Abstract
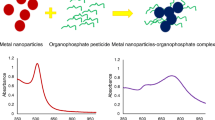
The present study reports a highly simple and rapid method for the detection of a widely used and extremely toxic organophosphorus pesticide, phorate. The detection employs a pesticide-specific aptamer as the recognition element and gold nanoparticles as the optical sensors. The aptamer, owing to its random coil structure, provides stability to the gold nanoparticles upon linking, thereby keeping the nanoparticles well dispersed. However, on the addition of the target pesticide, the aptamer acquires a rigid conformation resulting in the aggregation of the gold nanoparticles. Consequently, the color of the solution changes from red to blue and is easily observable with the naked eye. The proposed method was linear in the concentration range of 0.01 nM to 1.3 μm with the limit of detection as low as 0.01 nM. Moreover, the proposed assay selectively recognized phorate in the presence of other interfering substances and, thus, can be applied to real samples for the rapid and efficient screening of phorate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bala R, Sharma RK, Wangoo N (2015) Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of ethyl parathion using gold nanoprobes. Sens Actuators B 210:425–430
Li X, Zhang S, Yu Z, Yang T (2014) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic analysis of phorate and fenthion pesticide in apple skin using silver nanoparticles. Appl Spectrosc 68:483–487
Shi Y, Li L, Yang M, Jiang X, Zhao Q, Zhan J (2014) A disordered silver nanowires membrane for extraction and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. Analyst 139:2525–2530
Pang S, Labuza TP, He L (2014) Development of a single aptamer-based surface enhanced Raman scattering method for rapid detection of multiple pesticides. Analyst 139:1895–1901
Zhang C, Wang L, Tu Z, Sun X, He Q, Lei Z, Xu C, Liu Y, Zhang X, Yang J, Liu X, Xu Y (2014) Organophosphorus pesticides detection using broad-specific single-stranded DNA based fluorescence polarization aptamer assay. Biosens Bioelectron 55:216–219
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Department of Science & Technology (DST) INSPIRE of India (grant no. IFA12-CH-52) and Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) of India (grant F. No. SB/SO/BB/0040/2013). RB thanks University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bala, R., Sharma, R.K. & Wangoo, N. Development of gold nanoparticles-based aptasensor for the colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticide phorate. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 333–338 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9085-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9085-4