Abstract
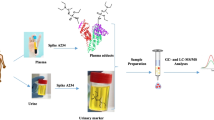
Highly toxic organophosphorous nerve agents (OPAs) have been used in several armed conflicts and terror attacks in the last few decades. A new method for retrospective determination of alkyl methylphosphonic acid (AMPA) metabolites in urine after exposure to VX, GB and GF nerve agents was developed. This method enables a rapid, sensitive and selective determination of trace levels of the nerve agent biomarkers ethyl methylphosphonic acid (EMPA), isopropyl methylphosphonic acid (IMPA) and cyclohexyl methylphosphonic acid (CMPA) in urine. The new technique involves a unique combination of two solid phase extraction (SPE) cartridges: a Ba/Ag/H cartridge for urine interference removal, and a ZrO2 cartridge for selective reconstitution and enrichment of the AMPAs. Extraction of AMPAs from the ZrO2 cartridge was accomplished with a 1% ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) solution and was followed by analysis via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS). The limits of quantitation (LOQs) were in the range of 10–100 pg/mL with recoveries of 64–71% (± 5–19%) after fast sample preparation and a total LC–MS analysis cycle time of 15 min and 13 min, respectively. This method was successfully applied in vivo in a rabbit that was exposed to 0.5 LD50 (7.5 µg/kg, i.v.) sarin for retrospective monitoring of the IMPA metabolite in urine. For the first time, IMPA was determined in rabbit urine samples for 15 days post-exposure, which is longer than any reported post-exposure method for AMPAs. To the best of our knowledge, this new method is the most sensitive and rapid for AMPA determination in urine by LC–MS/MS analysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Kalra H, Gupta A, Raut B, Hussain A, Rahman MA (2012) HybridSPE: a novel technique to reduce phospholipid-based matrix effect in LC-ESI-MS Bioanalysis. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 4:267–275. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.103234
Barr JR, Driskell WJ, Aston LS, Martinez RA (2004) Quantitation of metabolites of the nerve agents sarin, soman, cyclohexylsarin, VX, and Russian VX in human urine using isotope-dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 28:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/28.5.372
Baygildiev T, Zatirakha A, Rodin I, Braun A, Stavrianidi A, Koryagina N, Rybalchenko I, Shpigun O (2017) Rapid IC–MS/MS determination of methylphosphonic acid in urine of rats exposed to organophosphorus nerve agents. J Chromatogr B 1058:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.005
Black RM (2008) An overview of biological markers of exposure to chemical warfare agents. Ann Toxicol Anal 32:2–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/32.1.2
Black RM (2010) History and perspectives of bioanalytical methods for chemical warfare agent detection. J Chromatogr B 878:1207–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.11.025
Black RM, Hambrook JL, Howells DJ, Read RW (1992) Biological fate of sulfur mustard, 1,1'-thiobis(2-chloroethane). Urinary excretion profiles of hydrolysis products and beta-lyase metabolites of sulfur mustard after cutaneous application in rats. J Anal Toxicol 16:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/16.2.79
Black RM, Muir B (2003) Derivatisation reactions in the chromatographic analysis of chemical warfare agents and their degradation products. J Chromatogr A 1000:253–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(03)00183-3
Blanca M, Shifrovitch A, Madmon M, Elgarisi M, Dachir S, Lazar S, Baranes S, Egoz I, Avraham M, Dekel Jaoui H, Dagan S, Weissberg A (2020) Retrospective determination of regenerated nerve agent sarin in human blood by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and in vivo implementation in rabbit. Arch Toxicol 94:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02622-3
Cha H-J, Kim N-H, Jeong E-K, Na Y-C (2010) Analysis of heterocyclic amines in human urine using multiple solid-phase extraction by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Bull Korean Chem Soc 31:2322–2328. https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.8.2322
Ciner FL, McCord CE, Plunkett RW, Martin MF, Croley TR (2007) Isotope dilution LC/MS/MS for the detection of nerve agent exposure in urine. J Chromatogr B 846:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.08.008
Dolan JW (2002) Temperature selectivity in reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 965:195–205
Driskell WJ, Shih M, Needham LL, Barr DB (2002) Quantitation of organophosphorus nerve agent metabolites in human urine using isotope dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 26:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/26.1.6
Dulaurent S, Saint-Marcoux F, Marquet P, Lachâtre G (2006) Simultaneous determination of six dialkylphosphates in urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 831:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.12.012
Ellison DH (2008) Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fredriksson S-Å, Hammarström L-G, Henriksson L, Lakso H-Å (1995) Trace determination of alkyl methylphosphonic acids in environmental and biological samples using gas chromatography/negative-ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 30:1133–1143. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.1190300810
Gomez-Gomez A, Soldevila A, Pizarro N, Andreu-Fernandez V, Pozo OJ (2019) Improving liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of polycarboxylic acids in human urine by chemical derivatization. Comparison of o-benzyl hydroxylamine and 2-picolyl amine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 164:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.10.055
Grigoriu N, Epure G, Ginghina R, Mosteanu D (2015) An overview of the OPCW’s programme for biomedical samples analysis. Int Conf Knowl Based Organ 21:815–820. https://doi.org/10.1515/kbo-2015-0138
Hayes TL, Kenny DV, Hernon-Kenny L (2004) Feasibility of direct analysis of saliva and urine for phosphonic acids and thiodiglycol-related species associated with exposure to chemical warfare agents using LC-MS/MS. J Med Chem Def 2:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/ww/9780199540884.013.u156323
Hosoya K, Kimata K, Araki T, Tanaka N (1995) Temperature controlled high performance liquid chromatography using a uniformly sized temperature responsive polymer based packing material. Anal Chem 67:1907–1911
Hui DM, Minami M (2000) Monitoring of fluorine in urine samples of patients involved in the Tokyo sarin disaster, in connection with the detection of other decomposition products of sarin and the by-products generated during sarin synthesis. Clin Chim Acta 302:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-8981(00)00364-8
Jakubowski EM, Sidell FR, Evans RA, Carter MA, Keeler JR, McMonagle JD, Swift A, Smith JR, Dolzine TW (2000) Quantification of thiodiglycol in human urine after an accidental sulfur mustard exposure. Toxicol Methods 10:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1080/10517230050083375
Kanaujia PK, Pardasani D, Tak V, Purohit AK, Dubey DK (2011) Selective enrichment of the degradation products of organophosphorus nerve agents by zirconia based solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1218:6612–6620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.07.091
Kataoka M, Seto Y (2003) Discriminative determination of alkyl methylphosphonates and methylphosphonate in blood plasma and urine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after tert.-butyldimethylsilylation. J Chromatogr B 795:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1570-0232(03)00548-8
Kataoka M, Tsuge K, Seto Y (2000) Efficiency of pretreatment of aqueous samples using a macroporous strong anion-exchange resin on the determination of nerve gas hydrolysis products by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after tert.-butyldimethylsilylation. J Chromatogr A 891:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(00)00640-3
Koryagina NL, Saveleva EI, Khlebnikova NS, Ukolov AI, Ukolova ES, Karakashev GV, Radilov AS (2016) Chromatography–mass spectrometry determination of alkyl methylphosphonic acids in urine. J Anal Chem 71:1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1061934816140069
Lee JY, Lee YH (2014) Rapid screening and determination of nerve agent metabolites in human urine by LC–MS/MS. J Anal Chem 69:909–916. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1061934814090081
Lin Y, Chen J, Yan L, Guo L, Wu B, Li C, Feng J, Liu Q, Xie J (2014) Determination of nerve agent metabolites in human urine by isotope-dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after solid phase supported derivatization. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:5213–5220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7695-x
Lu X, Claus JE, Bell DS (2013) Enrichment of phospholipids from biological matrices with zirconium oxide-modified silica sorbents. Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte
Mawhinney DB, Hamelin EI, Fraser R, Silva SS, Pavlopoulos AJ, Kobelski RJ (2007) The determination of organophosphonate nerve agent metabolites in human urine by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 852:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.01.023
Miki A, Katagi M, Tsuchihashi H, Yamashita M (1999) Determination of alkylmethylphosphonic acids, the main metabolites of organophosphorus nerve agents, in biofluids by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid-liquid-solid-phase-transfer-catalyzed pentafluorobenzylation. J Anal Toxicol 23:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/23.2.86
Minami M, Hui D-M, Katsumata M, Inagaki H, Boulet CA (1997) Method for the analysis of the methylphosphonic acid metabolites of sarin and its ethanol-substituted analogue in urine as applied to the victims of the Tokyo sarin disaster. J Chromatogr B 695:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4347(97)00203-x
Munro NB, Talmage SS, Griffin GD, Waters LC, Watson AP, King JF, Hauschild V (1999) The sources, fate, and toxicity of chemical warfare agent degradation products. Environ Health Perspect 107:933–974. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107933
Nakajima T, Sasaki K, Ozawa H, Sekijima Y, Morita H, Fukushima Y, Yanagisawa N (1998) Urinary metabolites of sarin in a patient of the Matsumoto sarin incident. Arch Toxicol 72:601–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050549
Nawrocki J, Rigney M, McCormick A, Carr PW (1993) Chemistry of zirconia and its use in chromatography. J Chromatogr A 657:229–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(93)80284-f
Piao H, Marx RB, Schneider S, Irvine DA, Staton J (2005) Analysis of VX nerve agent hydrolysis products in wastewater effluents by ion chromatography with amperometric and conductivity detection. J Chromatogr A 1089:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.06.056
Pucci V, Di Palma S, Alfieri A, Bonelli F, Monteagudo E (2009) A novel strategy for reducing phospholipids-based matrix effect in LC–ESI-MS bioanalysis by means of HybridSPE. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.05.037
Putnam DF (1971) Composition and concentrative properties of human urine, NASA contractor report, CR-1802, NASA-CR-1802, DAC-61125-F. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19710023044
Riches J, Morton I, Read RW, Black RM (2005) The trace analysis of alkyl alkylphosphonic acids in urine using gas chromatography–ion trap negative ion tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 816:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.11.039
Rodin I, Braun A, Stavrianidi A, Baygildiev T, Shpigun O, Oreshkin D, Rybalchenko I (2015) ‘Dilute-and-shoot’ RSLC–MS-MS method for fast detection of nerve and vesicant chemical warfare agent metabolites in urine. J Anal Toxicol 39:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bku119
Røen BT, Sellevåg SR, Lundanes E (2013) On-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for trace determination of nerve agent degradation products in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 761:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.053
Røen BT, Sellevåg SR, Dybendal KE, Lundanes E (2014a) Trace determination of primary nerve agent degradation products in aqueous soil extracts by on-line solid phase extraction–liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry using ZrO2 for enrichment. J Chromatogr A 1329:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.01.004
Røen BT, Sellevåg SR, Lundanes E (2014b) Quantification of nerve agent biomarkers in human serum and urine. Anal Chem 86:11833–11840. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503408x
Sega GA, Tomkins BA, Griest WH (1997) Analysis of methylphosphonic acid, ethyl methylphosphonic acid and isopropyl methylphosphonic acid at low microgram per liter levels in groundwater. J Chromatogr A 790:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(97)00747-4
Shih ML, McMonagle JD, Dolzine TW, Gresham VC (1994) Metabolite pharmacokinetics of soman, sarin and GF in rats and biological monitoring of exposure to toxic organophosphorus agents. J Appl Toxicol 14:195–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2550140309
Shih ML, Smith JR, McMonagle JD, Dolzine TW, Gresham VC (1991) Detection of metabolites of toxic alkylmethylphosphonates in biological samples. Biol Mass Spectrom 20:717–723. https://doi.org/10.1002/bms.1200201111
Solano MI, Thomas JD, Taylor JT et al (2008) Quantification of nerve agent VX-butyrylcholinesterase adduct biomarker from an accidental exposure. J Anal Toxicol 32:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/32.1.68
Subramaniam R, Åstot C, Nilsson C, Östin A (2009) Combination of solid phase extraction and in vial solid phase derivatization using a strong anion exchange disk for the determination of nerve agent markers. J Chromatogr A 1216:8452–8459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.10.017
Suzuki O, Seno H, Watanabe-Suzuki K, Ishii A (2000) Situations of poisoning and analytical toxicology in Japan. Forensic Sci Int 113:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0379-0738(00)00255-3
Scientific T (2017) Dionex onguard II cartridges, product manual 031688. Thermo Scientific, Waltham
van der Schans MJ, Polhuijs M, van Dijk C, Degenhardt CEAM, Pleijsier K, Langenberg JP, Benschop HP (2004) Retrospective detection of exposure to nerve agents: analysis of phosphofluoridates originating from fluoride-induced reactivation of phosphylated BuChE. Arch Toxicol 78:508–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0568-x
Wan H, Yan J, Yu L, Zhang X, Xue X, Li X, Liang X (2010) Zirconia layer coated mesoporous silica microspheres used for highly specific phosphopeptide enrichment. Talanta 82:1701–1707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.07.050
Wooten JV, Ashley DL, Calafat AM (2002) Quantitation of 2-chlorovinylarsonous acid in human urine by automated solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 772:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1570-0232(02)00069-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MB designed the in vitro and in vivo studies, performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. AS performed the experiments and analyzed the data, ME and TS performed the instrumental experiments, and DM performed the experiments. SD and SL designed the in vivo study and performed the in vivo experiment, SB, MA and HDJ performed the in vivo experiments, SD wrote the manuscript and AW designed the studies and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures involving animals were in accordance with the NIH Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory animals and were approved by the institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Number RB-01–19.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanca, M., Shifrovitch, A., Dachir, S. et al. Highly sensitive retrospective determination of organophosphorous nerve agent biomarkers in human urine implemented in vivo in rabbit. Arch Toxicol 94, 3033–3044 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02827-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02827-x