Abstract
Rationale
The treatment of opiate addiction is an unmet medical need. Repeated exposure to opiates disrupts cognitive performance. Opioid substitution therapy, with, e.g., methadone, may further exacerbate the cognitive deficits. Growing evidence suggests that mitragynine, the primary alkaloid from the Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) leaves, may serve as a promising alternative therapy for opiate addiction. However, the knowledge of its health consequences is still limited.
Objectives
We aimed to examine the cognitive effects of mitragynine substitution in morphine-withdrawn rats. Furthermore, we asked whether neuronal addiction markers like the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II alpha (αCaMKII) might mediate the observed effects.
Methods
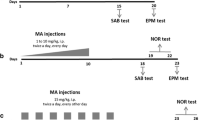
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were given morphine at escalating doses before treatment was discontinued to induce a spontaneous morphine withdrawal. Then, vehicle or mitragynine (5 mg/kg, 15 mg/kg, or 30 mg/kg) substitution was given for 3 days. A vehicle-treated group was used as a control. Withdrawal signs were scored after 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h, while novel object recognition (NOR) and attentional set-shifting (ASST) were tested during the substitution period.
Results
Discontinuation of morphine significantly induced morphine withdrawal signs and cognitive deficit in the ASST. The substitution with mitragynine was able to alleviate the withdrawal signs. Mitragynine did not affect the recognition memory in the NOR but significantly improved the reversal learning deficit in the morphine-withdrawn rats.
Conclusions
These data support the idea that mitragynine could be used as safe medication therapy to treat opiate addiction with beneficial effects on cognitive deficits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins EJ, Boyer EW, McCurdy CR (2011) Mitragyna speciosa, a psychoactive tree from Southeast Asia with opioid activity. Curr Top Med Chem 11(9):1165–1175
Akkerman S, Blokland A, Reneerkens O et al (2012) Object recognition testing: methodological considerations on exploration and discrimination measures. Behav Brain Res 232(2):335–347
Andersen JM, Opdal SH, Müller CP et al (2020) Opioid induced conditioned place preference activates calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and β-actin in mice, but αCaMKII Thr286 phosphorylation is not necessary for its establishment. Behav Brain Res 390:112676
Apryani E, Hidayat MT, Moklas MAA et al (2010) Effects of mitragynine from Mitragyna speciosa Korth leaves on working memory. J Ethnopharmacol 129(3):357–360
Arias F, Arnsten JH, Cunningham CO et al (2016) Neurocognitive, psychiatric, and substance use characteristics in opioid dependent adults. Addict Behav 60:137–143
Assanangkornchai S, Muekthong A, Sam-Angsri N et al (2007) The use of Mitragynina speciosa (“Krathom”), an addictive plant, in Thailand. Subst Use Misuse 42(14):2145–2157
Bachis A, Campbell LA, Jenkins K et al (2017) Morphine withdrawal increases brain derived neurotrophic factor precursor. Neurotox Res 32(3):509–517
Baldacchino A, Balfour DJK, Passetti F et al (2012) Neuropsychological consequences of chronic opioid use: a quantitative review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(9):2056–2068
Bathina S, Das UN (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch Med Sci 11(6):1164–1178
Bicks LK, Koike H, Akbarian S et al (2015) Prefrontal cortex and social cognition in mouse and man. Front Psychol 6:1–15
Birrell JM, Brown VJ (2000) Medial frontal cortex mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in the rat. J Neurosci 20(11):4320–4324
Bondi CO, Rodriguez G, Gould GG et al (2008) Chronic unpredictable stress induces a cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in rats that is prevented by chronic antidepressant drug treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(2):320–331
Bonhomme J, Shim RS, Gooden R et al (2012) Opioid addiction and abuse in primary care practice: a comparison of methadone and buprenorphine as treatment options. J Natl Med Assoc 104(7–8):342–350
Caplehorn JR, Drummer OH (1999) Mortality associated with New South Wales methadone programs in 1994: lives lost and saved. Med J Aust 170(3):104–109
Chen Y, Jiang Y, Yue W et al (2008) Chronic, but not acute morphine treatment, up-regulates alpha-Ca2þ/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II gene expression in rat brain. Neurochem Res 33:2092–2098
Clarke HF, Dalley JW, Crofts HS et al (2004) Cognitive inflexibility after prefrontal serotonin depletion. Science 304(5672):878–880
Clarke HF, Walker SC, Crofts HS et al (2005) Prefrontal serotonin depletion affects reversal learning but not attentional set shifting. J Neurosci 25(2):532–538
Clarke HF, Walker SC, Dalley JW et al (2007) Cognitive inflexibility after prefrontal serotonin depletion is behaviorally and neurochemically specific. Cereb Cortex 17(1):18–27
Dalley JW, Fryer TD, Brichard L et al (2007) Nucleus accumbens d2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. Science 315(5816):1267–1270
Danet M, Lapiz-Bluhm S, Soto-Pina AE et al (2009) Chronic intermittent cold stress and serotonin depletion induce deficits of reversal learning in an attentional set-shifting test in rats. Psychopharmacology 202(1–3):329–341
Danet M, Lapiz-Bluhm S, Morilak DA (2010) A cognitive deficit induced in rats by chronic intermittent cold stress is reversed by chronic antidepressant treatment. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13(8):997–1009
Dematteis M, Auriacombe M, D’Agnone O et al (2017) Recommendations for buprenorphine and methadone therapy in opioid use disorder: a European consensus. Expert Opin Pharmacother 18(18):1987–1999
Easton AC, Lourdusamy A, Loth E et al (2013a) CAMK2A polymorphisms predict spatial working memory performance in humans. Mol Psychiatry 18:850–852
Easton AC, Lucchesi W, Lourdusamy A et al (2013b) αCaMKII autophosphorylation controls the establishment of alcohol drinking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1636–1647
Ersche KD, Roiser JP, Abbott S et al (2011) Response perseveration in stimulant dependence is associated with striatal dysfunction and can be ameliorated by a D2/3 receptor agonist. Biol Psychiatry 70(8):754–762
Fan GH, Wang LZ, Qiu HC et al (1999) Inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat hippocampus attenuates morphine tolerance and dependence. Mol Pharmacol 56:39–45
Farahmandfar M, Kadivar M, Naghdi N (2015) Possible interaction of hippocampal nitric oxide and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II on reversal of spatial memory impairment induced by morphine. Eur J Pharmacol 751:99–111
Fox MT, Barense MD, Baxter MG (2003) Perceptual attentional set-shifting is impaired in rats with neurotoxic lesions of posterior parietal cortex. J Neurosci 23(2):676–681
Giese KP, Mizuno K (2013) The roles of protein kinases in learning and memory. Learn Mem 20:540–552
Goodman J, Packard MG (2016) Memory systems and the addicted brain. Front Psychiatry 7:24
Gould TJ (2010) Addiction and cognition. Addict Sci Clin Pract 5(2):4–14
Harun N, Johari IS, Mansor SM et al (2020) Assessing physiological dependence and withdrawal potential mitragynine using schedule-controlled behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology 237:855–867
Hassan Z, Muzaimi M, Navaratnam V et al (2013) From Kratom to mitragynine and its derivatives: physiological and behavioural effects related to use, abuse, and addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37(2):138–151
Hassan Z, Bosch OG, Singh D et al (2017) Novel psychoactive substances – an update on use, abuse, behavioural effects and mechanisms of action. Front Psychiatry 8:152
Hassan Z, Suhaimi FW, Ramanathan S et al (2019) Mitragynine (Kratom) impairs spatial learning and hippocampal synaptic transmission in rats. J Psychopharmacol 33(7):908–918
Hassan R, See CP, Sreenivasan S et al (2020) Mitragynine attenuates morphine withdrawal effects in rats—a comparison with methadone and buprenorphine. Front Psychiatry 11:411
Hatcher PD, Brown VJ, Tait DS et al (2005) 5-HT 6 receptor antagonists improve performance in an attentional set shifting task in rats. Psychopharmacology 181(2):253–259
Hazim AI, Mustapha M, Mansor SM (2011) The effects on motor behaviour and short-term memory tasks in mice following an acute administration of Mitragyna speciosa alkaloid extract and mitragynine. J Med Plants Res 5(24):5810–5817
Heisler JM, Morales J, Donegan JJ et al (2015) The attentional set shifting task: a measure of cognitive flexibility in mice. J Vis Exp 96:e51944
Hemby SE, McIntosh S, Leon F et al (2019) Abuse liability and therapeutic potential of the Mitragyna speciosa (Kratom) alkaloids mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine. Addict Biol 24(5):874–885
Henningfield JE, Fant RV, Wang DW (2018) The abuse potential of Kratom according the 8 factors of the controlled substances act: implications for regulation and research. Psychopharmacology 235(2):573–589
Hiranita T, Sharma A, Oyola FL et al (2020) Potential contribution of 7-hydroxymitragynine, a metabolite of the primary Kratom (Mitragyna Speciosa) alkaloid mitragynine, to the μ-opioid activity of mitragynine in rats. FASEB J 34(S1):1
Ilmie MU, Jaafar H, Mansor SM et al (2015) Subchronic toxicity study of standardized methanolic extract of Mitragyna speciosa Korth in Sprague-Dawley rats. Front Neurosci 9:189
Ismail NIW, Jayabalan N, Mansor SM et al (2017) Chronic mitragynine (Kratom) enhances punishment resistance in natural reward seeking and impairs place learning in mice. Addict Biol 22(4):967–976
Izquierdo A, Jentsch JD (2012) Reversal learning as a measure of impulsive and compulsive behavior in addictions. Psychopharmacology 219(2):607–620
Jamil MF, Subki MF, Lan TM et al (2013) The effect of mitragynine on cAMP formation and mRNA expression of mu-opioid receptors mediated by chronic morphine treatment in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cell. J Ethnopharmacol 148:135–143
Kruegel AC, Gassaway MM, Kapoor A et al (2016) Synthetic and receptor signaling explorations of the mitragyna alkaloids: mitragynine as an atypical molecular framework for opioid receptor modulators. J Am Chem Soc 138:6754–6764
Kutlu MG, Gould TJ (2016) Effects of drugs of abuse on hippocampal plasticity and hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: contributions to development and maintenance of addiction. Learn Mem 23(10):515–533
Lapiz-Bluhm MDS, Soto-Piña AE, Hensler JG et al (2009) Chronic intermittent cold stress and serotonin depletion induce deficits of reversal learning in an attentional set-shifting test in rats. Psychopharmacology 202(1–3):329–341
Liu D, Wang Z, Gao Z et al (2014) Effects of curcumin on learning and memory deficits, BDNF, and ERK protein expression in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress. Behav Brain Res 271:116–121
Lou L, Zhou T, Wang P et al (1999) Modulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity by acute and chronic morphine administration in rat hippocampus: differential regulation of alpha and beta isoforms. Mol Pharmacol 55:557–563
Mazhari S, Keshvari Z, Sabahi A, Mottaghian S (2015) Assessment of cognitive functions in methadone maintenance patients. Addict Health 7(3–4):109–116
McAlonan K, Brown VJ (2003) Orbital prefrontal cortex mediates reversal learning and not attentional set shifting in the rat. Behav Brain Res 146(1–2):97–103
Mesripour A, Hajhashemi V, Rabbani M (2007) The effects of spironolactone on morphine withdrawal induced memory loss by the object recognition task method in mice. Res Pharm Sci 2(2):77–84
Müller CP, Cunningham KA (eds) (2020) Handbook of The Behavioural Neurobiology of Serotonin, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Müller CP, Homberg J (2015) The role of serotonin in drug use and addiction. Behav Brain Res 277C:146–192
Müller CP, Quednow BB, Lourdusamy A et al (2016) CaM kinases – from memories to addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 37(2):153–166
Popova NK, Ilchibaeva TV, Antonov EV et al (2020) On the interaction between BDNF and serotonin systems: the effects of long-term ethanol consumption in mice. Alcohol 87:1–15
Rabbani M, Hajhashemi V, Mesripour A (2009) Increase in brain corticosterone concentration and recognition memory impairment following morphine withdrawal in mice. Stress 12(5):451–456
Rahman S, Khan RA, Kumar A (2002) Experimental study of the morphine de-addiction properties of Delphinium denudatum Wall. BMC Complement Altern Med 2(1):6
Rhein C, Mühle C, Lenz B et al (2020) Association of a CAMK2A genetic variant with logical memory performance and hippocampal volume in the elderly. Brain Res Bull 161:13–20
Senik MH, Mansor SM, Tharakan JKJ et al (2012) Effect of acute administration of Mitragyna speciosa Korth. standardized methanol extract in animal model of learning and memory. J Med Plants Res 6(6):1007–1014
Singh D, Narayanan S, Müller CP et al (2019a) Motives for using Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) among regular users in Malaysia. J Ethnopharmacol 233:34–40
Singh D, Narayanan S, Müller CP et al (2019) Long-term cognitive effects of Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa Korth.) use. J Psychoactive Drugs 51(1):19–27
Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC (2007) Influence of gender on working and spatial memory in the novel object recognition task in the rat. Behav Brain Res 177:117–125
Tait DS, Brown VJ (2008) Lesions of the basal forebrain impair reversal learning but not shifting of attentional set in rats. Behav Brain Res 187(1):100–108
Tait DS, Alexander Chase E, Brown VJ (2014) Attentional set-shifting in rodents: a review of behavioural methods and pharmacological results. Curr Pharm Des 20(31):5046–5059
Tanguay P (2011) Kratom in Thailand: decriminalization and community control? Legislative Reform of Drug Policies 13:1–16
Utar Z, Majid MIA, Adenan MI et al (2011) Mitragynine inhibits the COX-2 mRNA expression and prostaglandin E2 production induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264. 7 macrophage cells. J Ethnopharmacol 136(1):75–82
Varshneya NB, Walentiny DM, Moisa LT et al (2019) Opioid-like antinociceptive and locomotor effects of emerging fentanyl-related substances. Neuropharmacology 151:171–179
Verdejo A, Toribio I, Orozco C et al (2005) Neuropsychological functioning in methadone maintenance patients versus abstinent heroin abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend 78(3):283–288
Vicknasingam B, Narayanan S, Beng GT et al (2010) The informal use of Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) for opioid withdrawal in the northern states of peninsular Malaysia and implications for drug substitution therapy. Int J Drug Policy 21(4):283–288
Warner ML, Kaufman NC, Grundmann O (2016) The pharmacology and toxicology of Kratom: from traditional herb to drug of abuse. Int J Legal Med 130(1):127–138
Yue K, Kopajtic TA, Katz JL (2018) Abuse liability of mitragynine assessed with a self-administration procedure in rats. Psychopharmacology 235:2823–2829
Yusoff NHM, Suhaimi FW, Vadivelu RK et al (2016) Abuse potential and adverse cognitive effects of mitragynine (Kratom). Addict Biol 21(1):98–110
Yusoff NHM, Mansor SM, Müller CP et al (2017) Opioid receptors mediate the acquisition, but not the expression of mitragynine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Behav Brain Res 332:1–6
Zald DH, Cowan RL, Riccardi P et al (2008) Midbrain dopamine receptor availability is inversely associated with novelty-seeking traits in humans. J Neurosci 28(53):14372–14378
Zelazo PD (2015) Executive function: reflection, iterative reprocessing, complexity, and the developing brain. Dev Rev 38:55–68
Funding
The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Short-term Grant from Universiti Sains Malaysia (304/CDADAH/6315183) and Higher Education Centre of Excellence (HICoE) special funding (311/CDADAH/4401009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YCY, ZH, and FWS designed, performed research, and analyzed data. YCY, ZH, CPM, and FWS wrote the article. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, C., Hassan, Z., Müller, C. et al. Mitragynine improves cognitive performance in morphine-withdrawn rats. Psychopharmacology 239, 313–325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05996-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05996-4