Abstract
Rationale
The widely available hallucinogen salvinorin A is a unique example of a plant-derived compound selective for κ-opioid receptors and may produce effects distinct from those of other compounds with classic hallucinogenic or dissociative properties which are also abused in humans.
Objectives
The objective of this study is to characterize the salvinorin A discriminative cue in nonhuman primates with high κ-receptor genetic homology to humans.
Methods
Adult rhesus monkeys (n = 3) were trained to discriminate salvinorin A (0.015 mg/kg, s.c.) from vehicle, in a food-reinforced operant discrimination assay. Parallel studies, using unconditioned behavioral endpoints (facial relaxation and ptosis) also evaluated the κ-opioid receptor mediation of salvinorin A in vivo function.
Results
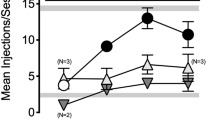
Monkeys trained to discriminate salvinorin A generalized structurally diverse, centrally penetrating κ-agonists (bremazocine, U69,593, and U50,488). By contrast, μ- and δ-opioid agonists (fentanyl and SNC80, respectively) were not generalized, nor were the serotonergic 5HT2 hallucinogen psilocybin or the dissociative N-methyl-D-aspartic acid antagonist, ketamine. The discriminative effects of salvinorin A were blocked by the opioid antagonist quadazocine (0.32 mg/kg), but not by the 5HT2 antagonist ketanserin (0.1 mg/kg). Consistent with these findings, salvinorin and κ-agonists (e.g., U69,593) produce effects in the unconditioned endpoints (e.g., ptosis), whereas psilocybin was inactive.
Conclusions
These findings support the conclusion that the interoceptive/discriminative cue produced by salvinorin A is mediated by agonism at κ-receptors and is mechanistically distinct from that produced by a classic serotonergic hallucinogen.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PT:
-
Pretreatment
References
Baker LE, Panos JJ, Killinger BA, Peet MM, Bell LM, Haliw LA, Walker SL (2009) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of salvinorin A and its derivatives to U69, 593 and U50, 488 in rats. Psychopharmacology 203:203–211
Brandt MR, Negus SS, Mello NK, Furness MS, Zhang X, Rice KC (1999) Discriminative stimulus effects of the nonpeptidic delta-opioid agonist SNC80 in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:1157–1164
Butelman ER, Harris TJ, Kreek MJ (1999) Effects of E-2078, a stable dynorphin A(1-8) analog, on sedation and serum prolactin levels in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147:73–80
Butelman ER, Harris TJ, Kreek MJ (2004) The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces kappa-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 172:220–224
Butelman ER, Mandau M, Tidgewell K, Prisinzano TE, Yuferov V, Kreek MJ (2007) Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in non-human primates with high kappa-receptor homology to humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:300–306
Butelman ER, Prisinzano TE, Deng H, Rus S, Kreek MJ (2008) Unconditioned behavioral effects of the powerful kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: fast onset and entry into cerebrospinal fluid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:588–597, PMC2682281
Carey GJ, Bergman J (2001) Enadoline discrimination in squirrel monkeys: effects of opioid agonists and antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:215–223
Castner SA, Goldman-Rakic PS (1999) Long-lasting psychotomimetic consequences of repeated low-dose amphetamine exposure in rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:10–28
Castner SA, Goldman-Rakic PS (2003) Amphetamine sensitization of hallucinatory-like behaviors is dependent on prefrontal cortex in non-human primates. Biol Psychiatry 54:105–110
Chavkin C, Sud S, Jin W, Stewart J, Zjawiony JK, Siebert DJ, Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (2004) Salvinorin A, an active component of the halucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum, is a highly efficacious kappa opioid receptor agonist: Structural and functional considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:1197–1203
Chernik DA, Gillings D, Laine H, Hendler J, Silver JM, Davidson AB, Schwam EM, Siegel JL (1990) Validity and reliability of the Observer’s Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale: study with intravenous midazolam. J Clin Psychopharmacol 10:244–251
Condy C, Wattiez N, Rivaud-Pechoux S, Gaymard B (2005) Ketamine-induced distractability: an oculomotor study in monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 57:366–372
Davis WM, Bedford JA, Guinn MM, Hatoum HT, Waters IW, Wilson MC, Braude MC (1978) Acute toxicity and gross behavioral effects of amphetamine, four methoxyamphetamines, and mescaline in rodents, dogs and monkeys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 45:49–62
Dykstra LA, Gmerek DE, Winger G, Woods JH (1987) Kappa opioids in rhesus monkeys. I. Diuresis, sedation, analgesia and discriminative stimulus effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:413–420
Fantegrossi WE, Woods JH, Winger G (2004) Transient reinforcing effects of phenylisopropylamine and indolealkylamine hallucinogens in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 15:149–158
France CP, Morse WH (1989) Pharmacological characterization of supersensitivity to naltrexone in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:937–943
France CP, Medzihradsky F, Woods JH (1994) Comparison of kappa opioids in rhesus monkeys: behavioral effects and receptor binding affinities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:47–58
Gerak LR, France CP (1996) Discriminative stimulus effects of nalbuphine in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:523–531
Gonzales D, Riba J, Bouso JC, Gomez-Jarabo G, Barbanoj MJ (2006) Pattern of use and subjective effects of Salvia divinorum among recreational users. Drug Alcohol Depend 85:157–162
Griffin OH, Miller BL, Khey DN (2008) Legally high? Legal considerations of Salvia divinorum. J Psychoactive Drugs 40:183–191
Hooker JM, Xu Y, Schiffer W, Shea C, Carter P, Fowler JS (2008) Pharmacokinetics of the potent hallucinogen, salvinorin A in primates parallels the rapid onset, short duration of effects in humans. Neuroimage 41:1044–1050
Hooker JM, Munro TA, Beguin C, Alexoff D, Shea C, Xu Y, Cohen BM (2009) Salvinorin A and derivatives: protection from metabolism does not prolong short-term whole body residence. Neuropharmacology 57:386–391
Hoover V, Marlowe DB, Patapis NS, Festinger DS, Forman RF (2007) Internet access to Salvia divinorum: implications for policy, prevention and treatment. J Subst Abuse Treat 35:22–27
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2009) Smoking continues gradual decline among U.S. teens, smokeless tobacco threatens a comeback. www.monitoringthefuture.org. Press Release, 14 Dec 2009
Khey DN, Miller BL, Griffin OH (2008) Salvia divinorum use among a college student sample. J Drug Educ 38:297–306
Ko MC, Butelman ER, Traynor JR, Woods JH (1998) Differentiation of kappa opioid agonist-induced antinociception by naltrexone apparent pA2 analysis in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:518–526
Koek W, Kleven MS, Colpaert FC (1995) Effects of the NMDA antagonist, dizocilpine, in various drug discriminations: characterization of intermediate levels of drug lever selection. Behav Pharmacol 6:590–600
Kumar V, Guo D, Cassel JA, Daubert JD, DeHaven RN, DeHaven-Hudkins DL, Gauntner EK, Gottshall SL, Greiner SL, Koblish M, Little PJ, Mansson E, Maycock AL (2005) Synthesis and evaluation of novel peripherally restricted kappa-opioid receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:1091–1095
Lange JE, Reed MB, Ketchie Croff JM, Clapp JD (2008) College student use of Salvia divinorum. Drug Alcohol Depend 94:263–266
Li JX, Rice KC, France CP (2008) Discriminative stimulus effects of 1-(2, 5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOM) in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:827–833
Li JX, Rice KC, France CP (2009) Discriminative stimulus effects of 1-(2, 5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2aminopropane (DOM) in rhesus monkeys: antagonism and apparent pA2 analyses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:976–981
Miner JR, Heegard W, Plummer D (2002) End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring during procedural sedation. Acad Emerg Med 9:275–280
Negus SS, Burke TF, Medzihradsky F, Woods JH (1993) Effects of opioid agonists selective for mu, kappa and delta opioid receptors on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys: antagonism by quadazocine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:896–903
Paglia-Boak A, Mann RE, Adlaf EM, Rehm J (2009) Drug use among Ontario students, 1977–2009: Highlights from the 2009 OSDUHS. Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Rose JE, Behm FM, Westman EC, Coleman RE (1999) Arterial nicotine kinetics during cigarette smoking and intravenous nicotine administration. Drug Alcohol Depend 56:99–107
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occuring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11934–11939
Schmidt MD, Schmidt MS, Butelman ER, Harding WW, Tidgewell K, Murry DJ, Kreek MJ, Prisinzano TE (2005) Pharmacokinetics of the plant-derived hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates. Synapse 58:208–210, PMID: 16138318
Shaw JS, Carroll JA, Alcock P, Main BG (1989) ICI204448: a k-opioid agonist with limited access to the CNS. Br J Pharmacol 96:986–992
Siebert DJ (1994) Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings. J Ethnopharmacol 43:53–56
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2008) The NSDUH report: use of specific hallucinogens: 2006. Available online: www.oas.samsha.gov/2k8/hallucinogens.pdf
Tanda G, Munzar P, Goldberg SR (2000) Self-administration behavior is maintained by the psychoactive ingredient of marijuana in squirrel monkeys. Nat Neurosci 3:1073–1074
Ur E, Wright DM, Bouloux PM, Grossman A (1997) The effects of spiradoline (U-62066E), a kappa-opioid receptor agonist, on neuroendocrine function in man. Br J Pharmacol 120:781–784
Wang Y, Tang K, Inan S, Siebert D, Holzgrabe U, Lee DYW, Huang P, Li JG, Cowan A, Liu-Chen LY (2004) Comparison of pharmacological activities of three distinct k-ligands (salvinorin A, TRK-820 and 3FLB) on kappa opioid receptors in vitro and their antipruritic and antinociceptive activities in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:220–230
Williams KL, Pakarinen ED, Woods JH (1999) Quadazocine decreases responding reinforced by ethanol, sucrose, and phencyclidine fluid deliveries in rhesus monkeys: comparison to naltrexone's effects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 144:316–322
Willmore-Fordham CB, Krall DM, McCurdy CR, Kinder DH (2007) The hallucinogen derived from Salvia divinorum, salvinorin A, has kappa-opioid agonist discriminative stimulus effects in rats. Neuropharmacology 53:481–486
Acknowledgements
These studies were funded by NIH-NIDA grants DA017369 (ERB), DA018151 (TEP), and DA05130 (MJK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butelman, E.R., Rus, S., Prisinzano, T.E. et al. The discriminative effects of the κ-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates: dissociation from classic hallucinogen effects. Psychopharmacology 210, 253–262 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1771-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1771-5