Abstract
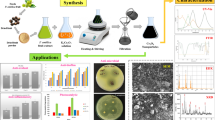
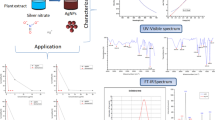
The distribution and phytochemistry of the non-nitrogen fixing, filamentous cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Lyngbya sp., and the inherent antimicrobial and anticancer activities of its phycochemicals as well as of the biosynthesized nanoparticles as their pharmaceutical potencies are considered. Several phycocompounds of curio, apramide, apratoxin, benderamide, cocosamides, deoxymajusculamide, flavonoids, lagunamides, lipids, proteins, amino acids, lyngbyabellin, lyngbyastatin, majusculamide, peptides, etc. were isolated from Lyngbya sp., which had a lot of potential pharmaceutical activities; those compounds had antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, ultraviolet protectant, and other activities. Particularly, several Lyngbya phycocompounds had potent antimicrobial potencies, seen through in vitro controlling of several frequently encountered multidrug-resistant (MDR) clinically belligerent strains of pathogenic bacteria isolated from clinical samples. The aqueous extracts of Lyngbya sp. were used for the synthesis of silver and copper oxide nanoparticles, which were used in pharmacological trials too. The nanoparticles biosynthesized with Lyngbya sp. had several uses such as biofuel, agro-based applications, in cosmetics, and industrial uses as biopolymers, and being potent antimicrobial and anticancer agents and in drug-delivery too, as medical applications. It could be concluded that the Lyngbya phycochemicals and the biosynthesized nanoparticles have future uses as antimicrobial namely as bacterial and fungal and anti-cancer agents, with promising medical and industrial uses.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Awadhi FH, Ratnayake R, Paul VJ, Luesch H (2016) Tasiamide F, a potent inhibitor of cathepsins D and E from a marine cyanobacterium. Bioorg Med Chem 24:3276–3282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2016.04.062
Armstrong GL, MacCannell DR, Taylor J et al (2020) Pathogen genomics in public health. Obstet Gynecol Surv 75:275–276
Ashaolu TJ, Samborska K, Lee CC et al (2021) Phycocyanin, a super functional ingredient from algae; properties, purification characterization, and applications. Int J Biol Macromol 193:2320–2331
Bela RB, Malliga P, Info P, Clewe V (2015) Treatment of textile dye effluent using marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. with different agrowastes and its effect on the growth of cyanobacterium. J Environ Sci 36:623–626
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA et al (2017) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 34:235–294. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6np00124f
Bonnard I, Rolland M, Francisco C, Banaigs B (1997) Total structure and biological properties of laxaphycins A and B, cyclic lipopeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Chandra R, Das P, Vishal G, Nagra S (2019) Factors affecting the induction of UV protectant and lipid productivity in Lyngbya for sequential biorefinery product recovery. Bioresour Technol 278:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.084
Chandra R, Pons-Faudoa FP, Parra Saldívar R, Rittmann BE (2020) Effect of ultra-violet exposure on production of mycosporine-like amino acids and lipids by Lyngbya purpurem. Biomass Bioenergy 134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105475
Chen J, Fu XG, Zhou L et al (2009) A convergent route for the total synthesis of malyngamides O, P, Q, and R. J Org Chem 74:4149–4157. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo9003103
Chen L, Li T, Guan L et al (2011) Flocculating activities of polysaccharides released from the marine mat-forming cyanobacteria Microcoleus and Lyngbya. Aquat Biol 11:243–248. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00309
Chen J and Forsyth CJ (2004) Total synthesis of the marine cyanobacterial cyclodepsipeptide apratoxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:12067–12072. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402752101
Choi H, Mevers E, Byrum T, et al (2012) Lyngbyabellins K-N from two Palmyra atoll collections of the marine cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii. European J Org Chem 5141–5150. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201200691
da Silva RMG, Amâncio IFN, de Andrade AR et al (2022) Phytotoxic, cytogenotoxic, and insecticidal activities of compounds from extracts of freshwater Lyngbya sp. J Toxic Environ Health Part a: Curr Issue 85:881–895. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2022.2102100
Dash S, Parida S, et al (2022) In vitro screening of antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticancer activities of cyanobacteria found across Odisha coast, India. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1272821/v1
Dawadi S, Katuwal S, Gupta A, et al (2021) Current research on silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and applications. J Nanomater 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6687290
Devi A, Prasanth S, Murugesh E et al (2016) A novel, poly(ethyl ethylene ether) inhibitor to trypsin from marine cyanobacteria, Lyngbya confervoides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1916-4
Ding CYG, Ong JFM, Goh HC, et al (2018) Benderamide A, a cyclic depsipeptide from a Singapore collection of marine cyanobacterium cf. Lyngbya sp. Mar Drugs 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16110409
El-Sheekh M, Abdel-Daim MM, Okba M, et al (2021) Green technology for bioremediation of the eutrophication phenomenon in aquatic ecosystems: a review. Afr J Aquat Sci 46:274–292. https://doi.org/10.2989/16085914.2020.1860892
Fuentes-Tristan S, Parra-Saldivar R, Iqbal HMN, Carrillo-Nieves D (2019) Bioinspired biomolecules: Mycosporine-like amino acids and scytonemin from Lyngbya sp. with UV-protection potentialities. Photobiol B, Biol 201:111684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111684
Fuwa H, Okuaki Y, Yamagata N, Sasaki M (2015) Total synthesis, stereochemical reassignment, and biological evaluation of (−)-lyngbyaloside B. Angew Chem 127:882–887. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201409629
Gunasekera SP, Owle CS, Montaser R et al (2011) Malyngamide 3 and cocosamides A and B from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula from Cocos lagoon, Guam. J Nat Prod 74:871–876. https://doi.org/10.1021/np1008015
Gutiérrez M, Suyama TL, Engene N et al (2008) Apratoxin D, a potent cytotoxic cyclodepsipeptide from Papua New Guinea collections of the marine cyanobacteria Lyngbya majuscula and Lyngbya sordida. J Nat Prod 71:1099–1103. https://doi.org/10.1021/np800121a
Gutiérrez M, Tidgewell K, Capson TL et al (2010) Malyngolide dimer, a bioactive symmetric cyclodepside from the Panamanian marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 73:709–711. https://doi.org/10.1021/np9005184
Han B, Goeger D, Maier CS, Gerwick WH (2005) The wewakpeptins, cyclic depsipeptides from a Papua New Guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J Org Chem 70:3133–3139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo0478858
Han B, Reinscheid UM, Gerwick WH, Gross H (2011) The structure elucidation of isomalyngamide K from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula by experimental and DFT computational methods. J Mol Struct 989:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.01.012
Harrigan GG, Yoshida WY, Moore RE et al (1998) Isolation, structure determination, and biological activity of dolastatin 12 and lyngbyastatin 1 from Lyngbya majuscula/Schizothrix calcicola cyanobacterial assemblages. J Nat Prod 61:1221–1225. https://doi.org/10.1021/np9801211
https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0060121B1/en. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://patents.google.com/patent/EP2935566A4. Accessed 27.02.2023
https://patents.google.com/patent/PT1888766E/en. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://patents.google.com/patent/US4342751A/en. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2012101459A2. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2019023524A3/en. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://patents.justia.com/patent/6812011. Accessed 27 February 2023
https://www.osti.gov/doepatents/biblio/1426794. Accessed 27 February 2023
Iwasaki A, Teruya T, Suenaga K (2010) Isolation and structure of koshikalide, a 14-membered macrolide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Tetrahedron Lett 51:959–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.12.041
Iwasaki A, Ohno O, Sumimoto S et al (2015) Jahanyne, an apoptosis-inducing lipopeptide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Org Lett 17:652–655. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol5036722
Janani B, Farraj al DA, Raju LL et al (2020) Cytotoxicological evaluation of copper oxide nanoparticles on green algae, bacteria and crustacean systems. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18:1465–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00561-1
Knights KM, Mangoni AA, Miners JO (2010) Defining the COX inhibitor selectivity of NSAIDs: implications for understanding toxicity. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 3:769–776
Kumar M, Tripathi MK, Srivastava A et al (2013) Cyanobacteria, Lyngbya aestuarii and Aphanothece bullosa as antifungal and antileishmanial drug resources. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:458–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60096-9
Kumar M, Singh P, Tripathi J et al (2014) Identification and structure elucidation of antimicrobial compounds from Lyngbyaaestuarii and Aphanothecebullosa. Cell Mol Biol 60:82–89. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2014.60.5.14
Kushwaha D, Srivastava N, Prasad D, et al (2020) Biobutanol production from hydrolysates of cyanobacteria Lyngbya limnetica and Oscillatoria obscura. Fuel 271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117583
Levert A, Alvariño R, Bornancin L et al (2018) Structures and activities of tiahuramides A-C, cyclic depsipeptides from a Tahitian collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 81:1301–1310. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00751
Liu L, Rein KS (2010) New peptides isolated from Lyngbya species: A review. Mar Drugs 8:1817–1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8061817
Lopez JAV, Al-Lihaibi SS, Alarif WM et al (2016) Wewakazole B, a Cytotoxic cyanobactin from the cyanobacterium Moorea producens collected in the red sea. J Nat Prod 79:1213–1218. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00051
López-Pacheco IY, Fuentes-Tristan S, Rodas-Zuluaga LI, et al (2020) Influence of low salt concentration on growth behavior and general biomass composition in Lyngbya purpurem (cyanobacteria). Mar Drugs 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120621
Luesch H, Yoshida WY, Moore RE, Paul VJ (2002) Structurally diverse new alkaloids from Palauan collections of the apratoxin-producing marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Tetrahedron 58:7959–7966. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00895-5
Luo D, Chen QY, Luesch H (2016) Total synthesis of the potent marine-derived elastase inhibitor lyngbyastatin 7 and in vitro biological evaluation in model systems for pulmonary diseases. J Org Chem 81:532–544. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.5b02386
MacMillan JB, Ernst-Russell MA, de Ropp JS, Molinski TF (2002) Lobocyclamides A-C, lipopeptides from a cryptic cyanobacterial mat containing Lyngbya confervoides. J Org Chem 67:8210–8215. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo0261909
Manogar P, Vijayakumar S, Praseetha PK (2020) Evaluation of antioxidant and neuroprotective activities of Lyngbya majuscula on human neural tissues. Gene Rep 19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100661
Matthew S, Ross C, Rocca JR et al (2007) Lyngbyastatin 4, a dolastatin 13 analogue with elastase and chymotrypsin inhibitory activity from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides. J Nat Prod 70:124–127. https://doi.org/10.1021/np060471k
Matthew S, Salvador LA, Schupp PJ et al (2010) Cytotoxic halogenated macrolides and modified peptides from the apratoxin-producing marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii from Guam. J Nat Prod 73:1544–1552. https://doi.org/10.1021/np1004032
McPhail KL, Correa J, Linington RG et al (2007) Antimalarial linear lipopeptides from a Panamanian strain of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 70:984–988. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0700772
Meerow A (2014) Anwer, Abdulkareem (2014) Antibacterial activity of Lyngbya and Chroococcus species isolated from Koya (Hizoop River). J Life Sci 8:925–930. https://doi.org/10.17265/1934-7391/2014.12.001
Mesguiche V, Valls R, Piovetti L, et al (1999) Characterization and synthesis of (-)-7-methoxydodec-4(E)-enoic acid, a novel fatty acid isolated from Lyngbya majuscula Tetrahedron Lett 40:7473–7476. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(99)01532-4
Montaser R, Paul VJ, Luesch H (2011) Pitipeptolides C-F, antimycobacterial cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula from Guam. Phytochemistry 72:2068–2074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.07.014
Moore RE and Entzeroth M (1988). Majusculamide D and deoxymajusculamide D, two cytotoxins from Lyngbya majuscula. Phytochem 27:3101-3103
Nandagopal P, Steven AN, Chan LW, et al (2021) Bioactive metabolites produced by cyanobacteria for growth adaptation and their pharmacological properties. Biology (Basel) 10:. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101061
Narayana S, Tapase S, Thamke V, et al (2020) Primary screening for the toxicity of marine cyanobacteria Lyngbya bouillonii (Cyanophyceae: Oscillatoriales) recorded for the first time from Indian Ocean. Reg Stud Mar Sci 40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101510
Ohno O, Watanabe A, Morita M, Suenaga K (2014) Biselyngbyolide B, a novel ER stress-inducer isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Chem Lett 43:287–289. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.130960
Ohta S, Ono F, Shiomi Y, et al (1998) Anti-herpes simplex Virus substances produced by the marine green alga, Dunaliella primolecta. J Appl Phycol 10:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008065226194
Omoregie EO, Crumbliss LL, Bebout BM, Zehr JP (2004) Comparison of diazotroph community structure in Lyngbya sp. and Microcoleus chthonoplastes dominated microbial mats from Guerrero Negro, Baja. Mexico FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:305–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00301-5
Patel V, Berthold D, Puranik P, Gantar M (2015) Screening of cyanobacteria and microalgae for their ability to synthesize silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity. Biotechnol Rep 5:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2014.12.001
Pereira AR, McCue CF, Gerwick WH (2010) Cyanolide A, a glycosidic macrolide with potent molluscicidal activity from the Papua New Guinea cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii. J Nat Prod 73:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1021/np9008128
Popplewell WL, Ratnayake R, Wilson JA et al (2011) Grassypeptolides F and G, cyanobacterial peptides from Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 74:1686–1691. https://doi.org/10.1021/np2005083
Prasannabalaji N, Ramya VP, Muralitharan G (2017) In vitro assessment of Lyngbya sp. and Phormidium sp. extracts for antibacterial and antioxidant properties. J Algal Biomass Util 8:16–29
Rai SK, Ganeshan S, Mariappan R et al (2021) Mesoporous nanoparticles for the delivery of (9S, E)-8-ethyl-9-methylnonadec-6-en-3-one (EME): A study of anti-inflammatory and tumor suppressing potential in RAW 264.7, He La and HepG2 cell lines. Process Biochem 111:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.10.004
Rastogi RP, Incharoensakdi A (2014) Characterization of UV-screening compounds, mycosporine-like amino acids, and scytonemin in the cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. CU2555. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:244–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12220
Rastogi RP, Sonani RR, Madamwar D (2015) Effects of PAR and UV radiation on the structural and functional integrity of phycocyanin, phycoerythrin and allophycocyanin isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. A09DM. Photochem Photobiol 91:837–844. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12449
Rivas L, Rojas V (2019) Cyanobacterial peptides as a tour de force in the chemical space of antiparasitic agents. Arch Biochem Biophys 664:24–39
Salvador LA, Paul VJ, Luesch H (2010) Caylobolide B, a macrolactone from symplostatin 1-producing marine cyanobacteria Phormidium spp. from Florida. J Nat Prod 73:1606–1609. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100467d
Sameer Kumar R, Shakambari G, Ashokkumar B, Varalakshmi P (2019) Inhibition of advanced glycation end products formation and inflammation in C. elegans: Studies of potential of Lyngbya sp. against expression of stress related genes and Live cell imaging. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.11.020
Sampathkumar Y, Elumali S, Halith AM (2020) GCMS determination of anticancer, anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial compounds from salt tolerance microalgae (Lyngbya sp. Nostoc sp. and Phormidium sp.) Isolated from Marakkanam Salt Pan, Tamil Nadu, India. Eng Sci 11:1139–1152
Sasaki H, Teruya T, Fukazawa H, Suenaga K (2011) Revised structure and structure-activity relationship of bisebromoamide and structure of norbisebromoamide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Tetrahedron 67:990–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2010.11.106
Singh IP, Milligan KE, Gerwick WH (1999) Tanikolide, a toxic and antifungal lactone from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 62:1333–1335. https://doi.org/10.1021/np990162c
Swain SS, Padhy RN, Singh PK (2015) Anticancer compounds from cyanobacterium Lyngbya species: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:223–265
Tan LT (2007) Bioactive natural products from marine cyanobacteria for drug discovery. Phytochemistry 68:954–979
Tan LT, Okino T, Gerwick WH (2000) Hermitamides A and B, toxic malyngamide-type natural products from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 63:952–955. https://doi.org/10.1021/np000037x
Tan LT, Márquez BL, Gerwick WH (2002) Lyngbouilloside, a novel glycosidic macrolide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii. J Nat Prod 65:925–928. https://doi.org/10.1021/np010526c
Tang YH, Liang TT, Fan TT et al (2020) Neo-debromoaplysiatoxin C, with new structural rearrangement, derived from debromoaplysiatoxin. Nat Prod Res 34:2151–2156. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1577840
Teruya T, Sasaki H, Fukazawa H, Suenaga K (2009) Bisebromoamide, a potent cytotoxic peptide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp.: Isolation, stereostructure, and biological activity. Org Lett 11:5062–5065. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol9020546
Thuan NH, An TT, Shrestha A, et al (2019) Recent advances in exploration and biotechnological production of bioactive compounds in three cyanobacterial genera: Nostoc, Lyngbya, and Microcystis. Front Chem 7:604. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00604
Todd’ JS, Gerwick’ WH (1995) Malyngamide I from the tropical marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula and the probable structure revision of stylocheilamide. Tetrahedron Lett 36:7837–7840. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4039(95)01662-2
Tripathi A, Puddick J, Prinsep MR et al (2010) Lagunamides A and B: cytotoxic and antimalarial cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 73:1810–1814. https://doi.org/10.1021/np100442x
Watanabe A, Ohno O, Morita M et al (2015) Structures and biological activities of novel biselyngbyaside analogs isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 88:1256–1264. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20150117
White JD, Xu Q, Lee CS, Valeriote FA et al (2004) Total synthesis and biological evaluation of (+)-kalkitoxin, a cytotoxic metabolite of the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Org Biomol Chem 2:2092–2102. https://doi.org/10.1039/B404205K
Williams PG, Yoshida WY, Moore RE, Paul VJ (2002) Isolation and structure determination of obyanamide, a novel cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides. J Nat Prod 65:29–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0102253
Williams PG, Moore RE, Paul VJ (2003) Isolation and structure determination of lyngbyastatin 3, a lyngbyastatin 1 homologue from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. determination of the configuration of the 4-amino-2,2-dimethyl-3-oxopentanoic acid unit in majusculamide c, dolastatin 12, lyngbyastatin 1, and lyngbyastatin 3 from cyanobacteria. J Nat Prod 66:1356–1363. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0302145
Youssef DT, Mufti SJ, Badiab AA, Shaala LA (2022) Anti-infective secondary metabolites of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya morphotype between 1979 and 2022. Mar Drugs 20:768. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120768
Zainuddin EN, Jansen R, Nimtz M et al (2009) Lyngbyazothrins A-D, antimicrobial cyclic undecapeptides from the cultured cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. J Nat Prod 72:1373–1378. https://doi.org/10.1021/np8007792
Zhang HH, Zhang XK, Si RR, et al (2020) Chemical and biological study of novel aplysiatoxin derivatives from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Toxins (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110733
Zheng LH, Wang YJ, Sheng J et al (2011) Antitumor peptides from marine organisms. Mar Drugs 9:1840–1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101840
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Prof. S. Mishra, Dean, IMS and Sum Hospital, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, for encouragements, and Prof. Dr. M.R. Nayak, President of the SOA University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: Writing – original draft, collected the reference materials. SB, AKB, CPM and CRS: Conceptualization, writing – original draft, reviewing and editing. RNP: reviewing and editing, and Supervision. All the authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors confirm that no paper mill and artificial intelligence was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• An overview of Lyngbya sp. and their pharmacological actions.
• Phycochemicals derived from Lyngbya sp. are described in detail.
• Synthesis of nanoparticles by Lyngbya sp. and their industrial applications.
• Providing an insightful reference for future research on drug development.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, S., Bej, S., Bishoyi, A.K. et al. Recent progression on phytochemicals and pharmacological properties of the filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp.. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 2197–2216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02488-4