Abstract
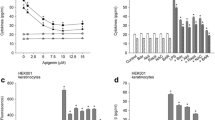
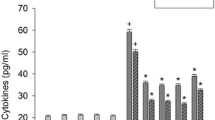
Microbial product lipopolysaccharide has been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory skin diseases. Parthenolide present in extracts of the herb feverfew has demonstrated an anti-inflammatory effect. However, the effect of parthenolide on the Akt/mTOR and NF-κB pathway activation-induced productions of inflammatory mediators in keratinocytes has not been studied. Using human keratinocytes, we investigated the effect of parthenolide on the inflammatory mediator production in relation to the Toll-like receptor-4-mediated-Akt/mTOR and NF-κB pathways, which regulate the transcription genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses. Parthenolide, Akt inhibitor, Bay 11–7085, and N-acetylcysteine each attenuated the lipopolysaccharide-induced production of IL-1β and PGE2, increase in the levels of cyclooxygenase, formation of reactive oxygen species, increase in the levels of Toll-like receptor-4, and activation of the Akt/mTOR and NF-κB in keratinocytes. The results show that parthenolide appears to attenuate the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of inflammatory mediators in keratinocytes by suppressing the Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of the Akt, mTOR, and NF-κB pathways. The activation of signaling transduction pathways appear to be regulated by reactive oxygen species. Parthenolide appears to attenuate the microbial product-mediated inflammatory skin diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Angelini F, Di Matteo G, Balestrero S, Brunetti E, Mancino G, Rossi P, Galli E (2007) Nuclear factor κB activity is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children affected by atopic and non-atopic eczema. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 20:59–67
Baker BS (2006) The role of microorganisms in atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Immunol 144:1–9
Begon E, Michel L, Flageul B, Beaudoil I, Jean-Louis F, Bachelez H, Dubertret L, Musette P (2007) Expression, subcellular localization and cytokinic modulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in normal human keratinocytes: TLR2 up-regulation in psoriatic skin. Eur J Dermatol 17:497–506
Feltenstein MW, Schühly W, Warnick JE, Fischer NH, Sufka KJ (2004) Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic effects of sesquiterpene lactones from Magnolia and Bear's foot. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:299–302
Fu W, Luo H, Parthasarathy S, Mattson MP (1998) Catecholamines potentiate amyloid β-peptide neurotoxicity: involvement of oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and perturbed calcium homeostasis. Neurobiol Dis 5:229–243
Ge Y, Xu Y, Sun W, Man Z, Zhu L, Xia X, Zhao L, Zhao Y, Wang X (2012) The molecular mechanisms of the effect of dexamethasone and cyclosporin A on TLR4 /NF-κB signaling pathway activation in oral lichen planus. 508:157–164.
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2008) New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:837–848
Gloire G, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J (2006) NF-κB activation by reactive oxygen species: fifteen years later. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1493–1505
Hsu HY, Wen MH (2002) Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:22131–22139
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkura Y, Ueno K (1997) A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 44:1299–1305
Juliana C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Datta P, Solorzano L, Yu JW, Meng R, Quong AA, Latz E, Scott CP, Alnemri ES (2010) Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11–7082 are direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J Biol Chem 285:9792–9802
Kang SS, Kauls LS, Gaspari AA (2006) Toll-like receptors: applications to dermatologic disease. J Am Acad Dermatol 54:951–983
Kwak JH, Jung JK, Lee H (2011) Nuclear factor-κB inhibitors; a patent review (2006–2010). Expert Opin Ther Pat 21:1897–1910
Kwok BH, Koh B, Ndubuisi MI, Elofsson M, Crews CM (2001) The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits IκB kinase. Chem Biol 8:759–766
Lee SA, Park SH, Kim BC (2008) Raloxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/nuclear factor-κB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Mol Cells 26:48–52
Lee CS, Jang ER, Kim YJ, Lee MS, Seo SJ, Lee MW (2010) Hirsutenone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-kappaB-induced inflammatory mediator production by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4 and ERK activation. Int Immunopharmacol 10:520–525
Li S, Gao X, Wu X, Wu Z, Cheng L, Zhu L, Shen D, Tong X (2015) Parthenolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines through the toll-like receptor 4 signal pathway in THP-1 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). Apr 4. pii: gmv019. [Epub ahead of print]
Li-Weber M, Giaisi M, Treiber MK, Krammer PH (2002) The anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide suppresses IL-4 gene expression in peripheral blood T. Eur J Immunol 32:3587–3597
López-Franco O, Hernández-Vargas P, Ortiz-Muñoz G, Sanjuán G, Suzuki Y, Ortega L, Blanco J, Egido J, Gómez-Guerrero C (2006) Parthenolide modulates the NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory responses in experimental atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1864–1870
Magni P, Ruscica M, Dozio E, Rizzi E, Beretta G, Maffei Facino R (2012) Parthenolide inhibits the LPS-induced secretion of IL-6 and TNF-α and NF-κB nuclear translocation in BV-2 microglia. Phytother Res 26:1405–1409
Marchi S, Giorgi C, Suski JM, Agnoletto C, Bononi A, Bonora M, De Marchi E, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Poletti F, Rimessi A, Duszynski J, Wieckowski MR, Pet P (2012) Mitochondria-ros crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J Signal Transduct 2012:329635
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Nam NH (2006) Naturally occurring NF-κB inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem 6:945–951
Napetschnig J, Wu H (2013) Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu Rev Biophys 42:443–468
Pålsson-McDermott EM, O'Neill LA (2004) Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunology 113:153–162
Park SJ, Shin HJ, Youn HS (2011) Parthenolide inhibits TRIF-dependent signaling pathway of Toll-like receptors in RAW264.7 macrophages. Mol Cells 31:261–265
Pastore S, Mascia F, Girolomoni G (2006) The contribution of keratinocytes to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol 16:125–131
Rebholz B, Haase I, Eckelt B, Paxian S, Fliag MJ, Ghoreshi K, Nedopasov SA, Mailhammer R, Debey-Pascher S, Schultz JL, Weindl G, Fӧrster I, Huss R, Stratis A, Ruzicka T, Rӧcken PK, Schmid RM, Rupec RA (2007) Crosstalk between keratinocytes and adaptive immune cells in an IκBα protein-mediated inflammatory disease of the skin. Immunity 27:296–307
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Müller MM, Schaffner W (1989) Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6419
Siomek A (2012) NF-κB signaling pathway and free radical impact. Acta Biochim Pol 59:323–331
Smolinski AT, Pestka JJ (2005) Comparative effects of the herbal constituent parthenolide (Feverfew) on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory gene expression in murine spleen and liver. J Inflamm (Lond) 2:6
Song PI, Park YM, Abraham T, Harten B, Zivony A, Neparidze N, Armstrong CA, Ansel JC (2002) Human keratinocytes express functional CD14 and toll-like receptor 4. J Invest Dermatol 119:424–432
Sun XF, Zhang H (2007) NFκB and NFκBI polymorphisms in relation to susceptibility of tumour and other diseases. Histol Histopathol 22:1387–1398
Takeda K, Akira S (2005) Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol 17:1–14
Thomson AW, Turnquist HR, Raimondi G (2009) Immunoregulatory functions of mTOR inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol 9:324–337
Tsuruta D (2009) NF-κB links keratinocytes and lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 3:40–48
Vane JR, Botting RM (1998) Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action. Inflamm Res 47(Suppl 2):S78–S87
Vestergaard C, Johansen C, Otkjaer K, Deleuran M, Iversen L (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced CTACK/CCL27 (cutaneous T-cell-attracting chemokine) production in keratinocytes is controlled by nuclear factor κB. Cytokine 29:49–55
Wong HR, Menendez IY (1999) Sesquiterpene lactones inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:375–380
Young CN, Koepke JI, Terlecky LJ, Borkin MS, Boyd SL, Terlecky SR (2008) Reactive oxygen species in tumor necrosis factor-α-activated primary human keratinocytes: implications for psoriasis and inflammatory skin disease. J Invest Dermatol 128:2606–2614
Yuan G, Wahlqvist ML, He G, Yang M, Li D (2006) Natural products and anti-inflammatory activity. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 15:143–152
Zhong LM, Zong Y, Sun L, Guo JZ, Zhang W, He Y, Song R, Wang WM, Xiao CJ, Lu D (2012) Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory responses via the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in cultured LPS-stimulated microglial cells. PLoS One 7, e32195
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Chung-Ang University Research Scholarship Grants in 2015, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, South Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, Y.J., Lee, D.H., Lee, M.S. et al. Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide attenuates production of inflammatory mediators by suppressing the Toll-like receptor-4-mediated activation of the Akt, mTOR, and NF-κB pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 921–930 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1132-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1132-3