Abstract
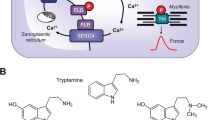
Serotonin (5-hydroxy-tryptamine, 5-HT) exerted concentration-dependent positive inotropic effects or positive chronotropic effects in transgenic (TG) mice which overexpress the human 5-HT4a receptor in the heart but not in littermate wild-type (WT) mice. These positive inotropic effects and positive chronotropic effects are thought to be mediated by cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cAMP) in TG cardiomyocytes. To determine whether these effects are antagonized by endogenous phosphodiesterases (PDEs), the inotropic and chronotropic effects of 5-HT were tested in the additional presence of the PDE inhibitor erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine hydrochloride (EHNA) (1 μM, a PDE2 inhibitor) or cilostamide (1 μM, a PDE3 inhibitor), rolipram (0.1 μM and 1 μM, a PDE4 inhibitor), and their combinations. For comparison, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), an unspecific PDE inhibitor, was investigated. The use of 10 μM IBMX, the combination of rolipram (1 μM) and EHNA (1 μM), and the combination of rolipram (0.1 μM) and cilostamide (1 μM) each increased the potency of 5-HT to elevate the force of contraction in TG mice, but not the potency of 5-HT to increase the beating rate in TG mice. This indicates that PDE4 and PDE2 regulate the inotropic but not the chronotropic effects of 5-HT in TG mice. In contrast, cilostamide (1 μM) alone, EHNA (1 μM) alone, or in combination decreased the potency of 5-HT to increase force of contraction in TG mice. In summary, our present data suggest that the positive chronotropic effect of 5-HT in TG mice does not involve PDE activities, whereas the positive inotropic effect of 5-HT and the basal force in TG mice are diminished by endogenous activity of PDE4. Phosphorylation of PDE4, when PDE2 or PDE3 is inhibited, might enhance the activity of PDE4.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal F, Andressen KW, Mørk HK, Aronsen JM, Sjaastad I, Dahl CP, Skomedal T, Levy FO, Osnes JB, Qvigstad E (2008) 5-HT4-elicited positive inotropic response is mediated by cAMP and regulated by PDE3 in failing rat and human cardiac ventricles. Br J Pharmacol 155(7):1005–1014. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.339
Barnes PJ (2013) Theophylline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188(8):901–906. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201302-0388PP
Bender AT, Beavo JA (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev 58(3):488–520. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.58.3.5
Berk E, Christ T, Schwarz S, Ravens U, Knaut M, Kaumann AJ (2016) In permanent atrial fibrillation, PDE3 reduces force responses to 5-HT, but PDE3 and PDE4 do not cause the blunting of atrial arrhythmias. Br J Pharmacol 173(16):2478–2489. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13525
Bethke T, Klimkiewicz A, Kohl C, von der Leyen H, Mehl H, Mende U, Meyer W, Neumann J, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Starbatty J, Stein B, Wenzlaff H, Döring V, Kalmár P, Haverich A (1991) Effects of isomazole on force of contraction and phosphodiesterase isoenzymes I-IV in nonfailing and failing human hearts. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18(3):386–397
Chiu YJ, Hu SH, Reid IA (1999) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase III with milrinone increases renin secretion in human subjects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290(1):16–19
D’Andrea MR, Qiu Y, Haynes-Johnson D, Bhattacharjee S, Kraft P, Lundeen S (2005) Expression of PDE11A in normal and malignant human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 53(7):895–903
Dal Piaz V, Giovannoni MP (2000) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, structurally unrelated to rolipram, as promising agents for the treatment of asthma and other pathologies. Eur J Med Chem 35(5):463–480
De Maeyer JH, Prins NH, Schuurkes JA, Lefebvre RA (2006) Differential effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine4 receptor agonists at gastric versus cardiac receptors: an operational framework to explain and quantify organ-specific behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317(3):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.101329
Galindo-Tovar A, Kaumann AJ (2008) Phosphodiesterase-4 blunts inotropism and arrhythmias but not sinoatrial tachycardia of (−)-adrenaline mediated through mouse cardiac beta(1)-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 153(4):710–720
Galindo-Tovar A, Vargas ML, Escudero E, Kaumann AJ (2009) Ontogenic changes of the control by phosphodiesterase-3 and -4 of 5-HT responses in porcine heart and relevance to human atrial 5-HT(4) receptors. Br J Pharmacol 156(2):237–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00023.x
Galindo-Tovar A, Vargas ML, Kaumann AJ (2016) Inhibitors of phosphodiesterases PDE2, PDE3, and PDE4 do not increase the sinoatrial tachycardia of noradrenaline and prostaglandin PGE1 in mice. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 389(2):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1178-2
Galindo-Tovar A, Vargas ML, Kaumann AJ (2018) Phosphodiesterase PDE2 activity, increased by isoprenaline, does not reduce β-adrenoceptor-mediated chronotropic and inotropic effects in rat heart. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 391:571–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1480-x
Gergs U, Neumann J, Simm A, Silber RE, Remmers FO, Läer S (2009) Phosphorylation of phospholamban and troponin I through 5-HT4-receptors in the isolated human atrium. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 379(4):349–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0371-y
Gergs U, Baumann M, Böckler A, Buchwalow IB, Ebelt H, Fabritz L, Günther S, Hauptmann S, Kirchhof P, Klöckner U, Pönicke K, Rückschloß U, Schmitz W, Schulz N, Werner F, Neumann J (2010) Cardiac overexpression of the human 5-HT4-receptor in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299(3):H788–H798. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00691.2009
Gergs U, Böckler A, Ebelt H, Hauptmann S, Keller N, Otto V, Pönicke K, Schmitz W, Neumann J (2013) Human 5-HT4-receptor stimulation in atria of transgenic mice. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 386(5):357–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0831-x
Gergs U, Jung F, Buchwalow IB, Hofmann B, Simm A, Treede H, Neumann J (2017) Pharmacological and physiological assessment of serotonin formation and degradation in isolated preparations from mouse and human heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 313(6):H1087–H1097. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00350.2017
Hayashi M, Matsushima K, Ohashi H, Tsunoda H, Murase S, Kawarada Y, Tanaka T (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of human PDE8B, a novel thyroid-specific isozyme of 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250(3):751–756
Kaumann AJ (1990) Piglet sinoatrial receptors resemble human atrial 5-HT4-like receptors. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 342(5):619–622
Kaumann AJ (2011) Phosphodiesterases reduce spontaneous sinoatrial beating but not the ‘fight or flight’ tachycardia elicited by agonists through Gs-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(7):377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2011.03.003
Kaumann AJ, Sanders L, Brown AM, Murray KJ, Brown MJ (1990) A 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor in human atrium. Br J Pharmacol 100(4):879–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14108.x
Kaumann AJ, Sanders L, Brown AM, Murray KJ, Brown MJ (1991) A 5-HT4-like receptor in human right atrium. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 344:150–159
Kim GE, Kass DA (2017) Cardiac phosphodiesterases and their modulation for treating heart disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol 243:249–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_82
Kirchhefer U, Baba HA, Hanske G, Jones LR, Kirchhof P, Schmitz W, Neumann J (2004) Age-dependent biochemical and contractile properties in atrium of transgenic mice overexpressing junctin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287(5):H2216–H2225. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00137.2004
Kloner RA, Chaitman B (2017) Angina and its management. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 22(3):199–209. https://doi.org/10.1177/1074248416679733 Epub 2016 Dec 14
Maurice DH, Ke H, Ahmad F, Wang Y, Chung J, Manganiello VC (2014) Advances in targeting cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(4):290–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4228
Neumann J, Boknik P, Matherne GP, Lankford A, Schmitz W (2003) Pertussis toxin sensitive and insensitive effects of adenosine and carbachol in murine atria overexpressing A1–adenosine receptors. Br J Pharmacol 138(1):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.070501
Orstavik O, Ata SH, Riise J, Dahl CP, Andersen GØ, Levy FO, Skomedal T, Osnes JB, Qvigstad E (2014) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-3 by levosimendan is sufficient to account for its inotropic effect in failing human heart. Br J Pharmacol 171(23):5169–5181. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12647
Packer M, Carver JR, Rodeheffer RJ, Ivanhoe RJ, DiBianco R, Zeldis SM, Hendrix GH, Bommer WJ, Elkayam U, Kukin ML, Mallis GI, Sollano JA, Shannon J, Tandon PK, DeMets DL (1991) Effect of oral milrinone on mortality in severe chronic heart failure. The PROMISE Study Research Group. N Engl J Med 325(21):1468–1475
Rabe KF, Bateman ED, O’Donnell D, Witte S, Bredenbröker D, Bethke TD (2005) Roflumilast—an oral anti-inflammatory treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366(9485):563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67100-0
Richter W, Xie M, Scheitrum C, Krall J, Movsesian MA, Conti M (2011) Conserved expression and functions of PDE4 in rodent and human heart. Basic Res Cardiol 106(2):249–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0138-8
Sanders L, Kaumann AJ (1992) A 5-HT4-like receptor in human left atrium. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 345(4):382–386
Sanders L, Lynham JA, Bond B, del Monte F, Harding S, Kaumann AJ (1995) Sensitization of human atrial 5-HT4 receptors by chronic β-blocker treatment. Circulation 92(9):2526–2539. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.92.9.2526
Soderling SH, Bayuga SJ, Beavo JA (1999) Isolation and characterization of a dual-substrate phosphodiesterase gene family: PDE10A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(12):7071–7076
Vinogradova TM, Lakatta EG (2009) Regulation of basal and reserve cardiac pacemaker function by interactions of cAMP-mediated PKA-dependent Ca2+ cycling with surface membrane channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol 47(4):456–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.06.014
Wang P, Wu P, Egan RW, Billah MM (2000) Cloning, characterization, and tissue distribution of mouse phosphodiesterase 7A1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 276(3):1271–1277
Wang P, Wu P, Egan RW, Billah MM (2003) Identification and characterization of a new human type 9 cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase splice variant (PDE9A5). Differential tissue distribution and subcellular localization of PDE9A variants. Gene. 314:15–27
Weninger S, De Maeyer JH, Lefebvre RA (2012) Study of the regulation of the inotropic response to 5-HT4 receptor activation via phosphodiesterases and its cross-talk with C-type natriuretic peptide in porcine left atrium. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 385(6):565–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0746-y
Weninger S, De Maeyer JH, Lefebvre RA (2013) Influence of phosphodiesterases and cGMP on cAMP generation and on phosphorylation of phospholamban and troponin I by 5-HT4 receptor activation in porcine left atrium. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 386:671–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0855-2
Weninger S, Van Craenenbroeck K, Cameron RT, Vandeput F, Movsesian MA, Baillie GS, Lefebvre RA (2014) Phosphodiesterase 4 interacts with the 5-HT4(b) receptor to regulate cAMP signaling. Cell Signal 26(11):2573–2582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.027
Zimmermann W, Scholz H, Schumacher C, Wenzlaff H, Haverich A (1994) Effects of saterinone and its enantiomers R(+)-saterinone and S(−)-saterinone on the phosphodiesterase isoenzymes from ventricular tissue of failing human hearts and porcine hearts. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 349(6):611–618
Zoraghi R, Corbin JD, Francis SH (2006) Phosphodiesterase-5 Gln817 is critical for cGMP, vardenafil, or sildenafil affinity: its orientation impacts cGMP but not cAMP affinity. J Biol Chem 281(9):5553–5558
Acknowledgements
The work contains parts of the medical thesis of Benedikt Käufler.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.N. designed the research, B.K. performed the research, B.K. and U.G. analyzed the data, and U.G. and J.N. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neumann, J., Käufler, B. & Gergs, U. Which phosphodiesterase can decrease cardiac effects of 5-HT4 receptor activation in transgenic mice?. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 991–1004 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01653-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01653-y