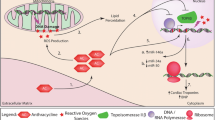
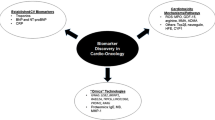
Abstract
Early detection strategies and improvements in cancer treatment have dramatically reduced the cancer mortality rate in the United States (US). However, cardiovascular (CV) side effects of cancer therapy are frequent among the 17 million cancer survivors in the US today, and cardiovascular disease (CVD) has become the second leading cause of morbidity and mortality among cancer survivors. Circulating biomarkers are ideal for detecting and monitoring CV side effects of cancer therapy. Here, we summarize the current state of clinical studies on conventional serum and plasma CVD biomarkers to detect and prevent cardiac injury during cancer treatment. We also review how novel exploratory tools such as genetic testing, human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Omics technologies, and artificial intelligence can elucidate underlying molecular and genetic mechanisms of CV injury and to improve predicting cancer therapy-related cardiotoxicity (CTRC). Current regulatory requirements for biomarker qualifications are also addressed. We present generally applicable lessons learned from published studies, particularly on how to improve reproducibility. The combination of conventional circulating biomarkers and novel exploratory tools will pave the way for precision medicine and improve the clinical practice of prediction, detection, and management of CTRC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y et al (2017) A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats. Comput Biol Med 89:389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.022
Alsentzer E, Murphy JR, Boag W, et al. (2019) Publicly available clinical BERT embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:190403323
Aminkeng F, Ross CJ, Rassekh SR et al (2016) Recommendations for genetic testing to reduce the incidence of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 82(3):683–695. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13008
Amur S, LaVange L, Zineh I, Buckman-Garner S, Woodcock J (2015) Biomarker qualification: toward a multiple stakeholder framework for biomarker development, regulatory acceptance, and utilization. Clin Pharmacol Ther 98(1):34–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.136
Armanious MA, Mohammadi H, Khodor S, Oliver DE, Johnstone PA, Fradley MG (2018) Cardiovascular effects of radiation therapy. Curr Probl Cancer 42(4):433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2018.05.008
Armenian SH, Lacchetti C, Barac A et al (2017) Prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 35(8):893–911. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.70.5400
BC Cancer Agency (2019) Doxorubicin Monograph. BC Cancer Drug Manual http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/drug-database-site/Drug%20Index/Doxorubicin_monograph.pdf Accessed 10 April 2020
Blank M, Thompson A, Hausner E, Rouse R (2018) Biomarkers of drug-induced acute kidney injury: a regulatory perspective. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 14(9):929–936. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2018.1511701
Boekhout AH, Gietema JA, Milojkovic Kerklaan B et al (2016) Angiotensin II-receptor inhibition with candesartan to prevent trastuzumab-related cardiotoxic effects in patients with early breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 2(8):1030–1037. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.1726
Burnett SD, Blanchette AD, Grimm FA et al (2019) Population-based toxicity screening in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 381:114711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2019.114711
Burridge PW, Li YF, Matsa E et al (2016) Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes recapitulate the predilection of breast cancer patients to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med 22(5):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4087
Cai C, Fang J, Guo P et al (2018) In silico pharmacoepidemiologic evaluation of drug-induced cardiovascular complications using combined classifiers. J Chem Inf Model 58(5):943–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00641
Cai C, Guo P, Zhou Y et al (2019) Deep learning-based prediction of drug-induced cardiotoxicity. J Chem Inf Model 59(3):1073–1084. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00769
Calvano J, Achanzar W, Murphy B et al (2016) Evaluation of microRNAs-208 and 133a/b as differential biomarkers of acute cardiac and skeletal muscle toxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 312:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.11.015
Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A et al (2004) Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy. Circulation 109(22):2749–2754
Chaudhari U, Ellis JK, Wagh V et al (2017) Metabolite signatures of doxorubicin induced toxicity in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Amino Acids 49(12):1955–1963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2419-0
Chaudhari U, Nemade H, Gaspar JA, Hescheler J, Hengstler JG, Sachinidis A (2016) MicroRNAs as early toxicity signatures of doxorubicin in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Arch Toxicol 90(12):3087–3098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1668-0
Chen C, Qin C, Qiu H et al (2020) Deep learning for cardiac image segmentation: a review. Front Cardiovasc Med 7:25–25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00025
Cheng Y, Tan N, Yang J et al (2010) A translational study of circulating cell-free microRNA-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Clin Sci (Lond) 119(2):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20090645
Choi E, Schuetz A, Stewart WF, Sun J (2017) Using recurrent neural network models for early detection of heart failure onset. J Am Med Inform Assoc 24(2):361–370. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocw112
Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ, Pinto YM (2012) Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers and extracellular communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res 110(3):483–495. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.247452
Cuocolo R, Perillo T, De Rosa E, Ugga L, Petretta M (2019) Current applications of big data and machine learning in cardiology. J Geriatr Cardiol 16(8):601–607. https://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.08.002
Curigliano G, Cardinale D, Dent S et al (2016) Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments: epidemiology, detection, and management. CA Cancer J Clin 66(4):309–325
Curigliano G, Cardinale D, Suter T et al (2012) Cardiovascular toxicity induced by chemotherapy, targeted agents and radiotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 7):vii155-66. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds293
Daher IN, Daigle TR, Bhatia N, Durand JB (2012) The prevention of cardiovascular disease in cancer survivors. Tex Heart Inst J 39(2):190–198
De Lorenzo C, Paciello R, Riccio G et al (2018) Cardiotoxic effects of the novel approved anti-ErbB2 agents and reverse cardioprotective effects of ranolazine. Onco Targets Ther 11:2241–2250. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157294
Demissei BG, Hubbard RA, Zhang L et al (2020) Changes in cardiovascular biomarkers with breast cancer therapy and associations with cardiac dysfunction. J Am Heart Assoc 9(2):e014708. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.014708
Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K (2018) Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:181004805
Dreyfuss AD, Bravo PE, Koumenis C, Ky B (2019) Precision cardio-oncology. J Nucl Med 60(4):443–450. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.220137
Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy (2016) Facilitating biomarker development: strategies for scientific communication, pathway prioritization, data-sharing, and stakeholder collaboration. https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/sites/default/files/atoms/files/Facilitating%20Biomarker%20Development.pdf (2016). Accessed 8 May 2020.
Eldridge S, Guo L, Mussio J, Furniss M, Hamre J 3rd, Davis M (2014) Examining the protective role of ErbB2 modulation in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol Sci 141(2):547–559. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfu150
Freres P, Bouznad N, Servais L et al (2018) Variations of circulating cardiac biomarkers during and after anthracycline-containing chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 18(1):102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4015-4
FDA draft guidance (2018) Biomarker qualification: evidentiary framework guidance for industry and FDA Staff. https://www.fda.gov/media/122319/download (2018). Accessed 8 May 2020.
FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group (2016) BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools) Resource. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK326791/ Accessed 10 April 2020
Gintant G, Burridge P, Gepstein L et al (2019) Use of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in preclinical cancer drug cardiotoxicity testing: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Res 125(10):e75–e92. https://doi.org/10.1161/RES.0000000000000291
Gkantaifi A, Papadopoulos C, Spyropoulou D et al (2019) Breast radiotherapy and early adverse cardiac effects. The role of serum biomarkers and strain echocardiography. Anticancer Res 39(4):1667–1673. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13272
Grimm FA, Blanchette A, House JS et al (2018) A human population-based organotypic in vitro model for cardiotoxicity screening. Altex 35(4):441–452. https://doi.org/10.14573/altex.1805301
Gulati G, Heck SL, Rosjo H et al (2017) Neurohormonal blockade and circulating cardiovascular biomarkers during anthracycline therapy in breast cancer patients: results from the PRADA (Prevention of Cardiac Dysfunction During Adjuvant Breast Cancer Therapy) Study. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.006513
Gullo G, A JE, Canonici A, et al (2019) Pilot study of bevacizumab in combination with docetaxel and cyclophosphamide as adjuvant treatment for patients with early stage HER-2 negative breast cancer, including analysis of candidate circulating markers of cardiac toxicity: ICORG 08–10 trial. Ther Adv Med Oncol 11:1758835919864236. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835919864236
Hawkins PG, Sun Y, Dess RT et al (2019) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of radiation-induced cardiac toxicity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145(6):1635–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02903-5
Holmgren G, Synnergren J, Andersson CX, Lindahl A, Sartipy P (2016) MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol In Vitro 34:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2016.03.009
Isin A, Ozdalili S (2017) Cardiac arrhythmia detection using deep learning. Proc Comput Sci 120:268–275
Johnson DB, Balko JM, Compton ML et al (2016) Fulminant myocarditis with combination immune checkpoint blockade. New Engl J Med 375(18):1749–1755. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1609214
Kachuee M, Fazeli S, Sarrafzadeh M (2018) ECG heartbeat classification: a deep transferable representation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), 4–7 June 2018. p 443–444
Kitani T, Ong SG, Lam CK et al (2019) Human-induced pluripotent stem cell model of trastuzumab-induced cardiac dysfunction in patients with breast cancer. Circulation 139(21):2451–2465. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037357
Knowles DA, Burrows CK, Blischak JD et al (2018) Determining the genetic basis of anthracycline-cardiotoxicity by molecular response QTL mapping in induced cardiomyocytes. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33480
Kopljar I, De Bondt A, Vinken P et al (2017) Chronic drug-induced effects on contractile motion properties and cardiac biomarkers in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Br J Pharmacol 174(21):3766–3779. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13713
Kura B, Babal P, Slezak J (2017) Implication of microRNAs in the development and potential treatment of radiation-induced heart disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95(10):1236–1244. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0741
Kurokawa YK, Shang MR, Yin RT, George SC (2018) Modeling trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity in vitro using human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol Lett 285:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.01.001
Ky B, Putt M, Sawaya H et al (2014) Early increases in multiple biomarkers predict subsequent cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer treated with doxorubicin, taxanes, and trastuzumab. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(8):809–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.061
Leger KJ, Leonard D, Nielson D, de Lemos JA, Mammen PP, Winick NJ (2017) Circulating microRNAs: potential markers of cardiotoxicity in children and young adults treated with anthracycline chemotherapy. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.004653
Lenneman CG, Sawyer DB (2016) Cardio-oncology: an update on cardiotoxicity of cancer-related treatment. Circ Res 118(6):1008–1020. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303633
Leonard P, Freedman IMC, Simcoe TS (2015) The economics of reproducibility in preclinical research. PLOS Biolog 13(6):e1002165. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002165
Linschoten M, Teske AJ, Cramer MJ, van der Wall E, Asselbergs FW (2018) Chemotherapy-related cardiac dysfunction: a systematic review of genetic variants modulating individual risk. Circ Genom Precis Med 11(1):e001753. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGEN.117.001753
Lipshultz SE, Landy DC, Lopez-Mitnik G et al (2012) Cardiovascular status of childhood cancer survivors exposed and unexposed to cardiotoxic therapy. J Clin Oncol 30(10):1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.33.7907
Lipshultz SE, Miller TL, Scully RE et al (2012) Changes in cardiac biomarkers during doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with long-term echocardiographic outcomes. J Clin Oncol 30(10):1042–1049. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.3404
Louisse J, Wust RCI, Pistollato F et al (2017) Assessment of acute and chronic toxicity of doxorubicin in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 42:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2017.04.023
Maddah M, Mandegar MA, Dame K, Grafton F, Loewke K, Ribeiro AJS (2020) Quantifying drug-induced structural toxicity in hepatocytes and cardiomyocytes derived from hiPSCs using a deep learning method. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2020.106895
Mahmood SS, Fradley MG, Cohen JV et al (2018) Myocarditis in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(16):1755–1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.037
Maillet A, Tan K, Chai X et al (2016) Modeling doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in human pluripotent stem cell derived-cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep 6:25333. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25333
Manolagas SC, Kronenberg HM (2014) Reproducibility of results in preclinical studies: a perspective from the bone field. J Bone Miner Res 29(10):2131–2140. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2293
Menetski JP, Hoffmann SC, Cush SS et al (2019) The Foundation for the National Institutes Of Health Biomarkers Consortium: Past Accomplishments And New Strategic Direction. Clin Pharmacol Ther 105(4):829–843. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1362
Moavenian M, Khorrami H (2010) A qualitative comparison of artificial neural networks and support vector machines in ECG arrhythmias classification. Expert Syst Appl 37(4):3088–3093
Mythili S, Malathi N (2015) Diagnostic markers of acute myocardial infarction. Biomed Rep 3(6):743–748. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2015.500
Nakano MH, Udagawa C, Shimo A et al (2019) A genome-wide association study identifies five novel genetic markers for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in Japanese population. Biol Pharm Bull 42(12):2045–2053. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b19-00527
NCI Cancer Statistics (2018) National Cancer Institute Cancer Statistics https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics (2018). Accessed 10 April 2020
Necela BM, Axenfeld BC, Serie DJ et al (2017) The antineoplastic drug, trastuzumab, dysregulates metabolism in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Clin Transl Med 6(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-016-0133-2
Oatmen KE, Toro-Salazar OH, Hauser K et al (2018) Identification of a novel microRNA profile in pediatric patients with cancer treated with anthracycline chemotherapy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 315(5):H1443–H1452. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00252.2018
Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA et al (2006) Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. N Engl J Med 355(15):1572–1582. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa060185
Oliveira-Carvalho V, Ferreira LR, Bocchi EA (2015) Circulating mir-208a fails as a biomarker of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. J Appl Toxicol 35(9):1071–1072. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3185
Onitilo AA, Engel JM, Stankowski RV et al (2012) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) as a biomarker for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer: a pilot study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134(1):291–298
Özçift A (2011) Random forests ensemble classifier trained with data resampling strategy to improve cardiac arrhythmia diagnosis. Comput Biol Med 41(5):265–271
Palmer JA, Smith AM, Gryshkova V, Donley ELR, Valentin JP, Burrier RE (2020) A targeted metabolomics-based assay using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes identifies structural and functional cardiotoxicity potential. Toxicol Sci 174(2):218–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfaa015
Pang L (2020) Toxicity testing in the Era of iPSC: a perspective regarding the use of patient-specific iPSC-CMs for cardiac safety evaluation. Curr Opin Toxicol 23–24:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2020.04.001
Pang L, Sager P, Yang X et al (2019) Workshop report: FDA workshop on improving cardiotoxicity assessment with human-relevant platforms. Circ Res 125(9):855–867. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315378
Piccoli SP, et al. (2017) Points to consider document: scientific and regulatory considerations for the analytical validation of assays used in the qualification of biomarkers in biological matrices https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/sites/default/files/atoms/files/cpath_ptc_biomarker_qualification_assays_20170623.pdf Accessed 8 May 2020
Pinheiro EA, Fetterman KA, Burridge PW (2019) hiPSCs in cardio-oncology: deciphering the genomics. Cardiovasc Res 115(5):935–948. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz018
Putt M, Hahn VS, Januzzi JL et al (2015) Longitudinal changes in multiple biomarkers are associated with cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin, taxanes, and trastuzumab. Clin Chem 61(9):1164–1172. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.241232
Qin X, Chang F, Wang Z, Jiang W (2018) Correlation of circulating pro-angiogenic miRNAs with cardiotoxicity induced by epirubicin/cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Biomark 23(4):473–484. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-181301
Riddell E, Lenihan D (2018) The role of cardiac biomarkers in cardio-oncology. Curr Probl Cancer 42(4):375–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2018.06.012
Rigaud VO, Ferreira LR, Ayub-Ferreira SM et al (2017) Circulating miR-1 as a potential biomarker of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 8(4):6994–7002. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14355
Romano S, Fratini S, Ricevuto E et al (2011) Serial measurements of NT-proBNP are predictive of not-high-dose anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 105(11):1663–1668. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.439
Santoni M, Guerra F, Conti A et al (2017) Incidence and risk of cardiotoxicity in cancer patients treated with targeted therapies. Cancer Treat Rev 59:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.07.006
Sawaya H, Sebag IA, Plana JC et al (2012) Assessment of echocardiography and biomarkers for the extended prediction of cardiotoxicity in patients treated with anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab. Circ Cardiovas Imaging 5(5):596–603
Serie DJ, Crook JE, Necela BM et al (2017) Genome-wide association study of cardiotoxicity in the NCCTG N9831 (Alliance) adjuvant trastuzumab trial. Pharmacogenet Genom 27(10):378–385. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0000000000000302
Sevakula Rahul K, Au-Yeung Wan-Tai M, Singh Jagmeet P, Heist EK, Isselbacher Eric M, Armoundas Antonis A (2020) State-of-the-art machine learning techniques aiming to improve patient outcomes pertaining to the cardiovascular system. J Am Heart Assoc 9(4):e013924. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.013924
Sharma A, Burridge PW, McKeithan WL et al (2017) High-throughput screening of tyrosine kinase inhibitor cardiotoxicity with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf2584
Singh P, Wang X, Hageman L et al (2020) Association of GSTM1 null variant with anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy after childhood cancer-A Children’s Oncology Group ALTE03N1 report. Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32948
Skala M, Hanouskova B, Skalova L, Matouskova P (2019) MicroRNAs in the diagnosis and prevention of drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 93(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2356-z
Sturgeon KM, Deng L, Bluethmann SM et al (2019) A population-based study of cardiovascular disease mortality risk in US cancer patients. Eur Heart J 40(48):3889–3897. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz766
Tan LL, Lyon AR (2018) Role of biomarkers in prediction of cardiotoxicity during cancer treatment. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 20(7):55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-018-0641-z
Tian S, Hirshfield KM, Jabbour SK et al (2014) Serum biomarkers for the detection of cardiac toxicity after chemotherapy and radiation therapy in breast cancer patients. Front Oncol 4:277. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00277
USDHHS (2018) NCI common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) Version 5.0. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (2018). Accessed 21 April 2020
Vejpongsa P, Yeh ETJJotACoC (2014) Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: challenges and opportunities. 64(9):938–945
Virizuela JA, Garcia AM, de Las PR et al (2019) SEOM clinical guidelines on cardiovascular toxicity (2018). Clin Transl Oncol 21(1):94–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-018-02017-3
Vohra A, Asnani A (2018) Biomarker discovery in cardio-oncology. Curr Cardiol Rep 20(7):52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-018-1002-y
Wan Q, Xu T, Ding W et al (2018) miR-499-5p Attenuates Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis via p21 in Doxorubicin Cardiotoxicity. Front Genet 9:734. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00734
Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT et al (2010) Circulating microRNA: a novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur Heart J 31(6):659–666. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq013
Wang H, Sheehan RP, Palmer AC et al (2019) Adaptation of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes to tyrosine kinase inhibitors reduces acute cardiotoxicity via metabolic reprogramming. Cell Syst 8(5):412-426 e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2019.03.009
Wang JX, Jiao JQ, Li Q et al (2011) miR-499 regulates mitochondrial dynamics by targeting calcineurin and dynamin-related protein-1. Nat Med 17(1):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2282
Yeh ET, Bickford CL (2009) Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: incidence, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(24):2231–2247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.050
Zhang C, Shi D, Yang P (2019) BNP as a potential biomarker for cardiac damage of breast cancer after radiotherapy: a meta-analysis. Med (Baltim) 98(29):e16507. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016507
Zhang N, Yang G, Gao Z et al (2019) Deep learning for diagnosis of chronic myocardial infarction on nonenhanced cardiac cine MRI. Radiology 291(3):606–617
Zhao Z, He J, Zhang J et al (2014) Dysregulated miR1254 and miR579 for cardiotoxicity in patients treated with bevacizumab in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol 35(6):5227–5235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1679-5
Zreik M, van Hamersvelt RW, Wolterink JM, Leiner T, Viergever MA, Išgum I (2018) A recurrent CNN for automatic detection and classification of coronary artery plaque and stenosis in coronary CT angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(7):1588–1598
Acknowledgements
We thank Ellen Wertheimer, Drs. Laura Schnackenberg and Varsha Desai for medical editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical statements
This article reflects the views of the author and should not be construed to represent FDA’s views or policies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, L., Liu, Z., Wei, F. et al. Improving cardiotoxicity prediction in cancer treatment: integration of conventional circulating biomarkers and novel exploratory tools. Arch Toxicol 95, 791–805 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02952-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02952-7