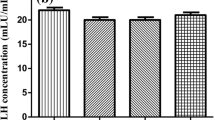
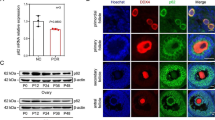
Abstract
Chemotherapeutic platinum-containing drugs are widely used to treat a variety of cancer types; however, they cause ovarian failure and infertility. The aim of this study is to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying the potential protective effect of resveratrol against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in a rat model. Female rats were given either cisplatin (6 mg/kg, i.p., once per week for two consecutive weeks) and/or resveratrol (10 mg/kg, orally for 17 days). Follicular development, ovarian function markers, as well as apoptotic and inflammatory markers were assessed 24 h after the last resveratrol dose. Resveratrol ameliorated the marked follicular loss and the significant reduction in anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) level triggered by cisplatin. Mechanistically, cisplatin elicited a potent inflammatory response in ovarian tissue as evidenced by the elevated expression of tumor necrosis factor, nuclear factor kappa-B, and proinflammatory enzymes. Co-treatment with resveratrol inhibited the elevation in inflammatory mediators induced by cisplatin. Further, cisplatin switched on the apoptotic machinery in ovarian tissues via increasing the expression of both cytochrome c and caspase-3 which was reversed upon resveratrol co-treatment. Resveratrol also counteracts the upregulating poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase expression which could attribute to the inflammatory and apoptotic effects of cisplatin. Resveratrol protects the ovary from cisplatin-induced toxicity through preventing the loss of the AMH-secreting granulosa cells, diminishing PARP-1 expression, and downregulating the inflammatory and apoptotic events implicated in cisplatin toxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altuner D, Gulaboglu M, Yapca OE, Cetin N (2013) The effect of mirtazapine on cisplatin-induced oxidative damage and infertility in rat ovaries. Sci World J 2013:327240. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/327240
Atli M, Engin-Ustun Y, Tokmak A, Caydere M, Hucumenoglu S, Topcuoglu C (2017) Dose dependent effect of resveratrol in preventing cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in rats: an experimental study. Reprod Biol 17:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbio.2017.07.001
Blumenfeld Z (2012) Chemotherapy and fertility. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 26:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2011.11.008
Boots C, Jungheim E (2015) Inflammation and human ovarian follicular dynamics. Semin Reprod Med 33:270–275. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1554928
Braw RH, Tsafriri A (1980) Effect of PMSG on follicular atresia in the immature rat ovary. J Reprod Fertil 59:267–272
Britt KL, Drummond AE, Cox VA, Dyson M, Wreford NG, Jones MEE, Simpson ER, Findlay JK (2000) An age-related ovarian phenotype in mice with targeted disruption of the Cyp 19 (aromatase) gene. Endocrinology 141:2614–2623. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.141.7.7578
Carter LG, D’Orazio JA, Pearson KJ (2014) Resveratrol and cancer: focus on in vivo evidence. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:R209–R225. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-13-0171
Chang Z, Wang HL, Du H (2014) Protective effect of Ginkgo flavonoids, amifostine, and leuprorelin against platinum-induced ovarian impairment in rats. Genet Mol Res 13:5276–5284. https://doi.org/10.4238/2014.July.24.6
Chang EM, Lim E, Yoon S, Jeong K, Bae S, Lee DR, Yoon TK, Choi Y, Lee WS (2015) Cisplatin induces overactivation of the dormant primordial follicle through PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a pathway which leads to loss of ovarian reserve in mice. PLoS One 10:e0144245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144245
Chen Z-G, Luo L-L, Xu J-J, Zhuang XL, Kong XX, Fu YC (2010) Effects of plant polyphenols on ovarian follicular reserve in aging rats. Biochem Cell Biol 88:737–745. https://doi.org/10.1139/O10-012
Chowdhury S, Sinha K, Banerjee S, Sil PC (2016) Taurine protects cisplatin induced cardiotoxicity by modulating inflammatory and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Biofactors 42:647–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1301
Codacci-Pisanelli G, Del Pup L, Del Grande M, Peccatori FA (2017) Mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage in breast cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 113:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.009
Deorukhkar A, Krishnan S (2010) Targeting inflammatory pathways for tumor radiosensitization. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1904–1914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.039
Engelke LH, Hamacher A, Proksch P, Kassack MU (2016) Ellagic acid and resveratrol prevent the development of cisplatin resistance in the epithelial ovarian cancer cell line A2780. J Cancer 7:353–363. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.13754
Fabbri R, Macciocca M, Vicenti R, Paradisi R, Klinger FG, Pasquinelli G, Spisni E, Seracchioli R, Papi A (2016) Doxorubicin and cisplatin induce apoptosis in ovarian stromal cells obtained from cryopreserved human ovarian tissue. Future Oncol 12:1699–1711. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2016-0032
Fanchin R, Schonäuer LM, Righini C, Guibourdenche J, Frydman R, Taieb J (2003) Serum anti-Müllerian hormone is more strongly related to ovarian follicular status than serum inhibin B, estradiol, FSH and LH on day 3. Hum Reprod 18:323–327
Gruijters MJG, Visser JA, Durlinger ALL, Themmen APN (2003) Anti-Müllerian hormone and its role in ovarian function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 211:85–90
Hansen KR, Knowlton NS, Thyer AC, Charleston JS, Soules MR, Klein NA (2008) A new model of reproductive aging: the decline in ovarian non-growing follicle number from birth to menopause. Hum Reprod 23:699–708. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dem408
Hansen KR, Hodnett GM, Knowlton N, Craig LB (2011) Correlation of ovarian reserve tests with histologically determined primordial follicle number. Fertil Steril 95:170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.04.006
Honma S, Takahashi N, Shinohara M, Nakamura K, Mitazaki S, Abe S, Yoshida M (2013) Amelioration of cisplatin-induced mouse renal lesions by a cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 selective inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 715:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.023
Hu S, Li X, Xu R, Ye L, Kong H, Zeng X, Wang H, Xie W (2016) The synergistic effect of resveratrol in combination with cisplatin on apoptosis via modulating autophagy in A549 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai 48:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmw026
Jabbour HN, Sales KJ, Catalano RD, Norman JE (2009) Inflammatory pathways in female reproductive health and disease. Reproduction 138:903–919. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-09-0247
Jiang M, Wang C-Y, Huang S, Yang T, Dong Z (2009) Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient renal cells via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 296:F983–F993. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.90579.2008
Kaygusuzoglu E, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM et al (2018) Zingerone ameliorates cisplatin-induced ovarian and uterine toxicity via suppression of sex hormone imbalances, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in female Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.119
Kong X-X, Fu Y-C, Xu J-J, Zhuang XL, Chen ZG, Luo LL (2011) Resveratrol, an effective regulator of ovarian development and oocyte apoptosis. J Endocrinol Investig 34:e374–e381. https://doi.org/10.3275/7853
Kumar P, Barua CC, Sulakhiya K, Sharma RK (2017) Curcumin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and potentiates its anticancer activity in SD rats: potential role of curcumin in breast cancer chemotherapy. Front Pharmacol 8:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00132
Lee Y-J, Lee GJ, Yi SS, Heo SH, Park CR, Nam HS, Cho MK, Lee SH (2016) Cisplatin and resveratrol induce apoptosis and autophagy following oxidative stress in malignant mesothelioma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 97:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.08.033
Li D, Chen Y, Qi L, Ju X, Liu H, Wang G (2013a) Differentially expressed genes in cisplatin-induced premature ovarian failure in rats. Anim Reprod Sci 137:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2012.11.011
Li X, Yang S, Lv X et al (2013b) The mechanism of mesna in protection from cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in female rats. J Gynecol Oncol 24:177–185. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2013.24.2.177
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F, Shiloh A, Guarente L, Gu W (2001) Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell 107:137–148
Makogon N, Voznesenskaya T, Bryzgina T, Sukhina V, Grushka N, Alexeyeva I (2010) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, 3-aminobenzamide, protects against experimental immune ovarian failure in mice. Reprod Biol 10:215–226
Malhotra A, Bath S, Elbarbry F (2015) An organ system approach to explore the antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective actions of resveratrol. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:803971. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/803971
Mark-Kappeler CJ, Hoyer PB, Devine PJ (2011) Xenobiotic effects on ovarian preantral follicles. Biol Reprod 85:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.111.091173
Máthé C, Szénási G, Sebestény A, Blázovics A, Szentmihályi K, Hamar P, Albert M (2014) Protective effect of CV247 against cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327113480972
Meng H, Fu G, Shen J, Shen K, Xu Z, Wang Y, Jin B, Pan H (2017) Ameliorative effect of daidzein on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via modulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell death. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:3140680. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3140680
Morgan S, Anderson RA, Gourley C, Wallace WH, Spears N (2012) How do chemotherapeutic agents damage the ovary? Hum Reprod Update 18:525–535. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dms022
Morgan S, Lopes F, Gourley C, Anderson RA, Spears N (2013) Cisplatin and doxorubicin induce distinct mechanisms of ovarian follicle loss; imatinib provides selective protection only against cisplatin. PLoS One 8:e70117. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070117
Muttukrishna S, McGarrigle H, Wakim R, Khadum I, Ranieri DM, Serhal P (2005) Antral follicle count, anti-Mullerian hormone and inhibin B: predictors of ovarian response in assisted reproductive technology? BJOG 112:1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00670.x
Ndiaye M, Philippe C, Mukhtar H, Ahmad N (2011) The grape antioxidant resveratrol for skin disorders: promise, prospects, and challenges. Arch Biochem Biophys 508:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.12.030
Nguewa PA, Fuertes MA, Valladares B, Alonso C, Pérez JM (2005) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases: homology, structural domains and functions. Novel therapeutical applications. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 88:143–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2004.01.001
Özcan P, Fıçıcıoğlu C, Yıldırım ÖK, Özkan F, Akkaya H, Aslan İ (2015) Protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative damage to ovarian reserve in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Reprod BioMed Online 31:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.06.007
Özcan P, Fıçıcıoğlu C, Kizilkale O, Yesiladali M, Tok OE, Ozkan F, Esrefoglu M (2016) Can coenzyme Q10 supplementation protect the ovarian reserve against oxidative damage? J Assist Reprod Genet 33:1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-016-0751-z
Pepinsky RB, Sinclair LK, Chow EP, Mattaliano RJ, Manganaro TF, Donahoe PK, Cate RL (1988) Proteolytic processing of Mullerian inhibiting substance produces a transforming growth factor-beta-like fragment. J Biol Chem 263:18961–18964
Pervaiz S, Holme AL (2009) Resveratrol: its biologic targets and functional activity. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:2851–2897. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2412
Qin W-D, Liu G-L, Wang J, Wang H, Zhang JN, Zhang F, Ma Y, Ji XY, Li C, Zhang MX (2016) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibition protects cardiomyocytes from inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget 7:35618–35631. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8343
Rani N, Bharti S, Tomar A, Dinda AK, Arya DS, Bhatia J (2016) Inhibition of PARP activation by enalapril is crucial for its renoprotective effect in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Free Radic Res 50:1226–1236. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2016.1228923
Roness H, Kalich-Philosoph L, Meirow D (2014) Prevention of chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage: possible roles for hormonal and non-hormonal attenuating agents. Hum Reprod Update 20:759–774. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmu019
Rosendahl M, Andersen CY, la Cour Freiesleben N, Juul A, Løssl K, Andersen AN (2010) Dynamics and mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced ovarian follicular depletion in women of fertile age. Fertil Steril 94:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.02.043
Rossi V, Lispi M, Longobardi S, Mattei M, Rella FD, Salustri A, de Felici M, Klinger FG (2017) LH prevents cisplatin-induced apoptosis in oocytes and preserves female fertility in mouse. Cell Death Differ 24:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.97
Sahu BD, Kalvala AK, Koneru M, Mahesh Kumar J, Kuncha M, Rachamalla SS, Sistla R (2014) Ameliorative effect of fisetin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of NF-κB activation and antioxidant defence. PLoS One 9:e105070. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105070
Said RS, El-Demerdash E, Nada AS, Kamal MM (2016) Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory signaling implicated in ionizing radiation-induced premature ovarian failure through antagonistic crosstalk between silencing information regulator 1 (SIRT1) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1). Biochem Pharmacol 103:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.01.019
Tangir J, Zelterman D, Ma W, Schwartz PE (2003) Reproductive function after conservative surgery and chemotherapy for malignant germ cell tumors of the ovary. Obstet Gynecol 101:251–257
Tapodi A, Debreceni B, Hanto K, Bognar Z, Wittmann I, Gallyas F Jr, Varbiro G, Sumegi B (2005) Pivotal role of Akt activation in mitochondrial protection and cell survival by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 inhibition in oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 280:35767–35775. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507075200
Taskin MI, Yay A, Adali E, Balcioglu E, Inceboz U (2015) Protective effects of sildenafil citrate administration on cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in rats. Gynecol Endocrinol 31:272–277. https://doi.org/10.3109/09513590.2014.984679
Terraciano P, Garcez T, Ayres L, Durli I, Baggio M, Kuhl CP, Laurino C, Passos E, Paz AH, Cirne-Lima E (2014) Cell therapy for chemically induced ovarian failure in mice. Stem Cells Int 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/720753
Visser JA, Themmen APN (2005) Anti-Müllerian hormone and folliculogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 234:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2004.09.008
Vyas D, Laput G, Vyas AK (2014) Chemotherapy-enhanced inflammation may lead to the failure of therapy and metastasis. Onco Targets Ther 7:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S60114
Wallace WHB, Thomson AB, Saran F, Kelsey TW (2005) Predicting age of ovarian failure after radiation to a field that includes the ovaries. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:738–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.11.038
Yapca OE, Turan MI, Yilmaz I, Salman S, Gulapoglu M, Suleyman H (2014) Benefits of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of etoricoxib in the prevention of ovarian ischemia/reperfusion injury induced experimentally in rats. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 40:1674–1679. https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.12373
Yeh J, Kim BS, Peresie J (2008) Protection against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage by the antioxidant sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate (mesna) in female rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198:463.e1-6discussion 463.e6-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2007.12.027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS, EM, and EE conceived and designed the experiments. RS and EM performed the experiments. RS and EM analyzed the data. RS and EM contributed to the reagents/materials/analysis tools. RS, EM, and EE wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animals’ procedures in this study were conducted according to the Animal Ethics Committee, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt (Project no. 38).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Said, R.S., Mantawy, E.M. & El-Demerdash, E. Mechanistic perspective of protective effects of resveratrol against cisplatin-induced ovarian injury in rats: emphasis on anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 1225–1238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01662-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01662-x