Abstract
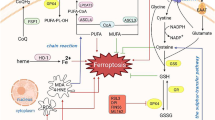
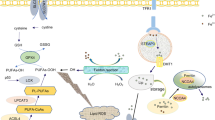
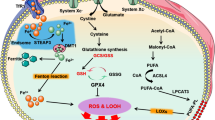
Ferroptosis is a novel type of regulated cell death (RCD) discovered in recent years, where abnormal intracellular iron accumulation leads to the onset of lipid peroxidation, which further leads to the disruption of intracellular redox homeostasis and triggers cell death. Iron accumulation with lipid peroxidation is considered a hallmark of ferroptosis that distinguishes it from other RCDs. Myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury (MIRI) is a process of increased myocardial cell injury that occurs during coronary reperfusion after myocardial ischemia and is associated with high post-infarction mortality. Multiple experiments have shown that ferroptosis plays an important role in MIRI pathophysiology. This review systematically summarized the latest research progress on the mechanisms of ferroptosis. Then we report the possible link between the occurrence of MIRI and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Finally, we discuss and analyze the related drugs that target ferroptosis to attenuate MIRI and its action targets, and point out the shortcomings of the current state of relevant research and possible future research directions. It is hoped to provide a new avenue for improving the prognosis of the acute coronary syndrome.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ambrosio G, Zweier JL, Jacobus WE, Weisfeldt ML, Flaherty JT (1987) Improvement of postischemic myocardial function and metabolism induced by administration of deferoxamine at the time of reflow: the role of iron in the pathogenesis of reperfusion injury. Circulation 76(4):906–915. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.76.4.906
Arosio P, Ingrassia R, Cavadini P (2009) Ferritins: a family of molecules for iron storage, antioxidation and more. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790(7):589–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.09.004
Baba Y, Higa JK, Shimada BK, Horiuchi KM, Suhara T, Kobayashi M, Woo JD et al (2018) Protective effects of the mechanistic target of rapamycin against excess iron and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314(3):H659-h668. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00452.2017
Bauer TM, Murphy E (2020) Role of mitochondrial calcium and the permeability transition pore in regulating cell death. Circ Res 126(2):280–293. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.119.316306
Berenshtein E, Vaisman B, Goldberg-Langerman C, Kitrossky N, Konijn AM, Chevion M (2002) Roles of ferritin and iron in ischemic preconditioning of the heart. Mol Cell Biochem 234–235(1–2):283–292
Cadenas S (2018) ROS and redox signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free Radic Biol Med 117:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.024
Cao Z, Qin H, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Chen Z, Hu J, Gao Q (2022) Crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-related mechanisms in sepsis-induced lung injury in a mouse model. Bioengineered 13(3):4810–4820. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2033381
Chan W, Taylor AJ, Ellims AH, Lefkovits L, Wong C, Kingwell BA, Natoli A et al (2012) Effect of iron chelation on myocardial infarct size and oxidative stress in ST-elevation-myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 5(2):270–278. https://doi.org/10.1161/circinterventions.111.966226
Chang HC, Wu R, Shang M, Sato T, Chen C, Shapiro JS, Liu T et al (2016) Reduction in mitochondrial iron alleviates cardiac damage during injury. EMBO Mol Med 8(3):247–267. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201505748
Chen HY, Xiao ZZ, Ling X, Xu RN, Zhu P, Zheng SY (2021a) ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. Mol Med 27(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00271-w
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D (2021b) Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med 218(6). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20210518
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2021c) Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy 17(9):2054–2081. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1810918
Chen X, Yu C, Kang R, Tang D (2020) Iron metabolism in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:590226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.590226
Chevion M, Jiang Y, Har-El R, Berenshtein E, Uretzky G, Kitrossky N (1993) Copper and iron are mobilized following myocardial ischemia: possible predictive criteria for tissue injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(3):1102–1106. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.3.1102
Chevion M, Leibowitz S, Aye NN, Novogrodsky O, Singer A, Avizemer O, Bulvik B et al (2008) Heart protection by ischemic preconditioning: a novel pathway initiated by iron and mediated by ferritin. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45(6):839–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.08.011
Chu B, Kon N, Chen D, Li T, Liu T, Jiang L, Song S et al (2019) ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway. Nat Cell Biol 21(5):579–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0305-6
Ciumărnean L, Milaciu MV, Runcan O, Vesa ȘC, Răchișan AL, Negrean V, Perné MG et al (2020) The Effects of Flavonoids in Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 25(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184320
Cohen MV, Yang XM, Downey JM (2007) The pH hypothesis of postconditioning: staccato reperfusion reintroduces oxygen and perpetuates myocardial acidosis. Circulation 115(14):1895–1903. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.106.675710
Çolakoğlu M, Tunçer S, Banerjee S (2018) Emerging cellular functions of the lipid metabolizing enzyme 15-Lipoxygenase-1. Cell Prolif 51(5):e12472 https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12472
Dabkowski ER, Williamson CL, Hollander JM (2008) Mitochondria-specific transgenic overexpression of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPx4) attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-associated cardiac dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 45(6):855–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.06.021
Daniels LJ, Varma U, Annandale M, Chan E, Mellor KM, Delbridge LMD (2019) Myocardial energy stress, autophagy induction, and cardiomyocyte functional responses. Antioxid Redox Signal 31(6):472–486. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2018.7650
DeBoer DA, Clark RE (1992) Iron chelation in myocardial preservation after ischemia-reperfusion injury: the importance of pretreatment and toxicity. Ann Thorac Surg 53(3):412–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-4975(92)90260-b
DeHart DN, Fang D, Heslop K, Li L, Lemasters JJ, Maldonado EN (2018) Opening of voltage dependent anion channels promotes reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 148:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.022
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Dixon SJ, Patel DN, Welsch M, Skouta R, Lee ED, Hayano M, Thomas AG et al (2014) Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. Elife 3:e02523. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02523
Dodson M, Castro-Portuguez R, Zhang DD (2019a) NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol 23:101107 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101107
Dodson M, de la Vega MR, Cholanians AB, Schmidlin CJ, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2019b) Modulating NRF2 in disease: timing is everything. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 59:555–575. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021856
Drakesmith H, Nemeth E, Ganz T (2015) Ironing out ferroportin. Cell Metab 22(5):777–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.09.006
Fan Q, Tao R, Zhang H, Xie H, Lu L, Wang T, Su M et al (2019) Dectin-1 contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating macrophage polarization and neutrophil infiltration. Circulation 139(5):663–678. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.118.036044
Fan Z, Cai L, Wang S, Wang J, Chen B (2021) Baicalin prevents myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting ACSL4 mediated ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol 12:628988. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.628988
Fang KM, Lee AS, Su MJ, Lin CL, Chien CL, Wu ML (2008) Free fatty acids act as endogenous ionophores, resulting in Na+ and Ca2+ influx and myocyte apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 78(3):533–545. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn030
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei J, Gu S et al (2019) Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(7):2672–2680. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821022116
Feng Y, Madungwe NB, Imam Aliagan AD, Tombo N, Bopassa JC (2019) Liproxstatin-1 protects the mouse myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing VDAC1 levels and restoring GPX4 levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 520(3):606–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.006
Forcina GC, Dixon SJ (2019) GPX4 at the crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics 19(18):e1800311. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201800311
Frank A, Bonney M, Bonney S, Weitzel L, Koeppen M, Eckle T (2012) Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: from basic science to clinical bedside. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 16(3):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/1089253211436350
Galaris D, Barbouti A, Pantopoulos K (2019) Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: an intimate relationship. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1866(12):118535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118535
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J, Jiang X (2016) Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res 26(9):1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.95
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R, Jiang X (2015) Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol Cell 59(2):298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.011
Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J, Minikes AM, Monian P, Thompson CB, Jiang X (2019) Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Mol Cell 73(2):354–363.e353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.042
Gaschler MM, Stockwell BR (2017) Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482(3):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
Granville DJ, Tashakkor B, Takeuchi C, Gustafsson AB, Huang C, Sayen MR, Wentworth P Jr et al (2004) Reduction of ischemia and reperfusion-induced myocardial damage by cytochrome P450 inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(5):1321–1326. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308185100
Guo J, Cao W, Chen C, Chen X (2020) Peroxiredoxin 6 overexpression regulates adriamycin-induced myocardial injury, oxidative stress and immune response in rats. Ann Transl Med 8(20):1320. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-6598
Gupta U, Ghosh S, Wallace CT, Shang P, Xin Y, Nair AP, Yazdankhah M et al (2023) Increased LCN2 (lipocalin 2) in the RPE decreases autophagy and activates inflammasome-ferroptosis processes in a mouse model of dry AMD. Autophagy 19(1):92–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2022.2062887
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2013) Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a neglected therapeutic target. J Clin Invest 123(1):92–100. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci62874
Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU, Galy B, Camaschella C (2010) Two to tango: regulation of mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 142(1):24–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.028
Holthuis JC, Menon AK (2014) Lipid landscapes and pipelines in membrane homeostasis. Nature 510(7503):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13474
Hong SH, Lee DH, Lee YS, Jo MJ, Jeong YA, Kwon WT, Choudry HA et al (2017) Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression. Oncotarget 8(70):115164–115178. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23046
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ 3rd, Kang R et al (2016) Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 12(8):1425–1428. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1187366
Høyer-Hansen M, Bastholm L, Szyniarowski P, Campanella M, Szabadkai G, Farkas T, Bianchi K et al (2007) Control of macroautophagy by calcium, calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-beta, and Bcl-2. Mol Cell 25(2):193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.12.009
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C, Yu S (2018) The C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial infection. Front Immunol 9:3083. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.03083
Hwang JW, Park JH, Park BW, Kim H, Kim JJ, Sim WS, Mishchenko NP et al (2021) Histochrome attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis-induced cardiomyocyte death. Antioxidants (Basel) 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101624
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JP, Doll S, Croix CS, Dar HH et al (2017) Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 13(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2238
Kamat P, Vandenberghe S, Christen S, Bongoni AK, Meier B, Rieben R, Khattab AA (2016) Dexrazoxane shows no protective effect in the acute phase of reperfusion during myocardial infarction in pigs. PLoS One 11(12):e0168541. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168541
Kang R, Zeng L, Zhu S, Xie Y, Liu J, Wen Q, Cao L et al (2018) Lipid peroxidation drives gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in lethal polymicrobial sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 24(1):97-108.e104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.009
Koppula P, Zhang Y, Zhuang L, Gan B (2018) Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond) 38(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-018-0288-x
Kumfu S, Chattipakorn S, Fucharoen S, Chattipakorn N (2012) Mitochondrial calcium uniporter blocker prevents cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction induced by iron overload in thalassemic mice. Biometals 25(6):1167–1175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9579-x
Kupatt C, Hinkel R, Horstkotte J, Deiss M, von Brühl ML, Bilzer M, Boekstegers P (2004) Selective retroinfusion of GSH and cariporide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in a preclinical pig model. Cardiovasc Res 61(3):530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.012
Kwon MY, Park E, Lee SJ, Chung SW (2015) Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 6(27):24393–24403. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5162
Lakhal-Littleton S, Wolna M, Carr CA, Miller JJ, Christian HC, Ball V, Santos A et al (2015) Cardiac ferroportin regulates cellular iron homeostasis and is important for cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(10):3164–3169. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422373112
Lakhal-Littleton S, Wolna M, Chung YJ, Christian HC, Heather LC, Brescia M, Ball V et al (2016) An essential cell-autonomous role for hepcidin in cardiac iron homeostasis. Elife 5. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19804
Lei Q, Yi T, Chen C (2018) NF-κB-Gasdermin D (GSDMD) axis couples oxidative stress and NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis following myocardial infarction. Med Sci Monit 24:6044–6052. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.908529
Lemasters JJ, Bond JM, Chacon E, Harper IS, Kaplan SH, Ohata H, Trollinger DR et al (1996) The pH paradox in ischemia-reperfusion injury to cardiac myocytes. EXS 76:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8988-9_7
Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y, Lambros M, Gout PW, Kalivas PW, Massie A et al (2013) The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(5):522–555. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4391
Li D, Li Y (2020) The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00216-5
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, Wu Q, Duan M, Liu C, Wu H et al (2020a) Ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med 160:303–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.08.009
Li S, Lei Z, Yang X, Zhao M, Hou Y, Wang D, Tang S et al. 2022a. Propofol Protects myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis through the AKT/p53 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 13:841410. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.841410
Li T, Tan Y, Ouyang S, He J, Liu L (2022b) Resveratrol protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuating ferroptosis. Gene 808:145968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2021.145968
Li W, Feng G, Gauthier JM, Lokshina I, Higashikubo R, Evans S, Liu X et al (2019) Ferroptotic cell death and TLR4/Trif signaling initiate neutrophil recruitment after heart transplantation. J Clin Invest 129(6):2293–2304. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci126428
Li W, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong Y, Xia Z (2020b) Ferroptosis is involved in diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress. DNA Cell Biol 39(2):210–225. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.5097
Li W, Li W, Wang Y, Leng Y, Xia Z (2021) Inhibition of DNMT-1 alleviates ferroptosis through NCOA4 mediated ferritinophagy during diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Discov 7(1):267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00656-0
Liang H, Van Remmen H, Frohlich V, Lechleiter J, Richardson A, Ran Q (2007) Gpx4 protects mitochondrial ATP generation against oxidative damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356(4):893–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.03.045
Liao Z, Liu D, Tang L, Yin D, Yin S, Lai S, Yao J et al (2015) Long-term oral resveratrol intake provides nutritional preconditioning against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: involvement of VDAC1 downregulation. Mol Nutr Food Res 59(3):454–464. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201400730
Lillo-Moya J, Rojas-Solé C, Muñoz-Salamanca D, Panieri E, Saso L, Rodrigo R (2021) Targeting ferroptosis against ischemia/reperfusion cardiac injury. Antioxidants (Basel) 10(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10050667
Lin D, Cui B, Ma J, Ren J (2020) MiR-183-5p protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through targeting VDAC1. BioFactors 46(1):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1571
Lin D, Cui B, Ren J, Ma J (2018) Regulation of VDAC1 contributes to the cardioprotective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Exp Cell Res 367(2):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.04.004
Lin JH, Yang KT, Lee WS, Ting PC, Luo YP, Lin DJ, Wang YS et al (2022) Xanthohumol protects the rat myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:9523491. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9523491
Lin JH, Yang KT, Ting PC, Luo YP, Lin DJ, Wang YS, Chang JC (2021) Gossypol acetic acid attenuates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via an antiferroptotic mechanism. Biomolecules 11(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111667
Linkermann A, Skouta R, Himmerkus N, Mulay SR, Dewitz C, De Zen F, Prokai A et al (2014) Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(47):16836–16841. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1415518111
Lipper CH, Stofleth JT, Bai F, Sohn YS, Roy S, Mittler R, Nechushtai R et al (2019) Redox-dependent gating of VDAC by mitoNEET. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(40):19924–19929. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1908271116
Liu J, Kuang F, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Kang R, Tang D (2020) Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Cell Chem Biol 27(4):420–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.02.005
Liuzzi JP, Aydemir F, Nam H, Knutson MD, Cousins RJ (2006) Zip14 (Slc39a14) mediates non-transferrin-bound iron uptake into cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(37):13612–13617. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606424103
Loos B, Genade S, Ellis B, Lochner A, Engelbrecht AM (2011) At the core of survival: autophagy delays the onset of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death in a model of ischemic cell injury. Exp Cell Res 317(10):1437–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.03.011
Lu B, Chen XB, Hong YC, Zhu H, He QJ, Yang B, Ying MD et al (2019) Identification of PRDX6 as a regulator of ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40(10):1334–1342. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0233-9
Lu H, Xiao H, Dai M, Xue Y, Zhao R (2022a) Britanin relieves ferroptosis-mediated myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion damage by upregulating GPX4 through activation of AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 signalling. Pharm Biol 60(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2021.2007269
Lu Z, Liu Z, Fang B (2022b) Propofol protects cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced toxic injury by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/glutathione peroxidase 4 signaling pathways. Bioengineered 13(4):9145–9155. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2036895
Lucas DT, Szweda LI (1998) Cardiac reperfusion injury: aging, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(2):510–514. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.2.510
Lv Z, Wang F, Zhang X, Zhang X, Zhang J, Liu R (2021) Etomidate attenuates the ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion rat model via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Shock 56(3):440–449. https://doi.org/10.1097/shk.0000000000001751
Ma S, Sun L, Wu W, Wu J, Sun Z, Ren J. 2020. USP22 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via the SIRT1-p53/SLC7A11-dependent inhibition of ferroptosis-induced cardiomyocyte death. Front Physiol 11:551318. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.551318
Maher P, van Leyen K, Dey PN, Honrath B, Dolga A, Methner A (2018) The role of Ca(2+) in cell death caused by oxidative glutamate toxicity and ferroptosis. Cell Calcium 70:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2017.05.007
Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J (2002) The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell 10(2):417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00599-3
Masaldan S, Bush AI, Devos D, Rolland AS, Moreau C (2019) Striking while the iron is hot: Iron metabolism and ferroptosis in neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med 133:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.033
Oudit GY, Sun H, Trivieri MG, Koch SE, Dawood F, Ackerley C, Yazdanpanah M et al (2003) L-type Ca2+ channels provide a major pathway for iron entry into cardiomyocytes in iron-overload cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 9(9):1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm920
Paraskevaidis IA, Iliodromitis EK, Vlahakos D, Tsiapras DP, Nikolaidis A, Marathias A, Michalis A et al (2005) Deferoxamine infusion during coronary artery bypass grafting ameliorates lipid peroxidation and protects the myocardium against reperfusion injury: immediate and long-term significance. Eur Heart J 26(3):263–270. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehi028
Park TJ, Park JH, Lee GS, Lee JY, Shin JH, Kim MW, Kim YS et al (2019) Quantitative proteomic analyses reveal that GPX4 downregulation during myocardial infarction contributes to ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cell Death Dis 10(11):835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2061-8
Paterek A, Mackiewicz U, Mączewski M (2019) Iron and the heart: a paradigm shift from systemic to cardiomyocyte abnormalities. J Cell Physiol 234(12):21613–21629. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28820
Pietta PG (2000) Flavonoids as antioxidants. J Nat Prod 63(7):1035–1042. https://doi.org/10.1021/np9904509
Qiu Z, Lei S, Zhao B, Wu Y, Su W, Liu M, Meng Q et al (2017) NLRP3 inflammasome activation-mediated pyroptosis aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:9743280. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9743280
Ramu E, Korach A, Houminer E, Schneider A, Elami A, Schwalb H (2006) Dexrazoxane prevents myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in the rat heart. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 20(5):343–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-006-0497-4
Reczek CR, Chandel NS (2015) ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 33:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2014.09.010
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM et al (2012) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125(1):188–197. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182456d46
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9(1):49–89. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.9.49
Shah R, Margison K, Pratt DA (2017) The potency of diarylamine radical-trapping antioxidants as inhibitors of ferroptosis underscores the role of autoxidation in the mechanism of cell death. ACS Chem Biol 12(10):2538–2545. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00730
Shan X, Lv ZY, Yin MJ, Chen J, Wang J, Wu QN (2021) The protective effect of cyanidin-3-glucoside on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:8880141. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8880141
Shen S, He F, Cheng C, Xu B, Sheng J (2021) Uric acid aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via ROS/NLRP3 pyroptosis pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110990
Shen Y, Liu X, Shi J, Wu X (2019) Involvement of Nrf2 in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Macromol 125:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.190
Shi B, Ma M, Zheng Y, Pan Y, Lin X (2019) mTOR and Beclin1: two key autophagy-related molecules and their roles in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol 234(8):12562–12568. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28125
Shintoku R, Takigawa Y, Yamada K, Kubota C, Yoshimoto Y, Takeuchi T, Koshiishi I et al (2017) Lipoxygenase-mediated generation of lipid peroxides enhances ferroptosis induced by erastin and RSL3. Cancer Sci 108(11):2187–2194. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13380
Skouta R, Dixon SJ, Wang J, Dunn DE, Orman M, Shimada K, Rosenberg PA et al (2014) Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc 136(12):4551–4556. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja411006a
Song L, Yang H, Wang HX, Tian C, Liu Y, Zeng XJ, Gao E et al (2014) Inhibition of 12/15 lipoxygenase by baicalein reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulation of multiple signaling pathways. Apoptosis 19(4):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0946-z
Song X, Zhu S, Chen P, Hou W, Wen Q, Liu J, Xie Y et al (2018) AMPK-mediated BECN1 phosphorylation promotes ferroptosis by directly blocking system X(c)(-) activity. Curr Biol 28(15):2388-2399.e2385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.094
Song Y, Wang B, Zhu X, Hu J, Sun J, Xuan J, Ge Z (2021) Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol 37(1):51–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-020-09530-8
Stamenkovic A, O’Hara KA, Nelson DC, Maddaford TG, Edel AL, Maddaford G, Dibrov E et al (2021) Oxidized phosphatidylcholines trigger ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 320(3):H1170-h1184. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00237.2020
Sun W, Wu X, Yu P, Zhang Q, Shen L, Chen J, Tong H et al (2022) LncAABR07025387.1 enhances myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via miR-205/ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:672391. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.672391
Sun Y, Chen P, Zhai B, Zhang M, Xiang Y, Fang J, Xu S et al (2020) The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110108
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G (2021a) Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res 31(2):107–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
Tang LJ, Luo XJ, Tu H, Chen H, Xiong XM, Li NS, Peng J (2021b) Ferroptosis occurs in phase of reperfusion but not ischemia in rat heart following ischemia or ischemia/reperfusion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394(2):401–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01932-z
Tang LJ, Zhou YJ, Xiong XM, Li NS, Zhang JJ, Luo XJ, Peng J (2021c) Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 promotes ferroptosis via activation of the p53/TfR1 pathway in the rat hearts after ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 162:339–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.307
Tang WH, Wu S, Wong TM, Chung SK, Chung SS (2008) Polyol pathway mediates iron-induced oxidative injury in ischemic-reperfused rat heart. Free Radic Biol Med 45(5):602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.05.003
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S (2002) Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res 62(18):5196–5203
Tian H, Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Leng Y, Tao J, Li L, Qiu Z et al (2021) Activation of NRF2/FPN1 pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by regulating iron homeostasis and ferroptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones 27(2):149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-022-01257-1
Tian Q, Qin B, Gu Y, Zhou L, Chen S, Zhang S, Zhang S et al (2020) ROS-mediated necroptosis is involved in iron overload-induced osteoblastic cell death. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:1295382. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1295382
Toldo S, Mauro AG, Cutter Z, Abbate A (2018) Inflammasome, pyroptosis, and cytokines in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 315(6):H1553-h1568. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00158.2018
Turer AT, Hill JA (2010) Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy. Am J Cardiol 106(3):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.03.032
Ursini F, Maiorino M (2020) Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med 152:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
van Meer G, Voelker DR, Feigenson GW (2008) Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(2):112–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2330
Vanden Hoek TL, Li C, Shao Z, Schumacker PT, Becker LB (1997) Significant levels of oxidants are generated by isolated cardiomyocytes during ischemia prior to reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29(9):2571–2583. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.1997.0497
Vinten-Johansen J (2004) Involvement of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of lethal myocardial reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 61(3):481–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.10.011
Wallert M, Ziegler M, Wang X, Maluenda A, Xu X, Yap ML, Witt R et al (2019) α-Tocopherol preserves cardiac function by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Redox Biol 26:101292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101292
Wang R, Wang M, Zhou J, Wu D, Ye J, Sun G, Sun X. 2020. Saponins in Chinese herbal medicine exerts protection in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: possible mechanism and target analysis. Front Pharmacol 11:570867. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.570867
Wang Z, Yao M, Jiang L, Wang L, Yang Y, Wang Q, Qian X et al (2022) Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced ferroptosis via AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 axis. Biomed Pharmacother 154:113572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113572
Ward DM, Cloonan SM (2019) Mitochondrial iron in human health and disease. Annu Rev Physiol 81:453–482. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114742
Williams RE, Zweier JL, Flaherty JT (1991) Treatment with deferoxamine during ischemia improves functional and metabolic recovery and reduces reperfusion-induced oxygen radical generation in rabbit hearts. Circulation 83(3):1006–1014. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.83.3.1006
Wofford JD, Chakrabarti M, Lindahl PA (2017) Mössbauer spectra of mouse hearts reveal age-dependent changes in mitochondrial and ferritin iron levels. J Biol Chem 292(13):5546–5554. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.777201
Wu X, Iroegbu CD, Peng J, Guo J, Yang J, Fan C (2021) Cell death and exosomes regulation after myocardial infarction and ischemia-reperfusion. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:673677. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.673677
Xu J, Zhang M, Liu F, Shi L, Jiang X, Chen C, Wang J et al (2021a) Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate post-resuscitation cardiac and cerebral injuries by inhibiting cell pyroptosis and ferroptosis in a swine model of cardiac arrest. Front Pharmacol 12:793829. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.793829
Xu S, Wu B, Zhong B, Lin L, Ding Y, Jin X, Huang Z et al (2021b) Naringenin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating the nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) /System xc-/ glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis to inhibit ferroptosis. Bioengineered 12(2):10924–10934. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1995994
Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E, Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ, Wolpaw AJ et al (2007) RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 447(7146):864–868. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05859
Yan B, Ai Y, Sun Q, Ma Y, Cao Y, Wang J, Zhang Z et al (2021) Membrane damage during ferroptosis is caused by oxidation of phospholipids catalyzed by the oxidoreductases POR and CYB5R1. Mol Cell 81(2):355-369.e310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.024
Yang L, Xie P, Wu J, Yu J, Li X, Ma H, Yu T et al (2020) Deferoxamine treatment combined with sevoflurane postconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by restoring HIF-1/BNIP3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy in GK rats. Front Pharmacol 11:6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00006
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR (2016) Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(34):E4966-4975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH et al (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156(1–2):317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2008) Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem Biol 15(3):234–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.02.010
Yao Y, Li F, Zhang M, Jin L, Xie P, Liu D, Zhang J et al (2022) Targeting CaMKII-δ9 ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting myocardial inflammation. Circ Res 130(6):887–903. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.121.319478
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ (2007) Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med 357(11):1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra071667
Yin H, Xu L, Porter NA (2011) Free radical lipid peroxidation: mechanisms and analysis. Chem Rev 111(10):5944–5972. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200084z
Yu L, Gong B, Duan W, Fan C, Zhang J, Li Z, Xue X et al (2017) Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats by preserving mitochondrial function: role of AMPK-PGC-1α-SIRT3 signaling. Sci Rep 7:41337. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41337
Yu LM, Dong X, Xue XD, Xu S, Zhang X, Xu YL, Wang ZS et al (2021) Melatonin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy and reduces myocardial vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial quality control: role of SIRT6. J Pineal Res 70(1):e12698. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12698
Yu P, Zhang J, Ding Y, Chen D, Sun H, Yuan F, Li S et al (2022) Dexmedetomidine post-conditioning alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by ferroptosis inhibition via SLC7A11/GPX4 axis activation. Hum Cell 35(3):836–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00682-9
Zhang B, Zhai M, Li B, Liu Z, Li K, Jiang L, Zhang M et al (2018) Honokiol ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis through activating the SIRT1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:3159801. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3159801
Zhang J, Huang L, Shi X, Yang L, Hua F, Ma J, Zhu W et al (2020) Metformin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 12(23):24270–24287. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202143
Zhang JK, Zhang Z, Guo ZA, Fu Y, Chen XJ, Chen WJ, Wu HF et al (2022) The BMSC-derived exosomal lncRNA Mir9-3hg suppresses cardiomyocyte ferroptosis in ischemia-reperfusion mice via the Pum2/PRDX6 axis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 32(2):515–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2021.10.017
Zhang M, Wei L, Xie S, Xing Y, Shi W, Zeng X, Chen S et al (2021a) Activation of Nrf2 by lithospermic acid ameliorates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by promoting phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα). Front Pharmacol 12:794982. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.794982
Zhang Q, Hu Y, Hu JE, Ding Y, Shen Y, Xu H, Chen H et al (2021b) Sp1-mediated upregulation of Prdx6 expression prevents podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy via mitigation of oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Life Sci 278:119529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119529
Zhang T, Tsutsuki H, Islam W, Ono K, Takeda K, Akaike T, Sawa T (2021c) ATP exposure stimulates glutathione efflux as a necessary switch for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol 41:101930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101930
Zhang Y, Ren X, Wang Y, Chen D, Jiang L, Li X, Li T et al (2021d) Targeting ferroptosis by polydopamine nanoparticles protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(45):53671–53682. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c18061
Zhao J, Wang F, Zhang Y, Jiao L, Lau WB, Wang L, Liu B et al (2013) Sevoflurane preconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via caveolin-3-dependent cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition. Circulation 128(11 Suppl 1):S121-129. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.112.000045
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Tang D (2020) Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 66:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.03.002
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Hu S, Shi C, Zhu P, Ma Q, Jin Q et al (2017) Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res 63(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12413
Zhu H, Zhou H (2021) Novel Insight into the role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:5529810. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5529810
Zilka O, Shah R, Li B, Friedmann Angeli JP, Griesser M, Conrad M, Pratt DA (2017) On the mechanism of cytoprotection by ferrostatin-1 and liproxstatin-1 and the role of lipid peroxidation in ferroptotic cell death. ACS Cent Sci 3(3):232–243. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00028
Zweier JL, Flaherty JT, Weisfeldt ML (1987) Direct measurement of free radical generation following reperfusion of ischemic myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84(5):1404–1407. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.5.1404
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81804045), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2021LZY038 and ZR2021LZY011), Shandong Provincial TCM Science and Technology Development Plan Project (2021M180), and Qilu School of Chinese Medicine Academic School Inheritance Project (Ip2022-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xijin Wei and Juan Zhang designed and directed the project. Ke Zhao and Xiaoshu Chen wrote the manuscript. Yujing Bian, Zhou Zhou, collected materials. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. The authors confirm that no paper mill and artificial intelligence was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, K., Chen, X., Bian, Y. et al. Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 2269–2286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02506-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02506-5