Abstract
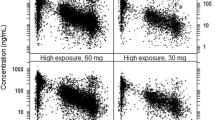
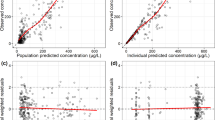
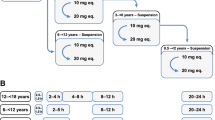
This study aimed to develop a population pharmacokinetic (PPK) model for rivaroxaban and establish a model-based dosing guideline tailored to Chinese patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). A nonlinear mixed-effects modeling approach was employed using Phoenix NLME 7.0 software to construct the PPK model for rivaroxaban. The PK of rivaroxaban was adequately characterized through a one-compartment model. Monte Carlo simulations were employed to formulate dosing guidelines applicable to different patient subgroups. Data from 60 Chinese DVT patients yielded 217 rivaroxaban plasma concentrations for analysis. The apparent clearance (CL/F) of rivaroxaban was found to be significantly influenced by the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), identified as a major covariate. Based on Monte Carlo simulations, for the acute DVT treatment, a regimen of 15 mg, 10 mg, or 5 mg twice daily was associated with the highest total probability target attainment (PTAtotal) in patients with normal, mildly impaired, or moderately impaired renal function, respectively. For the continued DVT treatment, a regimen of 20 mg, 15 mg, or 5 mg once daily exhibited the maximum PTAtotal in patients with normal, mildly impaired, or moderately impaired renal function, respectively. The recommendation label dose achieved the PK target in those with normal renal function. However, for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, dose adjustments below the label recommendation might be necessary. The PPK model associated CL/F with the covariate eGFR. Utilizing the PPK model, a dosage regimen table was constructed to offer tailored dosing recommendations for Chinese DVT patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Agnelli G, Gallus A, Goldhaber SZ et al (2007) Treatment of proximal deep-vein thrombosis with the oral direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban (BAY 59–7939) - the ODIXa-DVT (oral direct factor Xa inhibitor BAY 59–7939 in patients with acute symptomatic deep-vein thrombosis) study. Circulation 116(2):180–187
Bouget J, Balusson F, Maignan M et al (2020) Major bleeding risk associated with oral anticoagulant in real clinical practice. A multicentre 3-year period population-based prospective cohort study. Br J Clin Pharmacol 86(12):2519–2529
Buller HR, Lensing AWA, Prins MH et al (2008) A dose-ranging study evaluating once-daily oral administration of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban in the treatment of patients with acute symptomatic deep vein thrombosis: the Einstein-DVT Dose-Ranging Study. Blood 112(6):2242–2247
Derogis PBM, Sanches LR, de Aranda VF et al (2017) Determination of rivaroxaban in patient’s plasma samples by anti-Xa chromogenic test associated to high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). PLoS ONE 12(2):e0171272
Eriksson BI, Borris L, Dahl OE et al (2006) Oral, direct factor Xa inhibition with BAY 59–7939 for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement. J Thromb Haemost 4(1):121–128
Girgis IG, Patel MR, Peters GR et al (2014) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: results from ROCKET AF. J Clin Pharmacol 54(8):917–927
Gong IY, Kim RB (2013) Importance of pharmacokinetic profile and variability as determinants of dose and response to dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban. Can J Cardiol 29(7):S24–S33
Goto E, Horinaka S, Ishimitsu T et al (2020) Factor Xa inhibitors in clinical practice: comparison of pharmacokinetic profiles. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 35(1):151–159
Halperin JL, Hankey GJ, Wojdyla DM et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban compared with warfarin among elderly patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the rivaroxaban once daily, oral, direct factor Xa inhibition compared with vitamin K antagonism for prevention of stroke and embolism trial in atrial fibrillation (ROCKET AF). Circulation 130(2):138–146
Johnson JA (1997) Influence of race or ethnicity on pharmacokinetics of drugs. J Pharm Sci 86(12):1328–1333
Kaneko M, Tanigawa T, Hashizume K et al (2013) Confirmation of model-based dose selection for a Japanese phase III study of rivaroxaban in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28(4):321–331
Kong XL, Ma YC, Chen JH et al (2013) Evaluation of the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate in the Chinese population. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(3):641–651
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W et al (2010) Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol 70(5):703–712
Kvasnicka T, Malikova I, Zenahlikova Z et al (2017) Rivaroxaban - metabolism, pharmacologic properties and drug interactions. Curr Drug Metab 18(7):636–642
Laliberte F, Cloutier M, Nelson WW et al (2014) Real-world comparative effectiveness and safety of rivaroxaban and warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients. Curr Med Res Opin 30(7):1317–1325
Li XG, Wu YX, Sun SS et al (2015) Population pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in postoperative neurosurgical patients. J Pharm Sci 104(11):3960–3967
Li XG, Wu YX, Sun SS et al (2016) Population pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in postoperative neurosurgical patients and the application in dosing recommendation. J Pharm Sci 105(11):3425–3431
Li Z, Wang XZ, Li DD et al (2022) Real-world comparisons of low-dose NOACs versus standard-dose NOACs or warfarin on efficacy and safety in patients with AF: a meta-analysis. Cardiol Res Pract 2022:4713826
Liu XQ, Zhang YF, Ding HY et al (2022) Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of rivaroxaban in Chinese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(10):2723–2734
Liu XQ, Li ZR, Wang CY et al (2023) Is a lower dose of rivaroxaban required for Asians? A systematic review of a population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics analysis of rivaroxaban. Pharmaceutics 15(2):588
Mueck W, Borris LC, Dahl OE et al (2008) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once- and twice-daily rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Thromb Haemost 100(3):453–461
Mueck W, Lensing AWA, Agnelli G et al (2011) Rivaroxaban population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients treated for acute deep-vein thrombosis and exposure simulations in patients with atrial fibrillation treated for stroke prevention. Clin Pharmacokinet 50(10):675–686
Samama MM, Amiral J, Guinet C et al (2013) Monitoring plasma levels of factor Xa inhibitors: how, why and when? Expert Rev Hematol 6(2):155–164
Singkham N, Phrommintikul A, Pacharasupa P et al (2022) Population pharmacokinetics and dose optimization based on renal function of rivaroxaban in Thai patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Pharmaceutics 14(8):1744
Suzuki S, Yamashita T, Kasai H et al (2018) An analysis on distribution and inter-relationships of biomarkers under rivaroxaban in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (CVI ARO 1). Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 33(4):188–193
Tanigawa T, Kaneko M, Hashizume K et al (2013) Model-based dose selection for phase III rivaroxaban study in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28(1):59–70
Willmann S, Zhang LP, Frede M et al (2018) Integrated population pharmacokinetic analysis of rivaroxaban across multiple patient populations. CPT-Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 7(5):309–320
Xu XS, Moore K, Burton P et al (2012) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Brit J Clin Pharmacol 74(1):86–97
Yu HT, Yang PS, Jang E et al (2020) Label adherence of direct oral anticoagulants dosing and clinical outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 9(12):e014177
Zdovc J, Petre M, Pislar M et al (2019) Downregulation of ABCB1 gene in patients with total hip or knee arthroplasty influences pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban: a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 75(6):817–824
Zhang D, Chen WQ, Qin W et al (2023) Population pharmacokinetics and hemorrhagic risk analysis of rivaroxaban in elderly Chinese patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Clin Pharmacol 63(1):66–76
Zhang F, Chen X, Wu T et al (2022) Population pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in Chinese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Pharmacokinet 61(6):881–893
Funding
This study was funded by research and application of clinical characteristic diagnosis and treatment technology in Beijing (grant no. Z221100007422032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.L. was responsible for the study design, data analysis, data interpretation, drafting and critical revision of the manuscript. S.Y., Z.H. were responsible for the provision of study materials or patients. Y.L., X.L. were responsible for the study concept and design, data interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript, approval of the final submission. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This research was carried out at the Chinese PLA General Hospital with the official endorsement of the hospital’s institutional ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Yang, S., Hua, Z. et al. Population pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in Chinese deep vein thrombosis patients and the exposure simulation for dosing recommendation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02798-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02798-7