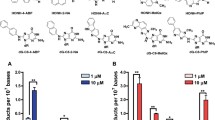
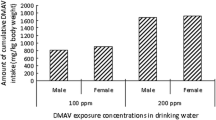
Abstract
Recent epidemiological studies have indicated that occupational exposure to the aromatic amine acetoaceto-o-toluidide (AAOT) was associated with a marked increase in urinary bladder cancers in Japan. However, little is known about the carcinogenicity of AAOT. To evaluate the urinary bladder carcinogenicity of AAOT, male and female F344 rats were treated with N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine (BBN) for 4 weeks followed by dietary administration of 0, 0.167, 0.5, or 1.5% AAOT for 31 weeks. The incidences and multiplicities of bladder tumors were significantly increased in the 0.5 and 1.5% groups of male and female rats in a dose-response manner. AAOT and seven downstream metabolites were detected in the urine of the male and female rats administered AAOT with levels increasing in a dose-dependent manner. The most abundant urinary metabolite of AAOT was the human bladder carcinogen o-toluidine (OTD), which was at least one order of magnitude higher than AAOT and the other AAOT metabolites. In a second experiment, male F344 rats were administered 0, 0.167, or 1.5% AAOT for 4 weeks. Gene expression analyses revealed that the expression of JUN and its downstream target genes was increased in the urothelium of male rats treated with 1.5% AAOT. These results demonstrate that AAOT promotes BBN-induced urinary bladder carcinogenesis in rats and suggest that overexpressed of JUN and its downstream target genes may be involved the bladder carcinogenicity of AAOT. In conclusion, AAOT, like other carcinogenic aromatic amines, is likely to be a carcinogen to the urinary bladder, and OTD metabolized from AAOT is the ultimate carcinogen.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggeli IK, Gaitanaki C, Beis I (2006) Involvement of JNKs and p38-MAPK/MSK1 pathways in H2O2-induced upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 mRNA in H9c2 cells. Cell Signal 18(10):1801–1812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.02.001
Agrawal U, Kumari N, Vasudeva P, Mohanty NK, Saxena S (2018) Overexpression of COX2 indicates poor survival in urothelial bladder cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol 34:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2018.01.008
Arthur-Farraj PJ, Latouche M, Wilton DK et al (2012) c-Jun reprograms Schwann cells of injured nerves to generate a repair cell essential for regeneration. Neuron 75(4):633–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.021
Arts J, Grimbergen J, Toet K, Kooistra T (1999) On the role of c-Jun in the induction of PAI-1 gene expression by phorbol ester, serum, and IL-1alpha in HepG2 cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19(1):39–46
Bejjani F, Evanno E, Zibara K, Piechaczyk M, Jariel-Encontre I (2019) The AP-1 transcriptional complex: Local switch or remote command? Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1872(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.04.003
Bohm F, Schmid D, Denzinger S, Wieland WF, Richter E (2011) DNA adducts of ortho-toluidine in human bladder. Biomarkers 16(2):120–128. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750x.2010.534556
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19(2):185–193
Chen CC, Cheng YY, Chen SC et al (2012) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is up-regulated by 2-aminobiphenyl in a ROS and MAPK-dependent signaling pathway in a bladder cancer cell line. Chem Res Toxicol 25(3):695–705. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx2004689
Chen J, Zhang N, Wen J, Zhang Z (2017) Silencing TAK1 alters gene expression signatures in bladder cancer cells. Oncol Lett 13(5):2975–2981. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.5819
Cohen SM (2002) Comparative pathology of proliferative lesions of the urinary bladder. Toxicol Pathol 30(6):663–671. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230290166751
Cumberbatch MG, Cox A, Teare D, Catto JW (2015) Contemporary occupational carcinogen exposure and bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 1(9):1282–1290. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.3209
Czachorowski MJ, Amaral AF, Montes-Moreno S et al (2012) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in bladder cancer and patient prognosis: results from a large clinical cohort and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45025. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045025
di Martino E, Kelly G, Roulson JA, Knowles MA (2015) Alteration of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion in urothelial cells: an oncogenic mechanism for mutant FGFR3. Mol Cancer Res 13(1):138–148. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-14-0022
Diaz-Munoz MD, Osma-Garcia IC, Cacheiro-Llaguno C, Fresno M, Iniguez MA (2010) Coordinated up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 transcription by nuclear factor kappa B and early growth response-1 in macrophages. Cell Signal 22(10):1427–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.011
Dupont (1994) Urinary bladder toxicity-14-day feeding study with o-toluidine in rats. Report DuPont HLR 699-93, OTS0557449
Eitaki Y, Nakano M, Kawai T, Omae K, Takebayashi T (2019) Biological monitoring of o-toluidine in urine pretreated by an enzymatic deconjugation method. J Occup Health 61(5):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/1348-9585.12058
English JC, Bhat VS, Ball GL, McLellan CJ (2012) Establishing a total allowable concentration of o-toluidine in drinking water incorporating early lifestage exposure and susceptibility. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 64(2):269–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2012.08.011
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R et al (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Ferrís J, Garcia J, Berbel O, Ortega JA (2013) Constitutional and occupational risk factors associated with bladder cancer. Actas Urol Esp 37(8):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acuro.2013.01.001
Frazier KS, Seely JC, Hard GC et al (2012) Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse urinary system. Toxicol Pathol 40(4 Suppl):14s–86s. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312438736
Friedman M (2018) Analysis, nutrition, and health benefits of tryptophan. Int J Tryptophan Res 11:1178646918802282. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646918802282
Garonna E, Botham KM, Birdsey GM, Randi AM, Gonzalez-Perez RR, Wheeler-Jones CP (2011) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 couples cyclo-oxygenase-2 with pro-angiogenic actions of leptin on human endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18823. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018823
Geng H, Zhao L, Liang Z et al (2017) Cigarette smoke extract-induced proliferation of normal human urothelial cells via the MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Oncol Lett 13(1):469–475. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5407
Grau R, Iniguez MA, Fresno M (2004) Inhibition of activator protein 1 activation, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by 15-deoxy-Delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 in colon carcinoma cells: evidence for a redox-sensitive peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-independent mechanism. Cancer Res 64(15):5162–5171. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-0849
Guan Z, Zeng J, Wang Z et al (2014) Urine tenascinC is an independent risk factor for bladder cancer patients. Mol Med Rep 9(3):961–966. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1873
Herdegen T, Leah JD (1998) Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 28(3):370–490
IARC (2010) Ortho-toluidine. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol 99, pp 407–469
IARC (2012) Ortho-toluidine. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol 100F, pp 93–100
Jackson MJ, McArdle A (2016) Role of reactive oxygen species in age-related neuromuscular deficits. J Physiol 594(8):1979–1988. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp270564
Kopparapu PK, Boorjian SA, Robinson BD et al (2013) Expression of VEGF and its receptors VEGFR1/VEGFR2 is associated with invasiveness of bladder cancer. Anticancer Res 33(6):2381–2390
Kristiansen M, Hughes R, Patel P, Jacques TS, Clark AR, Ham J (2010) Mkp1 is a c-Jun target gene that antagonizes JNK-dependent apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 30(32):10820–10832. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2824-10.2010
Lau MT, Wong AS, Leung PC (2010) Gonadotropins induce tumor cell migration and invasion by increasing cyclooxygenases expression and prostaglandin E(2) production in human ovarian cancer cells. Endocrinology 151(7):2985–2993. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1318
Liu M, Li M, Liu J et al (2016) Elevated urinary urea by high-protein diet could be one of the inducements of bladder disorders. J Transl Med 14:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-0809-9
Loda M, Capodieci P, Mishra R et al (1996) Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the early phases of human epithelial carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 149(5):1553–1564
Michalowska M, Znorko B, Kaminski T, Oksztulska-Kolanek E, Pawlak D (2015) New insights into tryptophan and its metabolites in the regulation of bone metabolism. J Physiol Pharmacol 66(6):779–791
Nakano M, Omae K, Takebayashi T, Tanaka S, Koda S (2018) An epidemic of bladder cancer: ten cases of bladder cancer in male Japanese workers exposed to ortho-toluidine. J Occup Health 60(4):307–311. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.2017-0220-OA
OECD (2003) SIDS Initial Assessment Report for SIAM 16. o-Acetoacetotoluidide, CAS No: 93-68-5. https://hpvchemicals.oecd.org/UI/handler.axd?id=78eb2091-65d9-452d-94e1-74793f1366c8 Accessed 16 July 2019
Okuno T, Gi M, Fujioka M et al (2019) Acetoaceto-o-toluidide enhances cellular proliferative activity in the urinary bladder of rats. Toxicol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz051
Peres R, Furuya H, Pagano I, Shimizu Y, Hokutan K, Rosser CJ (2016) Angiogenin contributes to bladder cancer tumorigenesis by DNMT3b-mediated MMP2 activation. Oncotarget 7(28):43109–43123. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10097
Quackenbush J (2002) Microarray data normalization and transformation. Nat Genet 32(Suppl):496–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1032
Riedel K, Scherer G, Engl J, Hagedorn HW, Tricker AR (2006) Determination of three carcinogenic aromatic amines in urine of smokers and nonsmokers. J Anal Toxicol 30(3):187–195
Shah S, King EM, Chandrasekhar A, Newton R (2014) Roles for the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase, DUSP1, in feedback control of inflammatory gene expression and repression by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem 289(19):13667–13679. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.540799
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4(5):E131–E136. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0502-e131
Siegel RL, Miller KD (2018) Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Silberman S, Janulis M, Schultz RM (1997) Characterization of downstream Ras signals that induce alternative protease-dependent invasive phenotypes. J Biol Chem 272(9):5927–5935
Singh NK, Quyen DV, Kundumani-Sridharan V, Brooks PC, Rao GN (2010) AP-1 (Fra-1/c-Jun)-mediated induction of expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 is required for 15S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-induced angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 285(22):16830–16843. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.106187
Son OS, Everett DW, Fiala ES (1980) Metabolism of o-[methyl-14C]toluidine in the F344 rat. Xenobiotica 10(7–8):457–468
Sun X, Deng Q, Liang Z et al (2017) Cigarette smoke extract induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human bladder cancer T24 cells through activation of ERK1/2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 86:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.022
Sundqvist A, Zieba A, Vasilaki E et al (2013) Specific interactions between Smad proteins and AP-1 components determine TGFbeta-induced breast cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 32(31):3606–3615. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.370
Tiniakos DG, Mellon K, Anderson JJ, Robinson MC, Neal DE, Horne CH (1994) c-jun oncogene expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Br J Urol 74(6):757–761
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Wang W, Bian K, Vallabhaneni S et al (2014) ERK3 promotes endothelial cell functions by upregulating SRC-3/SP1-mediated VEGFR2 expression. J Cell Physiol 229(10):1529–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24596
Wei M, Arnold L, Cano M, Cohen SM (2005) Effects of co-administration of antioxidants and arsenicals on the rat urinary bladder epithelium. Toxicol Sci 83(2):237–245. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi033
Ye N, Ding Y, Wild C, Shen Q, Zhou J (2014) Small molecule inhibitors targeting activator protein 1 (AP-1). J Med Chem 57(16):6930–6948. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm5004733
Zhao L, Zhang T, Geng H et al (2018) MAPK/AP-1 pathway regulates benzidine-induced cell proliferation through the control of cell cycle in human normal bladder epithelial cells. Oncol Lett 16(4):4628–4634. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9155
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan, and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research form Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS KAKENHI Grant number 18H06347 and 18K09146). We are grateful to Dr. Michiharu Matsumoto for his statistical consultant (Japan Bioassay Research Center, Japan Organization of Occupational Health and Safety). We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Rie Onodera, Keiko Sakata, Yuko Hisabayashi, and Yukiko Iura (Department of Molecular Pathology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine School), and Emi Donoue (Research Support Platform, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yukimatsu, N., Gi, M., Okuno, T. et al. Promotion effects of acetoaceto-o-toluidide on N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine-induced bladder carcinogenesis in rats. Arch Toxicol 93, 3617–3631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02605-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02605-4