, Chen K, Xu SF (2014) Analysis of human breath samples of lung cancer patients and healthy controls with solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and flow-modulated comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC x GC). Anal Methods 6(17):6841–6849. doi:10.1039/c4ay01220h
Ulanowska A, Kowalkowski T, Hrynkiewicz K, Jackowski M, Buszewski B (2011) Determination of volatile organic compounds in human breath for Helicobacter pylori detection by SPME-GC/MS. Biomed Chromatogr 25(3):391–397. doi:10.1002/Bmc.1460
Ulanowska A, Trawinska E, Sawrycki P, Buszewski B (2012) Chemotherapy control by breath profile with application of SPME-GC/MS method. J Sep Sci 35(21):2908–2913. doi:10.1002/jssc.201200333
Wang CS, Ke CF, Wang XY, Chi CJ, Guo L, Luo SQ, Guo ZG, Xu GW, Zhang FM, Li EY (2014) Noninvasive detection of colorectal cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. Anal Bioanal Chem 406(19):4757–4763
Cozzolino R, De Magistris L, Saggese P, Stocchero M, Martignetti A, Di Stasio M, Malorni A, Marotta R, Boscaino F, Malorni L (2014) Use of solid-phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for determination of urinary volatile organic compounds in autistic children compared with healthy controls. Anal Bioanal Chem 406(19):4649–4662
Poli D, Goldoni M, Corradi M, Acampa O, Carbognani P, Internullo E, Casalini A, Mutti A (2010) Determination of aldehydes in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer by means of on-fiber-derivatisation SPME-GC/MS. J Chromatogr B 878(27):2643–2651. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.01.022
Queralto N, Berliner AN, Goldsmith B, Martino R, Rhodes P, Lim SH (2014) Detecting cancer by breath volatile organic compound analysis: a review of array-based sensors. J Breath Res 8(2). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/8/2/027112
Bajtarevic A, Ager C, Pienz M, Klieber M, Schwarz K, Ligor M, Ligor T, Filipiak W, Denz H, Fiegl M, Hilbe W, Weiss W, Lukas P, Jamnig H, Hackl M, Haidenberger A, Buszewski B, Miekisch W, Schubert J, Amann A (2009) Noninvasive detection of lung cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. BMC Cancer 9. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-348
Gordon SM, Szidon JP, Krotoszynski BK, Gibbons RD, Oneill HJ (1985) Volatile organic compounds in exhaled air from patients with lung cancer. Clin Chem 31(8):1278–1282
Phillips M, Gleeson K, Hughes JMB, Greenberg J, Cataneo RN, Baker L, McVay WP (1999) Volatile organic compounds in breath as markers of lung cancer: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 353(9168):1930–1933. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07552-7
Fuchs P, Loeseken C, Schubert JK, Miekisch W (2010) Breath gas aldehydes as biomarkers of lung cancer. Int J Cancer 126(11):2663–2670. doi:10.1002/ijc.24970
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Ditkoff BA, Fisher P, Greenberg J, Gunawardena R, Kwon CS, Rahbari-Oskoui F, Wong C (2003) Volatile markers of breast cancer in the breath. Breast J 9(3):184–191
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Cummin AR, Gagliardi AJ, Gleeson K, Greenberg J, Maxfield RA, Rom WN (2003) Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 123(6):2115–2123
Phillips M, Altorki N, Austin JH, Cameron RB, Cataneo RN, Greenberg J, Kloss R, Maxfield RA, Munawar MI, Pass HI, Rashid A, Rom WN, Schmitt P (2007) Prediction of lung cancer using volatile biomarkers in breath. Cancer Biomark 3:95–109
Phillips M, Altorki N, Austin JHM, Cameron RB, Cataneo RN, Kloss R, Maxfield RA, Munawar MI, Pass HI, Rashid A, Rom WN, Schmitt P, Wai J (2008) Detection of lung cancer using weighted digital analysis of breath biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta 393(2):76–84. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2008.02.021
Preti G, Labows JN, Kostelc JG, Aldinger S, Daniele R (1988) Analysis of lung air from patients with bronchogenic carcinoma and controls using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 432:1–11. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)80627-1
Song G, Qin T, Liu H, Xu GB, Pan YY, Xiong FX, Gu KS, Sun GP, Chen ZD (2010) Quantitative breath analysis of volatile organic compounds of lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 67(2):227–231. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.03.029
Wang YS, Hu YJ, Wang D, Yu K, Wang L, Zou YC, Zhao C, Zhang XL, Wang P, Ying KJ (2012) The analysis of volatile organic compounds biomarkers for lung cancer in exhaled breath, tissues and cell lines. Cancer Biomark 11(4):129–137. doi:10.3233/Cbm-2012-0270
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Ditkoff BA, Fisher P, Greenberg J, Gunawardena R, Kwon CS, Tietje O, Wong C (2006) Prediction of breast cancer using volatile biomarkers in the breath. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99(1):19–21. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9176-1
Phillips M, Cataneo RN, Saunders C, Hope P, Schmitt P, Wai J (2010) Volatile biomarkers in the breath of women with breast cancer. J Breath Res 4(2). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/4/2/026003
Qin T, Liu H, Song Q, Song G, Wang HZ, Pan YY, Xiong FX, Gu KS, Sun GP, Chen ZD (2010) The screening of volatile markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark 19(9):2247–2253. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-10-0302
D’Amico A, Pennazza G, Santonico M, Martinelli E, Roscioni C, Galluccio G, Paolesse R, Di Natale C (2010) An investigation on electronic nose diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 68(2):170–176. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.11.003
Peng G, Hakim M, Broza YY, Billan S, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Tisch U, Haick H (2010) Detection of lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers from exhaled breath using a single array of nanosensors. Br J Cancer 103(4):542–551. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605810
Nugent P, Belmabkhout Y, Burd SD, Cairns AJ, Luebke R, Forrest K, Pham T, Ma SQ, Space B, Wojtas L, Eddaoudi M, Zaworotko MJ (2013) Porous materials with optimal adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics for CO2 separation. Nature 495(7439):80–84
Wehinger A, Schmid A, Mechtcheriakov S, Ledochowski M, Grabmer C, Gastl GA, Amann A (2007) Lung cancer detection by proton transfer reaction mass-spectrometric analysis of human breath gas. Int J Mass Spectrom 265(1):49–59. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2007.05.012
Kumar S, Huang JZ, Abbassi-Ghadi N, Spanel P, Smith D, Hanna GB (2013) Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry analysis of exhaled breath for volatile organic compound profiling of esophago-gastric cancer. Anal Chem 85(12):6121–6128. doi:10.1021/Ac4010309
Xu ZQ, Broza YY, Ionsecu R, Tisch U, Ding L, Liu H, Song Q, Pan YY, Xiong FX, Gu KS, Sun GP, Chen ZD, Leja M, Haick H (2013) A nanomaterial-based breath test for distinguishing gastric cancer from benign gastric conditions. Br J Cancer 108(4):941–950. doi:10.1038/Bjc.2013.44
Shehada N, Bronstrup G, Funka K, Christiansen S, Leja M, Haick H (2015) Ultrasensitive silicon nanowire for real-world gas sensing: noninvasive diagnosis of cancer from breath volatolome. Nano Lett 15(2):1288–1295. doi:10.1021/Nl504482t
Hakim M, Billan S, Tisch U, Peng G, Dvrokind I, Marom O, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Haick H (2011) Diagnosis of head-and-neck cancer from exhaled breath. Br J Cancer 104(10):1649–1655. doi:10.1038/Bjc.2011.128
Amal H, Shi DY, Ionescu R, Zhang W, Hua QL, Pan YY, Tao L, Liu H, Haick H (2015) Assessment of ovarian cancer conditions from exhaled breath. Int J Cancer 136(6):E614–E622. doi:10.1002/Ijc.29166
Ibrahim B, Basanta M, Cadden P, Singh D, Douce D, Woodcock A, Fowler SJ (2011) Non-invasive phenotyping using exhaled volatile organic compounds in asthma. Thorax 66(9):804–809
Trefz P, Rosner L, Hein D, Schubert JK, Miekisch W (2013) Evaluation of needle trap micro-extraction and automatic alveolar sampling for point-of-care breath analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(10):3105–3115. doi:10.1007/s00216-013-6781-9
Baumbach JI (2009) Ion mobility spectrometry coupled with multi-capillary columns for metabolic profiling of human breath. J Breath Res 3(3):034001. doi:10.1088/1752-7155/3/3/034001
Brodrick E, Davies A, Neill P, Hanna L, Williams EM (2015) Breath analysis: translation into clinical practice. J Breath Res 9(2). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/9/2/027109
Suresh M, Vasa NJ, Agarwal V, Chandapillai J (2014) UV photo-ionization based asymmetric field differential ion mobility sensor for trace gas detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 195:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.008
Mochalski P, Rudnicka J, Agapiou A, Statheropoulos M, Amann A, Buszewski B (2013) Near real-time VOCs analysis using an aspiration ion mobility spectrometer. J Breath Res 7(2). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/7/2/026002
Molina MA, Zhao W, Sankaran S, Schivo M, Kenyon NJ, Davis CE (2008) Design-of-experiment optimization of exhaled breath condensate analysis using a miniature differential mobility spectrometer (DMS). Anal Chim Acta 628(2):155–161. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.09.010
Basanta M, Jarvis RM, Xu Y, Blackburn G, Tal-Singer R, Woodcock A, Singh D, Goodacre R, Thomas CLP, Fowler SJ (2010) Non-invasive metabolomic analysis of breath using differential mobility spectrometry in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and healthy smokers. Analyst 135(2):315–320
Miller RA, Eiceman GA, Nazarov EG, King AT (2000) A novel micromachined high-field asymmetric waveform-ion mobility spectrometer. Sensors Actuators B Chem 67(3):300–306. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00535-9
Nazarov EG, Miller RA, Eiceman GA, Stone JA (2006) Miniature differential mobility spectrometry using atmospheric pressure photoionization. Anal Chem 78(13):4553–4563. doi:10.1021/ac052213i
Turner C, Parekh B, Walton C, Spanel P, Smith D, Evans M (2008) An exploratory comparative study of volatile compounds in exhaled breath and emitted by skin using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(4):526–532
King J, Kupferthaler A, Frauscher B, Hackner H, Unterkofler K, Teschl G, Hinterhuber H, Amann A, Hogl B (2012) Measurement of endogenous acetone and isoprene in exhaled breath during sleep. Physiol Meas 33(3):413–428. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/33/3/413
O’Hara ME, O’Hehir S, Green S, Mayhew CA (2008) Development of a protocol to measure volatile organic compounds in human breath: a comparison of rebreathing and on-line single exhalations using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. Physiol Meas 29(3):309–330. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/29/3/003
Righettoni M, Schmid A, Amann A, Pratsinis SE (2013) Correlations between blood glucose and breath components from portable gas sensors and PTR-TOF-MS. J Breath Res 7(3). doi:10.1088/1752-7155/7/3/037110
Kneepkens CMF, Lepage G, Roy CC (1994) The potential of the hydrocarbon breath test as a measure of lipid peroxidation. Free Radical Bio Med 17(2):127–160
Lee J, Jung M, Barthwal S, Lee S, Lim SH (2015) MEMS gas preconcentrator filled with CNT foam for exhaled VOC gas detection. Biochip J 9(1):44–49. doi:10.1007/s13206-014-9106-y
Zaric B, Petrovic S, Bjekic M, Rajic I, Popovic A, Dordevic D (2014) Analysis of human exhaled breath in a population of young volunteers. Arch Biol Sci 66(4):1529–1538. doi:10.2298/Abs1404529z
Yamazoe N (1991) New approaches for improving semiconductor gas sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 5(1–4):7–19
Barsan N, Schweizer-Berberich M, Gopel W (1999) Fundamental and practical aspects in the design of nanoscaled SnO2 gas sensors: a status report. Fresenius J Anal Chem 365(4):287–304
Yamazoe N, Kurokawa Y, Seiyama T (1983) Effects of additives on semiconductor gas sensors. Sensors Actuators 4(2):283–289
Korotcenkov G (2005) Gas response control through structural and chemical modification of metal oxide films: state of the art and approaches. Sensors Actuators B Chem 107(1):209–232
Korotcenkov G, Brinzari V, Boris Y, Ivanova M, Schwank J, Morante J (2003) Influence of surface Pd doping on gas sensing characteristics of SnO2 thin films deposited by spray pirolysis. Thin Solid Films 436(1):119–126
Malagu C, Fabbri B, Gherardi S, Giberti A, Guidi V, Landini N, Zonta G (2014) Chemoresistive gas sensors for the detection of colorectal cancer biomarkers. Sensors (Basel) 14(10):18982–18992. doi:10.3390/s141018982
Barsan N, Weimar U (2001) Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. J Electroceram 7(3):143–167
Zilberman Y, Ionescu R, Feng XL, Mullen K, Haick H (2011) Nanoarray of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and carbon nanotubes for accurate and predictive detection in real-world environmental humidity. ACS Nano 5(8):6743–6753
Peng G, Tisch U, Adams O, Hakim M, Shehada N, Broza YY, Billan S, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Haick H (2009) Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 4(10):669–673
Peng G, Trock E, Haick H (2008) Detecting simulated patterns of lung cancer biomarkers by random network of single-walled carbon nanotubes coated with nonpolymeric organic materials. Nano Lett 8(11):3631–3635
Lewis NS (2004) Comparisons between mammalian and artificial olfaction based on arrays of carbon black-polymer composite vapor detectors. Acc Chem Res 37(9):663–672
Zilberman Y, Tisch U, Shuster G, Pisula W, Feng XL, Mullen K, Hoick H (2010) Carbon nanotube/hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene bilayers for discrimination between nonpolar volatile organic compounds of cancer and humid atmospheres. Adv Mater 22(38):4317–4320
Peng G, Tisch U, Haick H (2009) Detection of nonpolar molecules by means of carrier scattering in random networks of carbon nanotubes: toward diagnosis of diseases via breath samples. Nano Lett 9(4):1362–1368. doi:10.1021/Nl8030218
Tisch U, Haick H (2010) Nanomaterials for cross-reactive sensor arrays. MRS Bull 35(10):797–803
Dovgolevsky E, Konvalina G, Tisch U, Haick H (2010) Mono layer-capped cubic platinum nanoparticles for sensing nonpolar analytes in highly humid atmospheres. J Phys Chem C 114(33):14042–14049
Barash O, Peled N, Hirsch FR, Haick H (2009) Sniffing the unique “odor print” of non-small-cell lung cancer with gold nanoparticles. Small 5(22):2618–2624
Matsuguchi M, Uno T (2006) Molecular imprinting strategy for solvent molecules and its application for QCM-based VOC vapor sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 113(1):94–99
Di Natale C, Macagnano A, Martinelli E, Paolesse R, D’Arcangelo G, Roscioni C, Finazzi-Agro A, D’Amico A (2003) Lung cancer identification by the analysis of breath by means of an array of non-selective gas sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 18(10):1209–1218
Jakubik WP (2011) Surface acoustic wave-based gas sensors. Thin Solid Films 520(3):986–993
Speller NC, Siraj N, Regmi BP, Marzoughi H, Neal C, Warner IM (2015) Rational design of QCM-D virtual sensor arrays based on film thickness, viscoelasticity, and harmonics for vapor discrimination. Anal Chem 87(10):5156–5166. doi:10.1021/Ac5046824
Kimura M, Liu Y, Sakai R, Sato S, Hirai T, Fukawa T, Mihara T (2011) Detection of volatile organic compounds by analyses of polymer-coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor arrays. Sensor Mater 23(7):359–368
Matsuguchi M, Uno T, Aoki T, Yoshida M (2008) Chemically modified copolymer coatings for mass-sensitive toluene vapor sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 131(2):652–659
Janzen MC, Ponder JB, Bailey DP, Ingison CK, Suslick KS (2006) Colorimetric sensor Arrays for volatile organic compounds. Anal Chem 78(11):3591–3600
Mazzone PJ, Wang XF, Xu YM, Mekhail T, Beukemann MC, Na J, Kemling JW, Suslick KS, Sasidhar M (2012) Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Colorimetric Sensor Array for the Identification and Characterization of Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 7(1):137–142
Oh JW, Chung WJ, Heo K, Jin HE, Lee BY, Wang E, Zueger C, Wong W, Meyer J, Kim C, Lee SY, Kim WG, Zemla M, Auer M, Hexemer A, Lee SW (2014) Biomimetic virus-based colourimetric sensors. Nat Commun 5
Dong MJ, Zhao M, Ou S, Zou C, Wu CD (2014) A luminescent dye@MOF platform: emission fingerprint relationships of volatile organic molecules. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(6):1575–1579. doi:10.1002/anie.201307331
Wu HH, Gong QH, Olson DH, Li J (2012) Commensurate adsorption of hydrocarbons and alcohols in microporous metal organic frameworks. Chem Rev 112(2):836–868
Ferey G, Serre C, Devic T, Maurin G, Jobic H, Llewellyn PL, De Weireld G, Vimont A, Daturi M, Chang JS (2011) Why hybrid porous solids capture greenhouse gases? Chem Soc Rev 40(2):550–562
Deng HX, Doonan CJ, Furukawa H, Ferreira RB, Towne J, Knobler CB, Wang B, Yaghi OM (2010) Multiple functional groups of varying ratios in metal-organic frameworks. Science 327(5967):846–850
Zhang M, Feng GX, Song ZG, Zhou YP, Chao HY, Yuan DQ, Tan TTY, Guo ZG, Hu ZG, Tang BZ, Liu B, Zhao D (2014) Two-dimensional metal-organic framework with wide channels and responsive turn-on fluorescence for the chemical sensing of volatile organic compounds. J Am Chem Soc 136(20):7241–7244. doi:10.1021/Ja502643p
Yaghi OM, O’Keeffe M, Ockwig NW, Chae HK, Eddaoudi M, Kim J (2003) Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 423(6941):705–714
Ferey G (2008) Hybrid porous solids: past, present, future. Chem Soc Rev 37(1):191–214
Cui YJ, Yue YF, Qian GD, Chen BL (2012) Luminescent functional metal-organic frameworks. Chem Rev 112(2):1126–1162
Kreno LE, Leong K, Farha OK, Allendorf M, Van Duyne RP, Hupp JT (2012) Metal-organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem Rev 112(2):1105–1125
Allendorf MD, Bauer CA, Bhakta RK, Houk RJT (2009) Luminescent metal-organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 38(5):1330–1352
Wang B, Cancilla JC, Torrecilla JS, Haick H (2014) Artificial sensing intelligence with silicon nanowires for ultraselective detection in the gas phase. Nano Lett 14(2):933–938. doi:10.1021/Nl404335p
Sato K, Takeuchi S (2014) Chemical vapor detection using a reconstituted insect olfactory receptor complex. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(44):11798–11802. doi:10.1002/anie.201404720
Touhara K, Vosshall LB (2009) Sensing odorants and pheromones with chemosensory receptors. Annu Rev Physiol 71:307–332
Hallem EA, Fox AN, Zwiebel LJ, Carlson JR (2004) Olfaction: mosquito receptor for human-sweat odorant. Nature 427(6971):212–213
Wu CS, Chen PH, Yu H, Liu QJ, Zong XL, Cai H, Wang P (2009) A novel biomimetic olfactory-based biosensor for single olfactory sensory neuron monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 24(5):1498–1502
Radhika V, Proikas-Cezanne T, Jayaraman M, Onesime D, Ha JH, Dhanasekaran DN (2007) Chemical sensing of DNT by engineered olfactory yeast strain. Nat Chem Biol 3(6):325–330
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the 1,000 Young Talents program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21422507, 21321003) and Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors whose names are listed in the manuscript certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection featuring Young Investigators in Analytical and Bioanalytical Science with guest editors S. Daunert, A. Baeumner, S. Deo, J. Ruiz Encinar, and L. Zhang.
Xiaohua Sun and Kang Shao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Shao, K. & Wang, T. Detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from exhaled breath as noninvasive methods for cancer diagnosis. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 2759–2780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9200-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9200-6