Abstract
Rationale and objectives
COR659 [methyl2-(4-chlorophenylcarboxamido)-4-ethyl-5-methylthiophene-3-carboxylate] is a new, positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the GABAB receptor. This study evaluated whether COR659 shared with previously tested GABAB PAMs the capacity to reduce alcohol self-administration in rats.
Results
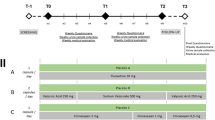
Treatment with non-sedative doses of COR659 (2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg; i.p.) suppressed lever-responding for alcohol (15% v/v) in Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) rats under the fixed ratio (FR) 4 (FR4) and progressive ratio (PR) schedules of reinforcement; COR659 was more potent and effective than the reference GABAB PAM, GS39783. Treatment with COR659, but not GS39783, suppressed (a) lever-responding for a sucrose solution (1–3% w/v) in sP rats under the FR4 and PR schedules, (b) lever-responding for a chocolate solution [5% (w/v) Nesquik®] in Wistar rats under the FR10 and PR schedules, and (c) cue-induced reinstatement of chocolate seeking in Wistar rats. Treatment with COR659 was completely ineffective on lever-responding (FR10) for regular food pellets in food-deprived Wistar rats. Pretreatment with the GABAB receptor antagonist, SCH50911, partially blocked COR659-induced reduction of alcohol self-administration, being ineffective on reduction of chocolate self-administration. Pretreatment with the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, AM4113, fully blocked COR659-induced reduction of chocolate self-administration, being ineffective on reduction of alcohol self-administration.
Conclusions
COR659 might exert its behavioral effects via a composite mechanism: (i) positive allosteric modulation of the GABAB receptor, responsible for a large proportion of reduction of alcohol self-administration; (ii) an action at other receptor system(s), including the cannabinoid CB1 receptor, through which COR659 affects seeking and consumption of highly palatable foods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agabio R, Leite-Morris KA, Addolorato G, Colombo G (2016) Targeting the GABAB receptor for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 287–307
Augier E, Dulman RS, Damadzic R, Pilling A, Hamilton JP, Heilig M (2017) The GABAB positive allosteric modulator ADX71441 attenuates alcohol self-administration and relapse to alcohol seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology, in press
Avena NM, Bocarsly ME, Murray S, Gold MS (2014) Effects of baclofen and naltrexone, alone and in combination, on the consumption of palatable food in male rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 22:460–467
Bains RS, Ebenezer IS (2013) Effects of the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen administered orally on normal food intake and intraperitoneally on fat intake in non-deprived rats. Eur J Pharmacol 698:267–271
Berner LA, Bocarsly ME, Hoebel BG, Avena NM (2009) Baclofen suppresses binge eating of pure fat but not a sugar-rich or sweet-fat diet. Behav Pharmacol 20:631–634
Bojanowska E, Ciosek J (2016) Can we selectively reduce appetite for energy-dense foods? An overview of pharmacological strategies for modification of food preference behavior. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:118–142
Bossert JM, Marchant NJ, Calu DJ, Shaham Y (2013) The reinstatement model of drug relapse: recent neurobiological findings, emerging research topics, and translational research. Psychopharmacology 229:453–476
Calu DJ, Chen YW, Kawa AB, Nair SG, Shaham Y (2014) The use of the reinstatement model to study relapse to palatable food seeking during dieting. Neuropharmacology 76:395–406
Castelli MP, Casu A, Casti P, Lobina C, Carai MAM, Colombo G, Solinas M, Giunta D, Mugnaini C, Pasquini S, Tafi A, Brogi S, Gessa GL, Corelli F (2012) Characterization of methyl 2-(1-adamantanecarboxamido)-4-ethyl-5-methylthiophene-3-carboxylate (COR627) and methyl 2-(cyclohexanecarboxamido)-4-ethyl-5-methylthiophene-3-carboxylate (COR628), two novel positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:529–538
Colombo G, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2005) Endocannabinoid system and alcohol addiction: pharmacological studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:369–380
Colombo G, Lobina C, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2006) Phenotypic characterization of genetically selected Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) and -non preferring (sNP) rats. Addict Biol 11:324–338
Colombo G, Lobina C, Maccioni P, Carai MAM, Lorrai I, Zaru A, Contini A, Mugnaini C, Corelli F, Gessa GL (2015) Anxiety-like behaviors at the end of the nocturnal period in sP rats with a “history” of unpredictable, limited access to alcohol. Alcohol 49:707–712
Corelli F, Mugnaini C (2016) Chemistry of GABAB receptor ligands: focus on agonists and antagonists. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 17–32
Corwin RL, Wojnicki FH (2009) Baclofen, raclopride, and naltrexone differentially affect intake of fat and sucrose under limited access conditions. Behav Pharmacol 20:537–548
Cristino L, Palomba L, Di Marzo V (2014) New horizons on the role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in palatable food intake, obesity and related dysmetabolism. Int J Obes 4(Suppl 1):S26–S30
Cryan JF, Kelly PH, Chaperon F, Gentsch C, Mombereau C, Lingenhoehl K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Spooren WP (2004) Behavioral characterization of the novel GABAB receptor-positive modulator GS39783 (N,N'-dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine): anxiolytic-like activity without side effects associated with baclofen or benzodiazepines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:952–963
De Oliveira LB, Kimura EH, Callera JC, De Luca LA Jr, Colombari DS, Menani JV (2011) Baclofen into the lateral parabrachial nucleus induces hypertonic sodium chloride and sucrose intake in rats. Neuroscience 183:160–170
Ding ZM, Ingraham CM, Rodd ZA, McBride WJ (2015) The reinforcing effects of ethanol within the nucleus accumbens shell involve activation of local GABA and serotonin receptors. J Psychopharmacol 29:725–733
Ebenezer IS (2012) Effects of intraperitoneal administration of the GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator 2,6-di tert-butyl-4-(2-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-propyl)-phenol (CGP7930) on food intake in non-deprived rats. Eur J Pharmacol 690:115–118
Ebenezer IS, Patel SM (2004) Effects of the GABAB receptor agonists baclofen and 3-aminopropylphosphinic acid (3-APA) on food intake in rats. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 26:627–630
Ebenezer IS, Prabhaker M (2007) The effects of intraperitoneal administration of the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen on food intake in CFLP and C57BL/6 mice. Eur J Pharmacol 569:90–93
Echo JA, Lamonte N, Ackerman TF, Bodnar RJ (2002) Alterations in food intake elicited by GABA and opioid agonists and antagonists administered into the ventral tegmental area region of rats. Physiol Behav 76:107–116
Felice D, O’Leary OF, Cryan JF (2016) Targeting the GABAB receptor for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 219–250
Frankowska M, Przegaliński E, Filip M (2016) Targeting the GABAB receptor for the treatment of substance use disorder. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 263–286
Froestl W (2010) Chemistry and pharmacology of GABAB receptor ligands. Adv Pharmacol 58:19–62
Henderson-Redmond AN, Guindon J, Morgan DJ (2016) Roles for the endocannabinoid system in ethanol-motivated behavior. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 65:330–339
Higgs S, Barber DJ (2004) Effects of baclofen on feeding behaviour examined in the runway. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:405–408
Hwa LS, Kalinichev M, Haddouk H, Poli S, Miczek KA (2014) Reduction of excessive alcohol drinking by a novel GABAB receptor positive allosteric modulator ADX71441 in mice. Psychopharmacology 231:333–343
Järbe TU, LeMay BJ, Olszewska T, Vemuri VK, Wood JT, Makriyannis A (2008) Intrinsic effects of AM4113, a putative neutral CB1 receptor selective antagonist, on open-field behaviors in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:84–90
Kelley AE (1993) Locomotor activity and exploration. In: Sahgal A (ed) Behavioural neuroscience: a practical approach, vol II. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–21
Khaimova E, Kandov Y, Israel Y, Cataldo G, Hadjimarkou MM, Bodnar RJ (2004) Opioid receptor subtype antagonists differentially alter GABA agonist-induced feeding elicited from either the nucleus accumbens shell or ventral tegmental area regions in rats. Brain Res 1026:284–294
Leite CE, Mocelin CA, Petersen GO, Leal MB, Thiesen FV (2009) Rimonabant: an antagonist drug of the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of obesity. Pharmacol Rep 61:217–224
Leite-Morris KA, Kerestes HB, Colombo G (2009) Intra-ventral tegmental area injection of the GABA B receptor positive allosteric modulator GS39783 inhibits ethanol seeking behavior in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:226A
Liang JH, Chen F, Krstew E, Cowen MS, Carroll FY, Crawford D, Beart PM, Lawrence AJ (2006) The GABAB receptor allosteric modulator CGP7930, like baclofen, reduces operant self-administration of ethanol in alcohol-preferring rats. Neuropharmacology 50:632–639
Linsenbardt DN, Boehm SL (2014) Alterations in the rate of binge ethanol consumption: implications for preclinical studies in mice. Addict Biol 19:812–825
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26
Loi B, Maccioni P, Lobina C, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Thomas AW, Malherbe P, Colombo G (2013) Reduction of alcohol intake by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, rac-BHFF, in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 47:69–73
Lorrai L, Piga V, Carai MAM, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Gessa GL, Colombo G, Maccioni P (2016) A Phaseolus vulgaris extract reduces cue-induced reinstatement of chocolate seeking in rats. Front Pharmacol 7:109. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00109
Maccioni P, Colombo G (2016) Operant self-administration of chocolate in rats: an addiction-like behavior. In: Philippou A (ed) In vivo neuropharmacology and neurophysiology. Springer, New York, pp 107–139
Maccioni P, Pes D, Orrù A, Froestl W, Gessa GL, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2007) Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783, on alcohol self-administration in alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology 193:171–178
Maccioni P, Fantini N, Froestl W, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2008a) Specific reduction of alcohol’s motivational properties by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783—comparison with the effect of the GABAB receptor direct agonist, baclofen. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:1558–1564
Maccioni P, Pes D, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2008b) Suppression by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, rimonabant, of the reinforcing and motivational properties of a chocolate-flavoured beverage in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:197–209
Maccioni P, Carai MAM, Kaupmann K, Guery S, Froestl W, Leite-Morris KA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2009a) Reduction of alcohol’s reinforcing and motivational properties by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, BHF177, in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1749–1756
Maccioni P, Fantini N, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2009b) Suppressing effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, rimonabant, on alcohol self-administration in alcohol-preferring rats. Open Neuropsychopharmacol J 2:40–44
Maccioni P, Flore P, Carai MAM, Mugnaini C, Pasquini S, Corelli F, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2010a) Reduction by the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783, of alcohol self-administration in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats exposed to the “sipper” procedure. Front Psychiatry 1:20. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2010.00020
Maccioni P, Thomas AW, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Malherbe P, Colombo G (2010b) The positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, rac-BHFF, suppresses alcohol self-administration. Drug Alcohol Depend 109:96–103
Maccioni P, Zaru A, Loi B, Lobina C, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Capra A, Mugnaini C, Pasquini S, Corelli F, Hyytiä P, Lumeng L, Colombo G (2012) Comparison of the effect of the GABAB receptor agonist, baclofen, and the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783, on alcohol self-administration in three different lines of alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:1748–1766
Maccioni P, Vargiolu D, Thomas AW, Malherbe P, Mugnaini C, Corelli F, Leite-Morris KA, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2015) Inhibition of alcohol self-administration by positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor in rats: lack of tolerance and potentiation of baclofen. Psychopharmacology 232:1831–1841
Markou A, Weiss F, Gold LH, Caine SB, Schulteis G, Koob GF (1993) Animal models of drug craving. Psychopharmacology 112:163–182
Martín-García E, Burokas A, Kostrzewa E, Gieryk A, Korostynski M, Ziolkowska B, Przewlocka B, Przewlocki R, Maldonado R (2011) New operant model of reinstatement of food-seeking behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 215:49–70
Mathes CM, Ferrara M, Rowland NE (2008) Cannabinoid-1 receptor antagonists reduce caloric intake by decreasing palatable diet selection in a novel dessert protocol in female rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R67–R75
Mugnaini C, Corelli F (2016) Chemistry of GABAB receptor ligands: focus on positive allosteric modulators. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 33–52
Mugnaini C, Pedani V, Casu A, Lobina C, Casti A, Maccioni P, Porcu A, Giunta D, Lamponi S, Solinas M, Dragoni S, Valoti M, Colombo G, Castelli MP, Gessa GL, Corelli F (2013) Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of 2-(acylamino)thiophene derivatives as metabolically stable, orally effective, positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor. J Med Chem 56:3620–3635
Natividad LA, Maccioni P, Parsons LH, Colombo G (2015) Cannabinoid-alcohol interactions. In: Fattore P, Campolongo P (eds) Cannabinoids and modulation of emotion, memory, and motivation. Springer, New York, pp 363–391
Orrù A, Lai P, Lobina C, Maccioni P, Piras P, Scanu L, Froestl W, Gessa GL, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2005) Reducing effect of the positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor, CGP7930 and GS39783, on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 525:105–111
Pulman KGT, Somerville EM, Clifton PG (2010) Intra-accumbens baclofen, but not muscimol, mimics the effects of food withdrawal on feeding behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:156–162
Pulman KGT, Somerville EM, Clifton PG (2012) Intra-accumbens baclofen, but not muscimol, increases second order instrumental responding for food reward in rats. PLoS One 7:e40057
Reis J, Cagide F, Chavarria D, Silva T, Fernandes C, Gaspar A, Uriarte E, Remiao F, Alcaro S, Ortuso F, Borges F (2016) Discovery of new chemical entities for old targets: insights on the lead optimization of chromone-based monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) inhibitors. J Med Chem 59:5879–5893
Richardson NR, Roberts DC (1996) Progressive ratio schedules in drug self-administration studies in rats: a method to evaluate reinforcing efficacy. J Neurosci Methods 66:1–11
Sink KS, McLaughlin PJ, Wood JA, Brown C, Fan P, Vemuri VK, Peng Y, Olszewska T, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A, Parker LA, Salamone JD (2008) The novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 suppresses food intake and food-reinforced behavior but does not induce signs of nausea in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:946–955
Smith MA, Yancey DL, Morgan D, Liu Y, Froestl W, Roberts DC (2004) Effects of positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor on cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 173:105–111
Addex Therapeutics (2015) http://www.addextherapeutics.com/investors/press-releases/news-details/article/addex-adx71441-included-in-the-ninds-anticonvulsant-screening-program/. Accessed March 15, 2017
Urwyler S (2016) Allosteric modulators: the new generation of GABAB receptor ligands. In: Colombo G (ed) GABAB receptor; the receptors 29. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 357–375
Urwyler S, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Mosbacher J, Lampert C, Froestl W, Koller M, Kaupmann K (2003) N,N'-Dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine (GS39783) and structurally related compounds: novel allosteric enhancers of gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:322–330
Urwyler S, Gjoni T, Koljatić J, Dupuis DS (2005) Mechanisms of allosteric modulation at GABAB receptors by CGP7930 and GS39783: effects on affinities and efficacies of orthosteric ligands with distinct intrinsic properties. Neuropharmacology 48:343–353
Ward SJ, Dykstra LA (2005) The role of CB1 receptors in sweet versus fat reinforcement: effect of CB1 receptor deletion, CB1 receptor antagonism (SR141716A) and CB1 receptor agonism (CP-55940). Behav Pharmacol 16:381–388
Ward BO, Somerville EM, Clifton PG (2000) Intraaccumbens baclofen selectively enhances feeding behavior in the rat. Physiol Behav 68:463–468
Zaru A, Maccioni P, Colombo G, Gessa GL (2016) Disulfiram inhibits chocolate self-administration and reinstatement to chocolate seeking in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 148:119–127
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mrs. Carla Acciaro for animal breeding and care and Ms. Anne Farmer for language editing of the manuscript. This work has been partially supported by grants (a) no. CRP-17596 from Regione Autonoma della Sardegna (L.R. 7 agosto 2007, n. 7) and (b) EA 13 20 from European Foundation for Alcohol Research (ERAB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental procedures employed in the present study were (a) in accordance with European Directive no. 2010/63/EU and subsequent Italian Legislative Decree no. 26, March 4, 2014, on the “Protection of animals used for scientific purposes” and (b) approved by the Italian Ministry of Health (authorization no. 342/2016-PR).
Conflict of interest
Mauro A.M. Carai, Giancarlo Colombo, Federico Corelli, Gian Luigi Gessa, Claudia Mugnaini, and Paola Maccioni are inventors on patent application no. 102016000030477 entitled “Use of 2-(acylamino)thiophene derivatives for the treatment of food dependence.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maccioni, P., Colombo, G., Lorrai, I. et al. Suppressing effect of COR659 on alcohol, sucrose, and chocolate self-administration in rats: involvement of the GABAB and cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Psychopharmacology 234, 2525–2543 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4644-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4644-3