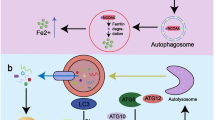
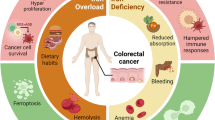
Abstract
Gastrointestinal cancer is a significant global health burden, necessitating the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Emerging evidence has highlighted the potential of targeting ferritinophagy as a promising approach for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Ferritinophagy is a form of selective autophagy that is mediated by the nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4). This process plays a crucial role in regulating cellular iron homeostasis and has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including cancer. This review discusses the molecular mechanisms underlying ferritinophagy and its relevance to gastrointestinal cancer. Furthermore, we highlight the potential therapeutic implications of targeting ferritinophagy in gastrointestinal cancer. Several approaches have been proposed to modulate ferritinophagy, including small molecule inhibitors and immunotherapeutic strategies. We discuss the advantages and challenges associated with these therapeutic interventions and provide insights into their potential clinical applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the fndings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Ahmed A, Tait SWG (2020) Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol Oncol 14(12):2994–3006. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12851
Ajoolabady A, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, Libby P et al (2021) Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in the management of metabolic diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab 32(7):444–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2021.04.010
Alvarez SW, Sviderskiy VO, Terzi EM et al (2017) NFS1 undergoes positive selection in lung tumours and protects cells from ferroptosis. Nature 551(7682):639–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24637
Anandhan A, Dodson M, Shakya A et al (2023) NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci Adv 9(5):eade9585. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ade9585
Arnold M, Abnet CC, Neale RE et al (2020a) Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 159(1):335-349.e15. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.068
Arnold M, Ferlay J, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Soerjomataram I (2020b) Global burden of oesophageal and gastric cancer by histology and subsite in 2018. Gut 69(9):1564–1571. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321600
Battaglia AM, Sacco A, Perrotta ID et al (2022) Iron administration overcomes resistance to erastin-mediated ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Front Oncol 12:868351. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.868351
Bordry N, Astaras C, Ongaro M, Goossens N, Frossard JL, Koessler T (2021) Recent advances in gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastroenterol 27(28):4493–4503. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4493
Cha J-H, Chan L-C, Song MS, Hung M-C (2020) New approaches on cancer immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 10(8):a036863. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a036863
Chen B, Das NK, Talukder I et al (2023) PTEN-induced kinase PINK1 supports colorectal cancer growth by regulating the labile iron pool. J Biol Chem 299(5):104691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104691
Daniels TR, Delgado T, Rodriguez JA, Helguera G, Penichet ML (2006) The transferrin receptor part I: biology and targeting with cytotoxic antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Clin Immunol 121(2):144–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2006.06.010
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB (2019) Colorectal cancer. The Lancet 394(10207):1467–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32319-0
Dixon SJ, Stockwell BR (2014) The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol 10(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1416
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Du J, Wang T, Li Y et al (2019) DHA inhibits proliferation and induces ferroptosis of leukemia cells through autophagy dependent degradation of ferritin. Free Radic Biol Med 131:356–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.011
Dukovski D, Li Z, Kelly DF, Mack E, Walz T (2009) Structural and functional studies on the stalk of the transferrin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381(4):712–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.133
Fan F, Liu P, Bao R et al (2021) A dual PI3K/HDAC inhibitor induces immunogenic ferroptosis to potentiate cancer immune checkpoint therapy. Cancer Res 81(24):6233–6245. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1547
Fang Y, Chen X, Tan Q, Zhou H, Xu J, Gu Q (2021) Inhibiting ferroptosis through disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction: a new mechanism of action. ACS Cent Sci 7(6):980–989. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c01592
Feng J, Li C, Xu R et al (2020) DpdtC-induced EMT inhibition in MGC-803 cells was partly through ferritinophagy-mediated ROS/p53 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:9762390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9762390
Fidyt K, Fiedorowicz A, Strzadala L, Szumny A (2016) β-caryophyllene and beta-caryophyllene oxide-natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer Med 5(10):3007–3017. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.816
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma. The Lancet 391(10127):1301–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30010-2
Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT (2017) The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell 170(4):605–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029
Fuhrmann DC, Mondorf A, Beifuß J, Jung M, Brüne B (2020) Hypoxia inhibits ferritinophagy, increases mitochondrial ferritin, and protects from ferroptosis. Redox Biol 36:101670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101670
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J, Jiang X (2016) Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res 26(9):1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.95
Ghosn M, Kourie HR, Tabchi S (2015) Gastrointestinal cancers in the era of theranostics: updates and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 21(28):8473–8477. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8473
Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF (2010) Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol 221(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2697
Griffin-Sobel JP (2017) Gastrointestinal cancers: screening and early detection. Semin Oncol Nurs 33(2):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soncn.2017.02.004
Guan D, Li C, Li Y et al (2021) The DpdtbA induced EMT inhibition in gastric cancer cell lines was through ferritinophagy-mediated activation of p53 and PHD2/hif-1α pathway. J Inorg Biochem 218:111413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111413
Guan D, Zhou W, Wei H et al (2022) Ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis and activation of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway were conducive to EMT inhibition of gastric cancer cells in action of 2,2′-di-pyridineketone hydrazone dithiocarbamate butyric acid ester. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:3920664. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3920664
Harada K, Rogers JE, Iwatsuki M, Yamashita K, Baba H, Ajani JA (2020) Recent advances in treating oesophageal cancer. F1000Research 9:1189. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.22926.1
Hartke J, Johnson M, Ghabril M (2017) The diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol 34(2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semdp.2016.12.011
Haschka D, Hoffmann A, Weiss G (2021) Iron in immune cell function and host defense. Semin Cell Dev Biol 115:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.12.005
Hill BG, Haberzettl P, Ahmed Y, Srivastava S, Bhatnagar A (2008) Unsaturated lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes activate autophagy in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J 410(3):525–534. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20071063
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X et al (2016) Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 12(8):1425–1428. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1187366
Hu Q, Wei W, Wu D et al (2022) Blockade of GCH1/BH4 axis activates ferritinophagy to mitigate the resistance of colorectal cancer to erastin-induced ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:810327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.810327
Jain V, Amaravadi RK (2022) Pumping iron: ferritinophagy promotes survival and therapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov 12(9):2023–2025. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-22-0734
Jelic MD, Mandic AD, Maricic SM, Srdjenovic BU (2021) Oxidative stress and its role in cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 17(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_862_16
Jin SM, Youle RJ (2012) PINK1- and Parkin-mediated mitophagy at a glance. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 4):795–799. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.093849
Jin K, Ren C, Liu Y, Lan H, Wang Z (2020) An update on colorectal cancer microenvironment, epigenetic and immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol 89:107041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107041
Jo HW, Kim MM (2022) β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits metastasis by downregulating MMP-2, p-p38 and p-ERK in human fibrosarcoma cells. J Food Biochem 46(12):e14468. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14468
Kishi-Itakura C, Koyama-Honda I, Itakura E, Mizushima N (2014) Ultrastructural analysis of autophagosome organization using mammalian autophagy-deficient cells. J Cell Sci 127(22):4984–4984. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.164293
Klionsky DJ, Emr SD (2000) Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 290(5497):1717–1721. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5497.1717
Knight ZA, Lin H, Shokat KM (2010) Targeting the cancer kinome through polypharmacology. Nat Rev Cancer 10(2):130–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2787
Kobayashi S, Liang Q (2015) Autophagy and mitophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852(2):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.020
Kollara A, Brown TJ (2012) Expression and function of nuclear receptor co-activator 4: evidence of a potential role independent of co-activator activity. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(23):3895–3909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1000-y
Krohne TU, Stratmann NK, Kopitz J, Holz FG (2010) Effects of lipid peroxidation products on lipofuscinogenesis and autophagy in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 90(3):465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2009.12.011
Kuno S, Fujita H, Tanaka YK, Ogra Y, Iwai K (2022) Iron-induced NCOA4 condensation regulates ferritin fate and iron homeostasis. EMBO Rep 23(5):e54278. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202154278
Li Y, Seto E (2016) HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6(10):a026831. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a026831
Li X, Lozovatsky L, Sukumaran A et al (2020) NCOA4 is regulated by HIF and mediates mobilization of murine hepatic iron stores after blood loss. Blood 136(23):2691–2702. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2020006321
Li J, Liu J, Xu Y et al (2021a) Tumor heterogeneity in autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Autophagy 17(11):3361–3374. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1872241
Li W, Li W, Wang Y, Leng Y, Xia Z (2021b) Inhibition of DNMT-1 alleviates ferroptosis through NCOA4 mediated ferritinophagy during diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Discov 7(1):267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00656-0
Li J, Lama R, Galster SL et al (2022) Small-molecule MMRi62 induces ferroptosis and inhibits metastasis in pancreatic cancer via degradation of ferritin heavy chain and mutant p53. Mol Cancer Ther 21(4):535–545. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-21-0728
Lin PL, Tang HH, Wu SY, Shaw NS, Su CL (2020) Saponin formosanin c-induced ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Antioxidants (basel) 9(8):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080682
Liu J, Kuang F, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Kang R, Tang D (2020) Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Cell Chem Biol 27(4):420–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.02.005
Lorenzen S, Schuster T, Porschen R et al (2009) Cetuximab plus cisplatin–5-fluorouracil versus cisplatin–5-fluorouracil alone in first-line metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a randomized phase II study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Ann Oncol 20(10):1667–1673. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp069
Ma S, Fu X, Liu L et al (2021) Iron-dependent autophagic cell death induced by radiation in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:723801. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.723801
Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC (2016) Mechanisms of selective autophagy in normal physiology and cancer. J Mol Biol 428(9 Pt A):1659–1680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.027
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC (2014) Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature 509(7498):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13148
Mancias JD, Pontano Vaites L, Nissim S et al (2015) Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. Elife 4:e10308. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.10308
Morel D, Jeffery D, Aspeslagh S, Almouzni G, Postel-Vinay S (2019) Combining epigenetic drugs with other therapies for solid tumours — past lessons and future promise. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(2):91–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0267-4
Mou Y, Wu J, Zhang Y, Abdihamid O, Duan C, Li B (2021) Low expression of ferritinophagy-related NCOA4 gene in relation to unfavorable outcome and defective immune cells infiltration in clear cell renal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 21(1):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07726-z
Nagaraju GP, Dariya B, Kasa P, Peela S, El-Rayes BF (2022) Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 86:622–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.017
Nakamura T, Naguro I, Ichijo H (2019) Iron homeostasis and iron-regulated ROS in cell death, senescence and human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1863(9):1398–1409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.06.010
Ng J, Lee P (2017) The role of radiotherapy in localized esophageal and gastric cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 31(3):453–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2017.01.005
Ni S, Yuan Y, Qian Z et al (2021) Hypoxia inhibits RANKL-induced ferritinophagy and protects osteoclasts from ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 169:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.04.027
Ohshima T, Yamamoto H, Sakamaki Y, Saito C, Mizushima N (2022) NCOA4 drives ferritin phase separation to facilitate macroferritinophagy and microferritinophagy. J Cell Biol 221(10):e202203102. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202203102
Panigrahi DP, Praharaj PP, Bhol CS et al (2020) The emerging, multifaceted role of mitophagy in cancer and cancer therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol 66:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.015
Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ (2014) An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(3):460–473. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5371
Poole LP, Macleod KF (2021) Mitophagy in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci 78(8):3817–3851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03774-1
Procaccio L, Schirripa M, Fassan M et al (2017) Immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Biomed Res Int 2017:4346576. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4346576
Qin X, Zhang J, Wang B et al (2021) Ferritinophagy is involved in the zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Autophagy 17(12):4266–4285. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1911016
Rochette L, Dogon G, Rigal E, Zeller M, Cottin Y, Vergely C (2022) Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci 24(1):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010449
Ryu MS, Duck KA, Philpott CC (2018) Ferritin iron regulators, PCBP1 and NCOA4, respond to cellular iron status in developing red cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis 69:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2017.09.009
Santana-Codina N, Mancias JD (2018) The role of NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in health and disease. Pharmaceuticals (basel) 11(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11040114
Santana-Codina N, Gikandi A, Mancias JD (2021) The role of NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in ferroptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 1301:41–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_4
Shabana SM, Gad NS, Othman AI, Mohamed AF, El-Missiry MA (2023) β-caryophyllene oxide induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells. Med Oncol 40(7):189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02022-9
Shao Y, Jia H, Li S et al (2021) Comprehensive analysis of ferroptosis-related markers for the clinical and biological value in gastric cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:7007933. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7007933
Shen L, Zhou Y, He H et al (2021) Crosstalk between macrophages, T cells, and iron metabolism in tumor microenvironment. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:8865791. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8865791
Song C, Pan S, Zhang J, Li N, Geng Q (2022) Mitophagy: a novel perspective for insighting into cancer and cancer treatment. Cell Prolif 55(12):e13327. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13327
Sottile R, Federico G, Garofalo C et al (2019) Iron and ferritin modulate MHC class I expression and NK cell recognition. Front Immunol 10:224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00224
Srinivas US, Tan BWQ, Vellayappan BA, Jeyasekharan AD (2019) ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol 25:101084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.101084
Su Y, Zhao B, Zhou L et al (2020) Ferroptosis, a novel pharmacological mechanism of anti-cancer drugs. Cancer Lett 483:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.015
Sui S, Zhang J, Xu S, Wang Q, Wang P, Pang D (2019) Ferritinophagy is required for the induction of ferroptosis by the bromodomain protein BRD4 inhibitor (+)-JQ1 in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 10(5):331. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1564-7
Sun X, Yan P, Zou C et al (2019) Targeting autophagy enhances the anticancer effect of artemisinin and its derivatives. Med Res Rev 39(6):2172–2193. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21580
Sun K, Li C, Liao S et al (2022a) Ferritinophagy, a form of autophagic ferroptosis: new insights into cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol 13:1043344. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1043344
Sun W, Yan J, Ma H, Wu J, Zhang Y (2022b) Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis-related signature is closely associated with the prognosis and tumor immune escape of patients with glioma. Int J Gen Med 15:253–270. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S343046
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Torti SV, Torti FM (2020) Iron: the cancer connection. Mol Aspects Med 75:100860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2020.100860
Truman-Rosentsvit M, Berenbaum D, Spektor L et al (2018) Ferritin is secreted via 2 distinct nonclassical vesicular pathways. Blood 131(3):342–352. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-02-768580
van den Brandt PA (2022) The impact of a healthy lifestyle on the risk of esophageal and gastric cancer subtypes. Eur J Epidemiol 37(9):931–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-022-00899-w
Vara-Perez M, Felipe-Abrio B, Agostinis P (2019) Mitophagy in cancer: a tale of adaptation. Cells 8(5):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050493
Vela D (2020) Iron in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 1259:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-43093-1_3
Venkataramani V (2021) Iron homeostasis and metabolism: two sides of a coin. Adv Exp Med Biol 1301:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_3
Wang L, Liu Y, Du T et al (2020) ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc–. Cell Death Differ 27(2):662–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0380-z
Wang H, Cheng Y, Mao C et al (2021a) Emerging mechanisms and targeted therapy of ferroptosis in cancer. Mol Ther 29(7):2185–2208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.03.022
Wang M, Wan C, He T et al (2021b) Sigma-1 receptor regulates mitophagy in dopaminergic neurons and contributes to dopaminergic protection. Neuropharmacology 196:108360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108360
Wang S, Jiang X, Xie X et al (2022) piR-823 inhibits cell apoptosis via modulating mitophagy by binding to PINK1 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 13(5):465. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04922-6
Wu J, Liu Q, Zhang X et al (2022) The interaction between STING and NCOA4 exacerbates lethal sepsis by orchestrating ferroptosis and inflammatory responses in macrophages. Cell Death Dis 13(7):653. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05115-x
Wu H, Liu Q, Shan X, Gao W, Chen Q (2023) ATM orchestrates ferritinophagy and ferroptosis by phosphorylating NCOA4. Autophagy 19(7):2062–2077. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2023.2170960
Xi Y, Xu P (2021) Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Translational Oncology 14(10):101174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101174
Xiu Z, Zhu Y, Han J et al (2022) Caryophyllene oxide induces ferritinophagy by regulating the NCOA4/FTH1/LC3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Pharmacol 13:930958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.930958
Xu Z, Feng J, Li Y et al (2020) The vicious cycle between ferritinophagy and ROS production triggered EMT inhibition of gastric cancer cells was through p53/AKT/mTor pathway. Chem Biol Interact 328:109196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109196
Yan Y, Liang Q, Xu Z et al (2021) Downregulated ferroptosis-related gene STEAP3 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic target for hepatocellular carcinoma and its roles in immune regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:743046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.743046
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ (2010) Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):814–822. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0910-814
Yang ND, Tan SH, Ng S et al (2014) Artesunate induces cell death in human cancer cells via enhancing lysosomal function and lysosomal degradation of ferritin. J Biol Chem 289(48):33425–33441. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.564567
Yang F, Sun S-Y, Wang S et al (2022) Molecular regulatory mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in gastrointestinal oncology: progress and updates. World J Gastrointest Oncol 14(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.1
Yeh S, Chang C (1996) Cloning and characterization of a specific coactivator, ARA70, for the androgen receptor in human prostate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(11):5517–5521. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.11.5517
Ying JF, Lu ZB, Fu LQ et al (2021) The role of iron homeostasis and iron-mediated ROS in cancer. Am J Cancer Res 11(5):1895–1912
Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2020) The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol 17(8):807–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6
Zhang Z, Yao Z, Wang L et al (2018) Activation of ferritinophagy is required for the RNA-binding protein ELAVL1/HuR to regulate ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy 14(12):2083–2103. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1503146
Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang R, Wang F, Wang T, Jiao Y (2020) The role of erastin in ferroptosis and its prospects in cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther 13:5429–5441. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S254995
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Tang D (2020) Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 66:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.03.002
Funding
Research by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31970728 and 82272409), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. ZR2020LZL005 and ZR2020MH050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors assert that they do not have any competing financial interests or personal ties that could have influenced the work disclosed in this study.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Luan, M., Zhu, W. et al. Targeted ferritinophagy in gastrointestinal cancer: from molecular mechanisms to implications. Arch Toxicol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-024-03745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-024-03745-y