Abstract
Rationale
Kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonists are antinociceptive but have side effects that limit their therapeutic utility. New KOR agonists have been developed that are fully efficacious at the KOR but may produce fewer or reduced side effects that are typical of KOR agonists.
Objectives
We determined behavioral profiles for typical and atypical KOR agonists purported to differ in intracellular-signaling profiles as well as a mu-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist, oxycodone, using a behavioral scoring system based on Novak et al. (Am J Primatol 28:124-138, 1992, Am J Primatol 46:213-227, 1998) and modified to quantify drug-induced effects (e.g., Duke et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 366:145-157, 2018).
Methods
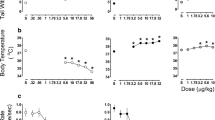
Six adult male rhesus monkeys were administered a range of doses of the typical KOR agonists, U50-488H (0.0032–0.1 mg/kg) and salvinorin A (0.00032–0.01 mg/kg); the atypical KOR agonists, nalfurafine (0.0001–0.001 mg/kg) and triazole 1.1 (0.01–0.32 mg/kg); the MOR agonist, oxycodone (0.0032–0.32 mg/kg); and as controls, cocaine (0.032–0.32 mg/kg) and ketamine (0.32–10 mg/kg). For time-course determinations, the largest dose of each KOR agonist or MOR agonist was administered across timepoints (10–320 min). In mixture conditions, oxycodone (0.1 mg/kg) was followed by KOR-agonist administration.
Results
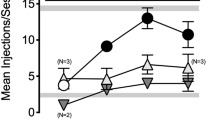
Typical KOR agonists produced sedative-like and motor-impairing effects. Nalfurafine was similar to typical KOR agonists on most outcomes, and triazole 1.1 produced no effects on its own except for reducing scratch during time-course determinations. In the mixture, all KOR agonists reduced oxycodone-induced scratching, U50-488H and nalfurafine reduced species-typical activity, and U50-488H increased rest/sleep posture.
Conclusions
Atypical “biased” KOR agonists produce side-effect profiles that are relatively benign (triazole 1.1) or reduced (nalfurafine) compared to typical KOR agonists.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich JV, McLaughlin JP (2009) Peptide kappa opioid receptor ligands: potential for drug development. AAPS J 11:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-009-9105-4
American Society of Anesthesiologists (2002) An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists task force on sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists practice: guidelines for sedation and analgesia by non-anesthesiologists. Anesthesiol 96:1004–1017
Baker LE, Panos JJ, Killinger BA, Peet MM, Bell LM, Haliw LA, Walker SL (2009) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of salvinorin A and its derivatives to U69,593 and U50,488 in rats. Psychopharmacol 203:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1458-3
Beck TC, Hapstack MA, Beck KR, Dix TA (2019) Therapeutic potential of kappa opioid agonists. Pharmaceuticals 12:95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020095
Becker JB, Chartoff E (2019) Sex differences in neural mechanisms mediating reward and addiction. Neuropsychopharmacol 44:166–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0125-6
Brust TF, Morgenweck J, Kim SA, Rose JH, Locke JL, Schmid CL, Zhou L, Stahl EL, Cameron MD, Scarry SM, Aube J, Jones SR, Martin TJ, Bohn LM (2016) Biased agonists of the kappa opioid receptor suppress pain and itch without causing sedation or dysphoria. Sci Signal 9:ra117. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aai8441
Butelman ER, Mandau M, Tidgewell K, Prisinzano TE, Yuferov V, Kreek MJ (2007) Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in nonhuman primates with high kappa-receptor homology to humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.112417
Butelman ER, Prisinzano TE, Deng H, Rus S, Kreek MJ (2009) Unconditioned behavioral effects of the powerful k-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: fast onset and entry into cerebrospinal fluid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:588–597. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.145342
Butelman ER, Rus S, Prisinzano TE, Kreek MJ (2010) The discriminative effects of the kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: dissociation from classic hallucinogen effects. Psychopharmacol 210:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1771-5
Chartoff EH, Mavrikaki M (2015) Sex differences in kappa opioid receptor function and their potential impact on addiction. Front Neurosci 9:466. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00466
Darcq E, Kieffer BL (2018) Opioid receptors: drivers to addiction? Nat Rev Neurosci 19:499–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0028-x
Dogra S, Yadav PN (2015) Biased agonism at kappa opioid receptors: implication in pain and mood disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 763:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.07.018
Duke AN, Meng Z, Platt DM, Atack JR, Dawson GR, Reynolds DS, Tiruveedhula V, Li G, Stephen MR, Sieghart W, Cook JM, Rowlett JK (2018) Evidence that sedative effects of benzodiazepines involve unexpected GABAA receptor subtypes: quantitative observation studies in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 366:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.118.249250
Dunn AD, Reed B, Erazo J, Ben-Ezra A, Kreek MJ (2019) Signaling properties of structurally diverse kappa opioid receptor ligands: toward in vitro models of in vivo responses. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:3590–3600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00195
Dykstra LA, Gmerek DE, Winger G, Woods JH (1987) Kappa opioids in rhesus monkeys. I. Diuresis, sedation, analgesia and discriminative stimulus effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:413–420
Endoh T, Matsuura H, Tajima A, Izumimoto N, Tajima C, Suzuki T et al (1999) Potent antinociceptive effects of TRK-820, a novel k-opioid receptor agonist. Life Sci 65:1685–1694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(99)00417-8
Endoh T, Tajima A, Izumimoto N, Suzuki T, Saitoh A, Suzuki T et al (2001) TRK-820, a selective k-opioid agonist, produces potent antinociception in cynomolgus monkeys. Jpn J Pharmacol 85:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.85.282
Hasebe K, Kawai K, Suzuki T, Kawamura K, Tanaka T, Narita M, Nagase H, Suzuki T (2004) Possible pharmacotherapy of the opioid kappa receptor agonist for drug dependence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:404–413. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1316.050
Huskinson SL, Myerson J, Green L, Rowlett JK, Woolverton WL, Freeman KB (2016) Shallow discounting of delayed cocaine by male rhesus monkeys when immediate food is the choice alternative. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 24:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1037/pha0000098
Inan S, Huerta AT, Jensen LE, Dun NJ, Cowan A (2019) Nalbuphine, a kappa opioid receptor agonist and mu opioid receptor antagonist attenuates pruritus, decreases IL-31, and increases IL-10 in mice with contact dermatitis. Eur J Pharmacol 864:172702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172702
Inui S (2015) Nalfurafine hydrochloride to treat pruritus: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 8:249–255. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S55942
Kamimura K, Yokoo T, Kamimura H, Sakamaki A, Abe S, Tsuchiya A, Takamura M, Kawai H, Yamagiwa S, Terai S (2017) Long-term efficacy and safety of nalfurafine hydrochloride on pruritus in chronic liver disease patients: patient-reported outcome based analyses. PLoS One 12:e0178991. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178991
Kaski SW, White AN, Gross JD, Trexler KR, Wix K, Harland AA, Prisinzano TE, Aube J, Kinsey SG, Kenakin T, Siderovski DP, Setola V (2019) Preclinical testing of nalfurafine as an opioid-sparing adjuvant that potentiates analgesia by the mu opioid receptor-targeting agonist morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 371:487–499. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.118.255661
Kivell B, Prisinzano TE (2010) Kappa opioids and the modulation of pain. Psychopharmacol 210:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1819-6
Ko MC, Husbands SM (2009) Effects of atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists on Intrathecal morphine-induced itch and analgesia in primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.143925
Kreek MJ, Schluger J, Borg L, Gunduz M, Ho A (1999) Dynorphin A1-13 causes elevation of serum levels of prolactin through an opioid receptor mechanism in humans: gender differences and implications for modulation of dopaminergic tone in the treatment of addictions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:260–269
Lazenka ML, Moerke MJ, Townsend EA, Freeman KB, Carroll FI, Negus SS (2018) Dissociable effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist nalfurafine on pain/itch-stimulated and pain/itch-depressed behaviors in male rats. Psychopharmacol 235:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4758-7
Minervini V, Lu HY, Padarti J, Osteicoechea DC, France CP (2018) Interactions between kappa and mu opioid receptor agonists: effects of the ratio of drugs in mixtures. Psychopharmacol 235:2245–2256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4920-x
Mores KL, Cummins BR, Cassell RJ, van Rijn RM (2019) A review of the therapeutic potential of recently developed G protein-biased kappa agonists. Front Pharmacol 10:407. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00407
Negus SS, Zuzga DS, Mello NK (2002) Sex differences in opioid antinociception in rhesus monkeys: antagonism of fentanyl and U50,488 by quadazocine. J Pain 3:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1054/jpai.2002.124734
Negus SS, Schrode K, Stevenson GW (2008) Mu/kappa opioid interactions in rhesus monkeys: implications for analgesia and abuse liability. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16:386–399. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013088
Novak MA, O’Neill P, Suomi SJ (1992) Adjustments and adaptations to indoor and outdoor environments: continuity and change in young adult rhesus monkeys. Am J Primatol 28:124–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.1350280205
Novak MA, Kinsey JH, Jorgensen MJ, Hazen TJ (1998) Effects of puzzle feeders on pathological behavior in individually housed rhesus monkeys. Am J Primatol 46:213–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2345(1998)46:3<213::AID-AJP3>3.0.CO;2-L
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3016896
Phan NQ, Lotts T, Antal A, Bernhard JD, Stander S (2012) Systemic kappa opioid receptor agonists in the treatment of chronic pruritus: a literature review. Acta Derm Venereol 92:555–560. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-1353
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD, Cook J, Ma C (2002) Selective antagonism of the ataxic effects of zolpidem and triazolam by the GABAA/alpha1-preferring antagonist beta-CCt in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacol 164:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1189-9
Prisinzano TE, Tidgewell K, Harding WW (2005) Kappa opioids as potential treatments for stimulant dependence. AAPS J 7:E592–E599. https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj070361
Robles CF, McMackin MZ, Campi KL, Doig IE, Takahashi EY, Pride MC, Trainor BC (2014) Effects of kappa opioid receptors on conditioned place aversion and social interaction in males and females. Behav Brain Res 262:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.003
Ruedi-Bettschen D, Rowlett JK, Rallapalli S, Clayton T, Cook JM, Platt DM (2013) Modulation of alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors alters alcohol drinking by rhesus monkeys. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:624–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12018
Russell SE, Rachlin AB, Smith KL, Muschamp J, Berry L, Zhao Z, Chartoff EH (2014) Sex differences in sensitivity to the depressive-like effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist U-50488 in rats. Biol Psychiatry 76:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.07.042
Schattauer SS, Kuhar JR, Song A, Chavkin C (2017) Nalfurafine is a G-protein biased agonist having significantly greater bias at the human than rodent form of the kappa opioid receptor. Cell Signal 32:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.01.016
Townsend EA, Naylor JE, Negus SS, Edwards SR, Qureshi HN, McLendon HW, McCurdy CR, Kapanda CN, do Carmo JM, da Silva FS, Hall JE, Sufka KJ, Freeman KB (2017) Effects of nalfurafine on the reinforcing, thermal antinociceptive, and respiratory-depressant effects of oxycodone: modeling an abuse-deterrent opioid analgesic in rats. Psychopharmacol 234:2597–2605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4652-3
Weerts EM, Ator NA, Grech DM, Griffiths RR (1998) Zolpidem physical dependence assessed across increasing doses under a one-daily dosing regimen in baboons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:41–53
Wootten D, Christopoulus A, Marti-Solano M, Babu MM, Sexton PM (2018) Mechanisms of signalling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:638–653. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0049-3
Zamarripa CA, Naylor JE, Huskinson SL, Townsend EA, Prisinzano TE, Freeman KB (2020) Kappa opioid agonists reduce oxycodone selfadministration in male rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05473-4
Zhou L, Lovell KM, Frankowski KJ, Slauson SR, Phillips AM, Streicher JM, Stahl E, Schmid CL, Hodder P, Madoux F, Cameron MD, Prisinzano TE, Aube J, Bohn LM (2013) Development of functionally selective, small molecule agonists at kappa opioid receptors. J Biol Chem 288:36703–36716. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.504381
Funding
This research was supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse or National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism grants DA039167 to K.B.F., DA018151 to T.E.P., AA016179 to D.M.P., and DA045011 to S.L.H. The authors would like to thank Josh Woods, Kandace Farmer, Jessica Howard, Jemma Cook, Lais Berro, Yvonne Zuchowski, Tanya Pareek, and John Overton for their technical assistance. Morgan Brasfield is now at William Carey University in Hattiesburg, MS 39401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures were approved by the University of Mississippi Medical Center’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were conducted in accordance with the National Research Council’s Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th edition, 2011).
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huskinson, S.L., Platt, D.M., Brasfield, M. et al. Quantification of observable behaviors induced by typical and atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists in male rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 237, 2075–2087 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05519-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05519-7