Abstract
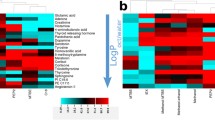
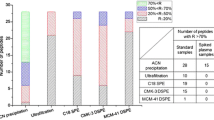
Eight human plasma preparation protocols were evaluated for their suitability for metabolomic studies by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: organic solvent protein precipitation (PPT) with either methanol or acetonitrile in 2:1 and 3:1 (v/v) ratios with plasma; solid-phase extraction (SPE) using C18 or HybridSPE cartridges; and a combination of PPT and SPE C18 cartridges and microextraction by packed sorbent. A study design in which the order of injection of the samples was not randomized is presented. The analyses were conducted in a BEH C18 column (1.7 μm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) using a linear gradient from 100 % water to 100 % methanol, both with 0.1 % formic acid, in 21 min. The most reproducible protocol considering both the univariate and the multivariate analysis results was PPT with acetonitrile in a 2:1 (v/v) ratio with plasma, offering a mean coefficient of variation of the area of all the detected features of 0.15 and one of the best clusterings in the principal component analysis plots. On the other hand, the highest number of extracted features was achieved using methanol in a 2:1 (v/v) ratio with plasma as the PPT solvent, closely followed by the same protocol with acetonitrile in a 2:1 (v/v) ratio with plasma, which offered only 1.2 % fewer repeatable features. In terms of concentration of remaining protein, protocols based on PPT with acetonitrile provided cleaner extracts than protocols based on PPT with methanol. Finally, pairwise comparison showed that the use of PPT- and SPE-based protocols offers a different coverage of the metabolome.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC, Holmes E (1999) ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 29:1181–1189
Goodacre R, Vaidyanathan S, Dunn WB, Harrigan GG, Kell DB (2004) Metabolomics by numbers: acquiring and understanding global metabolite data. Trends Biotechnol 22:245–252
Fiehn O, Kopka J, Dormann P, Altmann T, Trethewey RN, Willmitzer L (2000) Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat Biotechnol 18:1157–1161
Van der Greef J, Stroobant P, Van der Heijden R (2004) The role of analytical sciences in medical systems biology. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:559–565
Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Holmes E (2007) The handbook of metabonomics and metabolomics. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Griffiths WJ (2008) Metabolomics, metabonomics and metabolite profiling. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Lenz EM, Wilson ID (2007) Analytical strategies in metabolomics. J Proteome Res 6:443–458
Pan Z, Raftery D (2007) Comparing and combining NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry in metabolomics. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:525–527
Viswanathan CT, Bansal S, Booth B, DeStefano AJ, Rose MJ, Sailstad J, Shah VP, Skelly JP, Swann PG, Weiner R (2007) Quantitative bioanalytical methods validation and implementation: best practices for chromatographic and ligand binding assays. Pharm Res 24:1962–1973
Gika HG, Theodoridis GA, Wingate JE, Wilson ID (2007) Within-day reproducibility of an LC-MS-based method for metabonomic analysis: application to human urine. J Proteome Res 6(8):3291–3303
Masson P, Alves AC, Ebbels TM, Nicholson JK, Want EJ (2010) Optimization and evaluation of metabolite extraction protocols for untargeted metabolic profiling of liver samples by UPLC-MS. Anal Chem 82(18):7779–7786
Pan L, Qiu Y, Chen T, Lin J, Chi Y, Su M, Zhao A, Jia W (2010) An optimized procedure for metabonomic analysis of rat liver tissue using gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed 52(4):589–596
Jiye A, Trygg J, Gullberg J, Johansson AI, Jonsson P, Antti H, Marklund SL, Moritz T (2005) Extraction and GC/MS analysis of the human blood plasma metabolome. Anal Chem 77:8086–8094
Bruce SJ, Jonsson P, Antti H, Cioarec O, Trygg J, Marklund SL, Moritz T (2008) Evaluation of a protocol for metabolic profiling studies on human blood plasma by combined UPLC-MS: from extraction to data analysis. Anal Biochem 372:237–249
Want EJ, O’Maille G, Smith CA, Brandon TR, Uritboonthai W, Qin C, Trauger SA, Siuzdak G (2006) Solvent-dependent metabolite distribution, clustering, and protein extraction for serum profiling with mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:743–752
Bruce SJ, Tavazzi I, Parisod V, Rezzi S, Kochhar S, Guy PA (2009) Investigation of human blood plasma sample preparation for performing metabolomics using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:3285–3296
Michopoulos F, Lai L, Gika HG, Theodoridis G, Wilson ID (2009) UPLC-MS-based analysis of human plasma for metabolomics using solvent precipitation or solid phase extraction. J Proteome Res 8:2114–2121
Tulipani S, Llorach R, Urpi-Sarda M, Andres-Lacueva C (2013) Comparative analysis of sample preparation methods to handle the complexity of the blood fluid metabolome: when less is more. Anal Chem 85(1):341–348
Marcinowska R, Trygg J, Wolf-Watz H, Mortiz T, Surowiec I (2011) Optimization of a sample preparation method for the metabolomic analysis of clinically relevant bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 87(1):24–31
Madla S, Miura D, Wariishi H (2012) Optimization of extraction method for GC-MS based metabolomics for filamentous fungi. J Microb Biochem Technol 4(1):5–9
Sellick CA, Knight D, Croxford AS, Maqsood AR, Stephens GM, Goodacre R, Dickson AJ (2010) Evaluation of extraction processes for intracellular metabolite profiling of mammalian cells: matching extraction approaches to cell type and metabolite targets. Metabolomics 6(3):427–438
Dettmer K, Nurnberger N, Kaspar H, Gruber MA, Almstetter MF, Oefner PJ (2011) Metabolite extraction from adherently growing mammalian cells for metabolomics studies: optimization of harvesting and extraction protocols. Anal Bioanal Chem 399(3):1127–1139
Neubauer S, Haberhauer-Troyer C, Klavins K, Russmayer H, Steiger MG, Gasser B, Sauer M, Mattanovich D, Hann S, Koellensperger G (2012) U13C cell extract of Pichia pastoris - a powerful tool for evaluation of sample preparation in metabolomics. J Sep Sci 35:3091–3105
Kim S, Lee DY, Wohlgemuth G, Park HS, Fiehn O, Kim H (2013) Evaluation and optimization of metabolome sample preparation methods for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anal Chem 85(4):2169–2176
Wu J, An Y, Yao J, Wang Y, Tang H (2010) An optimised sample preparation method for NMR-based faecal metabonomic analysis. Analyst 135:1023–1030
Jiang H, Zhang Y, Ida M, LaFayette A, Fast DM (2011) Determination of carboplatin in human plasma using HybridSPE-precipitation along with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879(22):2162–2170
Smith CA, Want EJ, O’Maille G, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G (2006) XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal Chem 78:779–787
Tautenhahn R, Böttcher C, Neumann S (2008) Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinforma 9:504–519
Guy PA, Tavazzi I, Bruce SJ, Ramadan Z, Kochhar SJ (2008) Global metabolic profiling analysis on human urine by UPLC-TOF-MS: Issues and method validation in nutritional metabolomics. J Chromatogr B 871:253–260
ICH Expert Working Work (2005) ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology Q2(R1). ICH, Geneva
Polson C, Sarkar P, Incledon B, Raguvaran V, Grant R (2003) Optimization of protein precipitation based upon effectiveness of protein removal and ionization effect in liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 785:263–275
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) (project CTQ2013-46179), the University of Basque Country (UFI 11/23, PPM 12/06), and the Basque Country Government (project IT470-10 and IT789-13) for financial support, and SGIker for technical support (UPV/EHU, MICINN, GV/EJ, ERDF, and ESF). E.R., M.E.B., and O.G. also thank the Basque Country Government and UPV/EHU for their predoctoral and postdoctoral grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rico, E., González, O., Blanco, M.E. et al. Evaluation of human plasma sample preparation protocols for untargeted metabolic profiles analyzed by UHPLC-ESI-TOF-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 7641–7652 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8212-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8212-y