Abstract
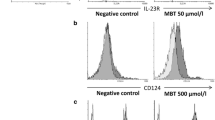
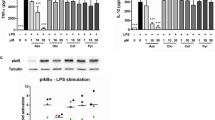
According to the current scientific consensus, one in vitro test is insufficient to cover the key events (KE) defined by the adverse outcome pathway (AOP) for skin sensitization. To address this issue we combined different end points in the same cell line to cover all KEs defined by the skin sensitization AOP. Since dendritic cells (DC) play a key role in the sensitization phase leading to the development of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), we used THP-1 cells as a surrogate for DC. We measured ROS production and GSH depletion for KE1 (binding to proteins), Nrf2 activation pathway and gene expressions for KE2 (keratinocyte response), phenotype modifications using cell-surface markers and cytokine production for KE3 (DC activation), and T-cell proliferation for KE4 (T-cell activation). These measurements were performed using the THP-1 cell line and an original THP-1/T-cell co-culture system following exposure to a variety of chemicals, including irritant, non-sensitizers, and chemicals sensitizers (pro/prehaptens). Results showed that treatment with sensitizers such as cinnamaldehyde (100 µM) or methylisothiazolinone (150 µM) was able to trigger the three main key events (KE1, KE2, and KE3) of the sensitization phase of ACD in THP-1 cells. In addition, all sensitizers were able to induce T lymphocyte proliferation (KE4), while non-sensitizers and irritants did not. Our study shows for the first time that addressing the four main KE of skin sensitization AOP in a single cell line is an achievable task.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACD:
-
Allergic contact dermatitis
- AOP:
-
Adverse outcome pathway
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- BZK:
-
Benzalkonium chloride
- CinA:
-
Cinnamaldehyde
- CS:
-
Contact sensitizer
- DC:
-
Dendritic cell
- DNCB:
-
Dinitrochlorobenzene
- DPRA:
-
Direct peptide reactivity assay
- EUG:
-
Eugenol
- FAR:
-
Farnesol
- GER:
-
Geraniol
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- h-CLAT:
-
human cell line activation test
- ITS:
-
Integrated testing strategy
- KE:
-
Key event
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- MIT:
-
Methylisothiazolinone
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- RESO:
-
Resorcinol
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- t-BHQ:
-
tert-butylhydroquinone
References
Ade N, Antonios D, Kerdine-Romer S, Boisleve F, Rousset F, Pallardy M (2007) NF-kappaB plays a major role in the maturation of human dendritic cells induced by NiSO(4) but not by DNCB. Toxicol Sci 99:488–501
Ade N, Leon F, Pallardy M, Peiffer J-L, Kerdine-Romer S, Tissier M-H, Bonnet P-A, Fabre I, Ourlin J-C (2009) HMOX1 and NQO1 genes are upregulated in response to contact sensitizers in dendritic cells and THP-1 cell line: role of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol Sci 107:451–460
Ashikaga T, Sakaguchi H, Sono S, Kosaka N, Ishikawa M, Nukada Y, Miyazawa M, Ito Y, Nishiyama N, Itagaki H (2010) A comparative evaluation of in vitro skin sensitisation tests: the human cell-line activation test (h-CLAT) versus the local lymph node assay (LLNA). Altern Lab Anim 38:275–284
Aw Yeang HX, Hamdam JM, Al-Huseini LMA, Sethu S, Djouhri L, Walsh J, Kitteringham N, Park BK, Goldring CE, Sathish JG (2012) Loss of transcription factor nuclear factor-erythroid 2 (NF-E2) p45-related factor-2 (Nrf2) leads to dysregulation of immune functions, redox homeostasis, and intracellular signaling in dendritic cells. J Biol Chem 287:10556–10564
Bechara R, Antonios D, Azouri H, Pallardy M (2017) Nickel sulfate promotes IL-17A producing cd4 + t cells by an il-23-dependent mechanism regulated by TLR4 and Jak-STAT pathways. J Invest Dermatol 137:2140–2148
Boislève F, Kerdine-Römer S, Rougier-Larzat N, Pallardy M (2004) Nickel and DNCB induce CCR7 expression on human dendritic cells through different signalling pathways: Role of TNF- and MAPK. J Invest Dermatol 123:494–502
Byamba D, Kim TG, Kim DH, Je JH, Lee M-G (2010) The roles of reactive oxygen species produced by contact allergens and irritants in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Ann Dermatol 22:269–278
Casati S, Aeby P, Basketter DA, Cavani A, Gennari A, Gerberick GF, Griem P, Hartung T, Kimber I, Lepoittevin J-P, Meade BJ, Pallardy M, Rougier N, Rousset F, Rubinstenn G, Sallusto F, Verheyen GR, Zuang V (2005) Dendritic cells as a tool for the predictive identification of skin sensitisation hazard. Altern Lab Anim 33:47–62
Cottrez F, Boitel E, Auriault C, Aeby P, Groux H (2015) Genes specifically modulated in sensitized skins allow the detection of sensitizers in a reconstructed human skin model. Development of the SENS-IS assay. Toxicol Vitr 29:787–802
Cottrez F, Boitel E, Ourlin JC, Peiffer JL, Fabre I, Henaoui IS, Mari B, Vallauri A, Paquet A, Barbry P, Auriault C, Aeby P, Groux H (2016) SENS-IS, a 3D reconstituted epidermis based model for quantifying chemical sensitization potency: reproducibility and predictivity results from an inter-laboratory study. Toxicol Vitr 32:248–260
Cruikshank WW, Berman JS, Theodore AC, Bernardo J, Center DM (1987) Lymphokine activation of T4 + T lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol 138:3817–3823
de Bourayne M, Gallais Y, Ali E, Rousseau Z, Damiens P, Cochet M-H, Filhol C, Chollet-Martin O, Pallardy S, Kerdine-Romer M, S (2017) Protein kinase CK2 controls T-cell polarization through dendritic cell activation in response to contact sensitizers. J Leukoc Biol 101:703–715
Dickinson DA, Levonen A-L, Moellering DR, Arnold EK, Zhang H, Darley-Usmar VM, Forman HJ (2004) Human glutamate cysteine ligase gene regulation through the electrophile response element. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1152–1159
El Ali Z, Delomenie C, Botton J, Pallardy M, Kerdine-Romer S (2017) Dendritic cells’ death induced by contact sensitizers is controlled by Nrf2 and depends on glutathione levels. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 322:41–50
Emter R, Ellis G, Natsch A (2010) Performance of a novel keratinocyte-based reporter cell line to screen skin sensitizers in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245:281–290
European Chemicals Agency (2016) Guidance on information requirements and chemical safety assessment. Chapter R7a: Endpoint specific guidance. European Chemicals Agency, Helsinki
Franco R, Cidlowski JA (2012) Glutathione efflux and cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 17:1694–1713
Gerberick GF, Vassallo JD, Bailey RE, Chaney JG, Morrall SW, Lepoittevin J-P (2004) Development of a peptide reactivity assay for screening contact allergens. Toxicol Sci 81:332–343
Gerberick GF, Vassallo JD, Foertsch LM, Price BB, Chaney JG, Lepoittevin J-P (2007) Quantification of chemical peptide reactivity for screening contact allergens: a classification tree model approach. Toxicol Sci 97:417–427
Hitzler M, Bergert A, Luch A, Peiser M (2013) Evaluation of selected biomarkers for the detection of chemical sensitization in human skin: a comparative study applying THP-1, MUTZ-3 and primary dendritic cells in culture. Toxicol In Vitro 27:1659–1669
Kim ST, Takeuchi K, Sun Z-YJ, Touma M, Castro CE, Fahmy A, Lang MJ, Wagner G, Reinherz EL (2009) The alphabeta T cell receptor is an anisotropic mechanosensor. J Biol Chem 284:31028–31037
Kimber I, Basketter DA, Gerberick GF, Ryan CA, Dearman RJ (2011) Chemical allergy: translating biology into hazard characterization. Toxicol Sci 120(Suppl):238–268
Lim Y-M, Moon S-J, An S-S, Lee S-J, Kim S-Y, Chang I-S, Park K-L, Kim H-A, Heo Y (2008) Suitability of macrophage inflammatory protein-1β production by THP-1 cells in differentiating skin sensitizers from irritant chemicals. Contact Dermatitis 58:193–198
Loetscher P, Seitz M, Clark-Lewis I, Baggiolini M, Moser B (1994) Monocyte chemotactic proteins MCP-1, MCP-2, and MCP-3 are major attractants for human CD4 + and CD8 + T lymphocytes. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 8:1055–1060
Migdal C, Tailhardat M, Courtellemont P, Haftek M, Serres M (2010) Responsiveness of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells to thimerosal and mercury derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 246:66–73
Migdal C, Botton J, Ali E, Azoury Z, Guldemann M-E, Gimenez-Arnau J, Lepoittevin E, Kerdine-Romer J-P, Pallardy S, M (2013) Reactivity of chemical sensitizers toward amino acids in cellulo plays a role in the activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in human monocyte dendritic cells and the THP-1 cell line. Toxicol Sci 133:259–274
Mizuashi M, Ohtani T, Nakagawa S, Aiba S (2005) Redox imbalance induced by contact sensitizers triggers the maturation of dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 124:579–586
Nukada Y, Ashikaga T, Sakaguchi H, Sono S, Mugita N, Hirota M, Miyazawa M, Ito Y, Sasa H, Nishiyama N (2011) Predictive performance for human skin sensitizing potential of the human cell line activation test (h-CLAT). Contact Dermatitis 65:343–353
OECD (2002) Test No. 429: skin sensitisation: local lymph node assay 1–7
OECD (2012) The adverse outcome pathway for skin sensitisation initiated by covalent binding for proteins. Part 1. Scientific evidence OECD environment, health and safety publications series on testing and assessment
OECD (2015a) Test No. 442C: In Chemico Skin Sensitisation: Direct Peptide Reactivity Assay (DPRA)
OECD (2015b) Test No. 442D: In Vitro Skin Sensitisation. OECD Environ. Heal. Saf. Publ., pp 1–20
OECD (2016a) Test No. 442E: In Vitro Skin Sensitisation: Human Cell Line Activation Test (h-CLAT)
OECD (2016b) Guidance document on the reporting of defined approaches and individual information sources to be used within integrated approaches to testing and assessment (IATA) for skin sensitization, ENV/JM/MONO. OECD Publishing, Paris
OECD (2017) Test No. 442E: in vitro skin sensitisation
Ouwehand K, Spiekstra SW, Reinders J, Scheper RJ, de Gruijl TD, Gibbs S (2010) Comparison of a novel CXCL12/CCL5 dependent migration assay with CXCL8 secretion and CD86 expression for distinguishing sensitizers from non-sensitizers using MUTZ-3 Langerhans cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24:578–585
Python F, Goebel C, Aeby P (2007) Assessment of the U937 cell line for the detection of contact allergens. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 220:113–124
Python F, Goebel C, Aeby P (2009) Comparative DNA microarray analysis of human monocyte derived dendritic cells and MUTZ-3 cells exposed to the moderate skin sensitizer cinnamaldehyde. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 239:273–283
Raffalli C, Clouet E, Kuresepi S, Damiens M-H, Lepoittevin J-P, Pallardy M, Ferret P-J, Giménez-Arnau E, Kerdine-Römer S (2017) Fragrance allergens linalool and limonene allylic hydroperoxides in skin allergy: mechanisms of action focusing on transcription factor Nrf2. Toxicol Sci 1–10
Reich K, Westphal G, Konig IR, Mossner R, Kruger U, Ziegler A, Neumann C, Schnuch A (2003) Association of allergic contact dermatitis with a promoter polymorphism in the IL16 gene. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:1191–1194
Saito K, Takenouchi O, Nukada Y, Miyazawa M, Sakaguchi H (2017) An in vitro skin sensitization assay termed EpiSensA for broad sets of chemicals including lipophilic chemicals and pre/pro-haptens. Toxicol Vitr 40:11–25
Sakaguchi H, Ashikaga T, Miyazawa M, Yoshida Y, Ito Y, Yoneyama K, Hirota M, Itagaki H, Toyoda H, Suzuki H (2006) Development of an in vitro skin sensitization test using human cell lines; human Cell Line Activation Test (h-CLAT). II. an inter-laboratory study of the h-CLAT. Toxicol In Vitro 20:774–784
Stepkowski TM, Kruszewski MK (2011) Molecular cross-talk between the NRF2/KEAP1 signaling pathway, autophagy, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 50:1186–1195
Taub DD, Proost P, Murphy WJ, Anver M, Longo DL, van Damme J, Oppenheim JJ (1995) Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), -2, and – 3 are chemotactic for human T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest 95:1370–1376
Uguccioni M, D’Apuzzo M, Loetscher M, Dewald B, Baggiolini M (1995) Actions of the chemotactic cytokines MCP-1, MCP-2, MCP-3, RANTES, MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta on human monocytes. Eur J Immunol 25:64–68
Vandebriel RJ, Loveren H (2010) Non-animal sensitization testing: state-of-the-art. Crit Rev Toxicol 40:389–404
Williams EH, Williams C, McLeod JD (2010) Identification of PDL-1 as a novel biomarker of sensitizer exposure in dendritic-like cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24:1727–1735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and also no sponsorship.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clouet, E., Bechara, R., Raffalli, C. et al. The THP-1 cell toolbox: a new concept integrating the key events of skin sensitization. Arch Toxicol 93, 941–951 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02416-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02416-7