Abstract
Rationale
Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) signaling modulates behaviors associated with psychostimulants and opioids. Psychostimulants, such as amphetamine (AMPH) and cocaine, bind to monoamine transporters and alter their functions. Both dopamine and norepinephrine transporters are regulated by NK1R activation suggesting a role for NK1R mediated catecholamine transporter regulation in psychostimulant-mediated behaviors.
Objectives
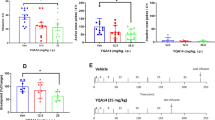
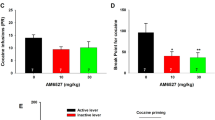
The effect of in vivo administration of aprepitant (10 mg/kg) on the expression of AMPH (0.5 and 2 mg/kg) and cocaine (5 and 20 mg/kg)-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) as well as locomotor activation was examined in C57BL/6J mice. The effect of aprepitant on morphine (1 and 5 mg/kg)-induced CPP was also examined to identify the specific actions of aprepitant on psychostimulant versus opioid-induced behaviors.
Results
Aprepitant administration significantly attenuated the CPP expression and locomotor activation produced by AMPH and cocaine. In contrast, aprepitant significantly enhanced the expression of CPP produced by morphine while significantly suppressing the locomotor activity of the mice conditioned with morphine. Aprepitant by itself did not induce significant CPP or conditioned place aversion or locomotor activation or suppression.
Conclusions
Attenuation of AMPH or cocaine-induced CPP and locomotor activation by aprepitant suggests a role for NK1R signaling in psychostimulant-mediated behaviors. Stimulation of morphine-induced CPP expression and suppression of locomotor activity of morphine-conditioned mice suggest differential effects of NK1R antagonism on conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward. Collectively, these findings indicate that clinically used NK1R antagonist, aprepitant may serve as a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of psychostimulant abuse.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadoro G, Pieri M, Ciotti MT, Carunchio I, Canu N, Calissano P, Zona C, Severini C (2007) Substance P provides neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells through Akt and MAPK/Erk activation: evidence for the involvement of the delayed rectifier potassium current. Neuropharmacology 52:1366–1377
Annamalai B, Mannangatti P, Arapulisamy O, Ramamoorthy S, Jayanthi LD (2010) Involvement of threonine 258 and serine 259 motif in amphetamine-induced norepinephrine transporter endocytosis. J Neurochem 115:23–35
Arapulisamy O, Mannangatti P, Jayanthi LD (2013) Regulated norepinephrine transporter interaction with the neurokinin-1 receptor establishes transporter subcellular localization. J Biol Chem 288:28599–28610
Badiani A, Belin D, Epstein D, Calu D, Shaham Y (2011) Opiate versus psychostimulant addiction: the differences do matter. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:685–700
Bohn LM, Xu F, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2000) Potentiated opioid analgesia in norepinephrine transporter knock-out mice. J Neurosci 20:9040–9045
Bowman SL, Soohoo AL, Shiwarski DJ, Schulz S, Pradhan AA, Puthenveedu MA (2015) Cell-autonomous regulation of Mu-opioid receptor recycling by substance P. Cell Rep 10:1925–1936
Caberlotto L, Hurd YL, Murdock P, Wahlin JP, Melotto S, Corsi M, Carletti R (2003) Neurokinin 1 receptor and relative abundance of the short and long isoforms in the human brain. Eur J Neurosci 17:1736–1746
Chen LW, Wei LC, Liu HL, Rao ZR (2000) Noradrenergic neurons expressing substance P receptor (NK1) in the locus coeruleus complex: a double immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res 873:155–159
Chu JM, Chen LW, Chan YS, Yung KK (2011) Neuroprotective effects of neurokinin receptor one in dopaminergic neurons are mediated through Akt/PKB cell signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 61:1389–1398
Commons KG (2010) Neuronal pathways linking substance P to drug addiction and stress. Brainresearch 1314:175–182
Drouin C, Darracq L, Trovero F, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Cotecchia S, Tassin JP (2002) Alpha1b-adrenergic receptors control locomotor and rewarding effects of psychostimulants and opiates. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 22:2873–2884
Ebner K, Sartori SB, Singewald N (2009) Tachykinin receptors as therapeutic targets in stress-related disorders. Curr Pharm Des 15:1647–1674
Fisher AS, Stewart RJ, Yan T, Hunt SP, Stanford SC (2007) Disruption of noradrenergic transmission and the behavioural response to a novel environment in NK1R-/- mice. Eur J Neurosci 25:1195–1204
Foster JD, Cervinski MA, Gorentla BK, Vaughan RA (2006) Regulation of the dopamine transporter by phosphorylation. Handb Exp Pharmacol:197–214
Gabrielian L, Helps SC, Thornton E, Turner RJ, Leonard AV, Vink R (2013) Substance P antagonists as a novel intervention for brain edema and raised intracranial pressure. Acta Neurochir Suppl 118:201–204
Gadd CA, Murtra P, De Felipe C, Hunt SP (2003) Neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons in the amygdala modulate morphine reward and anxiety behaviors in the mouse. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 23:8271–8280
Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2003) Monoamine transporters: from genes to behavior. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:261–284
George DT, Gilman J, Hersh J, Thorsell A, Herion D, Geyer C, Peng X, Kielbasa W, Rawlings R, Brandt JE, Gehlert DR, Tauscher JT, Hunt SP, Hommer D, Heilig M (2008) Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonism as a possible therapy for alcoholism. Science 319:1536–1539
Gonzalez-Nicolini V, McGinty JF (2002) NK-1 receptor blockade decreases amphetamine-induced behavior and neuropeptide mRNA expression in the striatum. Brain Res 931:41–49
Griffante C, Carletti R, Andreetta F, Corsi M (2006) [3H]GR205171 displays similar NK1 receptor binding profile in gerbil and human brain. Br J Pharmacol 148:39–45
Hall FS, Li XF, Randall-Thompson J, Sora I, Murphy DL, Lesch KP, Caron M, Uhl GR (2009) Cocaine-conditioned locomotion in dopamine transporter, norepinephrine transporter and 5-HT transporter knockout mice. Neuroscience 162:870–880
Hargreaves R (2002) Imaging substance P receptors (NK1) in the living human brain using positron emission tomography. The Journal of clinical psychiatry 63(Suppl 11):18–24
Hargreaves R, Ferreira JC, Hughes D, Brands J, Hale J, Mattson B, Mills S (2011) Development of aprepitant, the first neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1222:40–48
Jayanthi LD, Annamalai B, Samuvel DJ, Gether U, Ramamoorthy S (2006) Phosphorylation of the norepinephrine transporter at threonine 258 and serine 259 is linked to protein kinase C-mediated transporter internalization. J Biol Chem 281:23326–23340
Jayanthi LD, Ramamoorthy S (2005) Regulation of monoamine transporters: influence of psychostimulants and therapeutic antidepressants. AAPS J 7:E728–E738
Jones JD, Speer T, Comer SD, Ross S, Rotrosen J, Reid MS (2013) Opioid-like effects of the neurokinin 1 antagonist aprepitant in patients maintained on and briefly withdrawn from methadone. The American journal of drug and alcohol abuse 39:86–91
Kahlig KM, Galli A (2003) Regulation of dopamine transporter function and plasma membrane expression by dopamine, amphetamine, and cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 479:153–158
Kelley AE, Iversen SD (1978) Behavioural response to bilateral injections of substance P into the substantia nigra of the rat. Brain Res 158:474–478
Kertes E, Laszlo K, Berta B, Lenard L (2010) Positive reinforcing effects of substance P in the rat globus pallidus revealed by conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 215:152–155
Kraft M, Ahluwahlia S, Angulo JA (2001) Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists block acute cocaine-induced horizontal locomotion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937:132–139
Kramer MS, Winokur A, Kelsey J, Preskorn SH, Rothschild AJ, Snavely D, Ghosh K, Ball WA, Reines SA, Munjack D, Apter JT, Cunningham L, Kling M, Bari M, Getson A, Lee Y (2004) Demonstration of the efficacy and safety of a novel substance P (NK1) receptor antagonist in major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 29:385–392
Kristensen AS, Andersen J, Jorgensen TN, Sorensen L, Eriksen J, Loland CJ, Stromgaard K, Gether U (2011) SLC6 neurotransmitter transporters: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Rev 63:585–640
Lallemend F, Lefebvre PP, Hans G, Rigo JM, Van de Water TR, Moonen G, Malgrange B (2003) Substance P protects spiral ganglion neurons from apoptosis via PKC-Ca2+-MAPK/ERK pathways. J Neurochem 87:508–521
Leite-Morris KA, Kobrin KL, Guy MD, Young AJ, Heinrichs SC, Kaplan GB (2014) Extinction of opiate reward reduces dendritic arborization and c-Fos expression in the nucleus accumbens core. Behav Brain Res 263:51–59
Lewis KM, Harford-Wright E, Vink R, Ghabriel MN (2013) NK1 receptor antagonists and dexamethasone as anticancer agents in vitro and in a model of brain tumours secondary to breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 24:344–354
Lim R, Morrill JM, Prushik SG, Reed KL, Gower AC, Leeman SE, Stucchi AF, Becker JM (2008) An FDA approved neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist is effective in reducing intraabdominal adhesions when administered intraperitoneally, but not orally. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery: official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract 12:1754–1761
Lindefors N, Brodin E, Ungerstedt U (1989) Amphetamine facilitates the in vivo release of neurokinin A in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 160:417–420
Mannangatti P, Arapulisamy O, Shippenberg TS, Ramamoorthy S, Jayanthi LD (2011) Cocaine up-regulation of the norepinephrine transporter requires threonine 30 phosphorylation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 286:20239–20250
Mannangatti P, Narasimha Naidu K, Damaj MI, Ramamoorthy S, Jayanthi LD (2015) A role for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediated threonine 30 dependent norepinephrine transporter regulation in cocaine sensitization and conditioned place preference. J Biol Chem 290:10814–10827
Monastyrskaya K, Hostettler A, Buergi S, Draeger A (2005) The NK1 receptor localizes to the plasma membrane microdomains, and its activation is dependent on lipid raft integrity. J Biol Chem 280:7135–7146
Murtra P, Sheasby AM, Hunt SP, De Felipe C (2000) Rewarding effects of opiates are absent in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 405:180–183
Nakamura Y, Izumi H, Fukushige R, Shimizu T, Watanabe K, Morioka N, Hama A, Takamatsu H, Nakata Y (2014) Continuous infusion of substance P into rat striatum alleviates nociceptive behavior via phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J Neurochem 131:755–766
Noailles PA, Angulo JA (2002) Neurokinin receptors modulate the neurochemical actions of cocaine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 965:267–273
Olive MF (2015) Neurokinin-1 (NK(1)) receptor antagonists as possible therapeutics for psychostimulant use disorders. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets 14:700–706
Patel L, Lindley C (2003) Aprepitant—a novel NK1-receptor antagonist. Expert Opin Pharmacother 4:2279–2296
Pfeiffer M, Kirscht S, Stumm R, Koch T, Wu D, Laugsch M, Schroder H, Hollt V, Schulz S (2003) Heterodimerization of substance P and mu-opioid receptors regulates receptor trafficking and resensitization. J Biol Chem 278:51630–51637
Placenza FM, Fletcher PJ, Vaccarino FJ, Erb S (2006) Effects of central neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism on cocaine- and opiate-induced locomotor activity and self-administration behaviour in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:94–101
Placenza FM, Vaccarino FJ, Fletcher PJ, Erb S (2005) Activation of central neurokinin-1 receptors induces reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Neurosci Lett 390:42–47
Ramamoorthy S, Shippenberg TS, Jayanthi LD (2011) Regulation of monoamine transporters: role of transporter phosphorylation. Pharmacol Ther 129:220–238
Ramsey AJ, Laakso A, Cyr M, Sotnikova TD, Salahpour A, Medvedev IO, Dykstra LA, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2008) Genetic NMDA receptor deficiency disrupts acute and chronic effects of cocaine but not amphetamine. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2701–2714
Ripley TL, Gadd CA, De Felipe C, Hunt SP, Stephens DN (2002) Lack of self-administration and behavioural sensitisation to morphine, but not cocaine, in mice lacking NK1 receptors. Neuropharmacology 43:1258–1268
Robinson JE, Fish EW, Krouse MC, Thorsell A, Heilig M, Malanga CJ (2012) Potentiation of brain stimulation reward by morphine: effects of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 220:215–224
Rocha BA, Fumagalli F, Gainetdinov RR, Jones SR, Ator R, Giros B, Miller GW, Caron MG (1998) Cocaine self-administration in dopamine-transporter knockout mice. Nature Neurosci 1:132–137
Rudnick G, Kramer R, Blakely RD, Murphy DL, Verrey F (2014) The SLC6 transporters: perspectives on structure, functions, regulation, and models for transporter dysfunction. Pflugers Archiv: European journal of physiology 466:25–42
Ruzza C, Rizzi A, Malfacini D, Cerlesi MC, Ferrari F, Marzola E, Ambrosio C, Gro C, Severo S, Costa T, Calo G, Guerrini R (2014) Pharmacological characterization of tachykinin tetrabranched derivatives. Br J Pharmacol 171:4125–4137
Salahpour A, Ramsey AJ, Medvedev IO, Kile B, Sotnikova TD, Holmstrand E, Ghisi V, Nicholls PJ, Wong L, Murphy K, Sesack SR, Wightman RM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2008) Increased amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and reward in mice overexpressing the dopamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4405–4410
Saria A (1999) The tachykinin NK1 receptor in the brain: pharmacology and putative functions. Eur J Pharmacol 375:51–60
Schank JR, King CE, Sun H, Cheng K, Rice KC, Heilig M, Weinshenker D, Schroeder JP (2014) The role of the neurokinin-1 receptor in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol and cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 39:1093–1101
Sotnikova TD, Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2006) Molecular biology, pharmacology and functional role of the plasma membrane dopamine transporter. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets 5:45–56
Stinus L, Kelley AE, Iversen SD (1978) Increased spontaneous activity following substance Pinfusion into A10 dopaminergic area. Nature 276:616–618
Stuart SA, Butler P, Munafo MR, Nutt DJ, Robinson ES (2013) A translational rodent assay of affective biases in depression and antidepressant therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1625–1635
Uhl GR, Drgonova J, Hall FS (2014) Curious cases: altered dose-response relationships in addiction genetics. Pharmacol Ther 141:335–346
Utsumi D, Matsumoto K, Amagase K, Horie S, Kato S (2016) 5-HT3 receptors promote colonic inflammation via activation of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptors in dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis. Br J Pharmacol 173:1835–1849
Van Bockstaele EJ, Valentino RJ (2013) Neuropeptide regulation of the locus coeruleus and opiate-induced plasticity of stress responses. Adv Pharmacol 68:405–420
Van den Bos R, Cools AR, Ogren SO (1989) Neurokinin A enhances the stimulatory effects of d-amphetamine on motor activity in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 137:547–548
Van den Bos R, Cools AR, Ogren SO (1990) Neurokinin A enhances the stimulatory effects of d-amphetamine on motor activity in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 138:423–424
Ventura R, Alcaro A, Puglisi-Allegra S (2005) Prefrontal cortical norepinephrine release is critical for morphine-induced reward, reinstatement and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Cereb Cortex 15:1877–1886
Walsh SL, Heilig M, Nuzzo PA, Henderson P, Lofwall MR (2013) Effects of the NK1 antagonist, aprepitant, on response to oral and intranasal oxycodone in prescription opioid abusers. Addict Biol 18:332–343
Xu F, Gainetdinov RR, Wetsel WC, Jones SR, Bohn LM, Miller GW, Wang YM, Caron MG (2000) Mice lacking the norepinephrine transporter are supersensitive to psychostimulants. Nat Neurosci 3:465–471
Yamamoto K, Asano K, Tasaka A, Ogura Y, Kim S, Ito Y, Yamatodani A (2014) Involvement of substance P in the development of cisplatin-induced acute and delayed pica in rats. Br J Pharmacol 171:2888–2899
Yan TC, Hunt SP, Stanford SC (2009) Behavioural and neurochemical abnormalities in mice lacking functional tachykinin-1 (NK1) receptors: a model of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuropharmacology 57:627–635
Acknowledgements
Dr. Jayanthi and Dr. Ramamoorthy declare that the funding for this research was provided in part by NIH grants DA039451 and MH083928 as well as by Virginia Commonwealth University. Dr. Mannangatti gratefully acknowledges post-doctoral support from the department of Pharmacology and Toxicology at Virginia Commonwealth University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Virginia Commonwealth University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide (NIH) guidelines published in the National Research Council (2011) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory animals, 8th edition, National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannangatti, P., Sundaramurthy, S., Ramamoorthy, S. et al. Differential effects of aprepitant, a clinically used neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist on the expression of conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward. Psychopharmacology 234, 695–705 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4504-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4504-6