Abstract
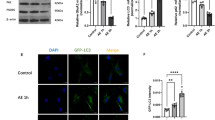
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), the third gasotransmitter, has been shown to act as a neuroprotective factor in numerous pathological processes; however, its underlying mechanism(s) of action remain unclear. It is widely accepted that activation of moderate autophagy and the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway play important roles in the biological self-defense systems. In the present study, we investigated whether exogenous H2S protects against the cytotoxicity of acrylonitrile (AN), a neurotoxin, in primary rat astrocytes. We found that pretreatment for 1 h with sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS), a donor of H2S (200–800 µM), significantly attenuated the AN-induced decrease in cell viability, increase in lactate dehydrogenase release and morphological changes. Furthermore, NaHS significantly attenuated AN-induced oxidative stress by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and increasing glutathione (GSH) concentration. Moreover, NaHS activated the autophagic flux, detectable as a change in autophagy-related proteins (Beclin-1, Atg5 and p62), the formation of acidic vesicular organelles and LC3B aggregation, confirmed by adenoviral expression of mRFP–GFP–LC3. Additionally, NaHS stimulated translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus and increased expression of heme oxygenase-1 and γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, downstream targets of Nrf2. Notably, the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine and Beclin-1, or Nrf2-targeted siRNA, significantly attenuated the neuroprotective effects of NaHS against AN-induced neurotoxicity. In conclusion, we identified a crucial role of autophagy and the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in H2S-mediated neuroprotection against AN-induced toxicity in primary rat astrocytes. Our findings provide novel insights into the mechanisms of H2S-mediated neuroprotection, and suggest that H2S-based donors may serve as potential new candidate drugs to treat AN-induced neurotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Kimura H (1996) The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci 16(3):1066–1071
Bae SH, Sung SH, Oh SY et al (2013) Sestrins activate Nrf2 by promoting p62-dependent autophagic degradation of Keap1 and prevent oxidative liver damage. Cell Metab 17(1):73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.12.002
Bai Y, Yin C, Zhao W et al (2015) Differential protection of pre- versus post-treatment with curcumin, Trolox, and N-acetylcysteine against acrylonitrile-induced cytotoxicity in primary rat astrocytes. Neurotoxicology 51:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2015.09.011
Bai Y, Zhao W, Yin C et al (2016) Preconditioning of endoplasmic reticulum stress protects against acrylonitrile-induced cytotoxicity in primary rat astrocytes: The role of autophagy. Neurotoxicology 55:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2016.05.020
Benavides GA, Squadrito GL, Mills RW et al (2007) Hydrogen sulfide mediates the vasoactivity of garlic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(46):17977–17982. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705710104
Benz FW, Nerland DE, Corbett D, Li J (1997) Biological markers of acute acrylonitrile intoxication in rats as a function of dose and time. Fundam Appl Toxicol 36(2):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1006/faat.1997.2294
Bigner DD, Bigner SH, Burger PC, Shelburne JD, Friedman HS (1986) Primary brain tumours in Fischer 344 rats chronically exposed to acrylonitrile in their drinking-water. Food Chem Toxicol 24(2):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(86)90347-9
Caito SW, Yu Y, Aschner M (2014) Differential inflammatory response to acrylonitrile in rat primary astrocytes and microglia. NeuroToxicology 42:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.02.006
Cao X, Cao L, Ding L, Bian JS (2017) a new hope for a devastating disease: hydrogen sulfide in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0617-0
Chen Y, Chen C, Jin S, Zhou L (2006) The diagnosis and treatment of acute acrylonitrile polsoning. A clinical study of 144 cases. J Occup Health 41(3):172–176. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.41.172
Cheng P, Wang F, Chen K et al (2014) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Mediators Inflamm 2014:935251. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/935251
Ci L, Yang X, Gu X et al (2017) Cystathionine gamma-Lyase deficiency exacerbates CCl4-induced acute hepatitis and fibrosis in the mouse liver. Antioxid Redox Signal. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6773
De Smedt T, De Cremer K, Vleminckx C et al (2014) Acrylonitrile exposure in the general population following a major train accident in Belgium: a human biomonitoring study. Toxicol Lett 231(3):344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.09.009
Decker T, Lohmannmatthes ML (1988) A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J Immunol Methods 115(1):61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(88)90310-9
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Fang YT, Guo CJ, Zhang PP et al (2016) Role of autophagy in methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in rat primary astrocytes. Arch Toxicol 90(2):333–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1425-1
Filipovic MR (2015) Persulfidation (S-sulfhydration) and H2S chemistry, biochemistry and pharmacology of hydrogen sulfide, vol 230. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 29–59 Handbook of Experimental Phamacology
Frankowska M, Wiliński B, Somogyi E, Piotrowska J, Filip M, Opoka W (2015) Cocaine exposure alters H2S tissue concentrations in peripheral mouse organs. Pharmacol Rep 67(3):421–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.11.001
Gao S, Li W, Zou W et al (2015) H2S protects PC12 cells against toxicity of corticosterone by modulation of BDNF-TrkB pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 47(11):915–924. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmv098
Garcia NA, Moncayo-Arlandi J, Vazquez A et al (2017) Hydrogen sulfide improves cardiomyocyte function in a cardiac arrest model. Ann Transpl 22:285–295. https://doi.org/10.12659/AOT.901410
Gheibi S, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M et al (2014) Hydrogen sulfide protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci 54(2):264–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0284-9
Gotor C, García I, Crespo JL, Romero LC (2013) Sulfide as a signaling molecule in autophagy. Autophagy 9(4):609–611. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.23460
Han J, Yang X, Chen X et al (2017) Hydrogen sulfide may attenuate methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity via mitochondrial preservation. Chem Biol Interact 263:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.12.020
He CH, Gong P, Fau - Hu B, Hu B, Fau-Stewart D et al (2001) Identification of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) as an Nrf2-interacting protein. Implication for heme oxygenase-1 gene regulation. J Biol Chem 276(24):20858–20865. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101198200
He Y, Wang S, Xing G et al (2013) Acrylonitrile has distinct hormetic effects on acetyl-cholinesterase activity in mouse brain and blood that are modulated by ethanol. Dose-Response 11(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.11-030.Yuanqing
Hori YS, Hosoda R, Akiyama Y, Sebori R et al (2015) Chloroquine potentiates temozolomide cytotoxicity by inhibiting mitochondrial autophagy in glioma cells. J Neurooncol 122(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1686-9
Ji K, Xue L, Cheng J, Bai Y (2016) Preconditioning of H2S inhalation protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by induction of HSP70 through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Brain Res Bull 121:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull
Jia J, Xiao Y, Wang W et al (2013) Differential mechanisms underlying neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide donors against oxidative stress. Neurochem Int 62(8):1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.04.001
Jiang JM, Zhou CF, Gao SL et al (2015) BDNF-TrkB pathway mediates neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against formaldehyde-induced toxicity to PC12 cells. PloS One 10(3):e0119478. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119478
Kamat PK, Kalani A, Tyagi SC, Tyagi N (2015) Hydrogen sulfide epigenetically attenuates homocysteine-induced mitochondrial toxicity mediated through NMDA receptor in mouse brain endothelial (bEnd3) cells. J Cell Physiol 230(2):378–394. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24722
Keum YS (2011) Regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 system by chemopreventive sulforaphane: implications of posttranslational modifications. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1229(1):184–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06092.x
Kimura Y, Kimura H (2004) Hydrogen sulphide protects neurons from oxidative stress. FASEB J 18(10):1165–1167. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-1815fje
Kimura Y, Dargusch R, Schubert D, Kimura H (2006) Hydrogen sulfide protects HT22 neuronal cells from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(3–4):661. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.661
Kimura S, Noda T, Fau - Yoshimori T, Yoshimori T (2007) Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy 3(5):452–460 https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.4451
Kimura Y, Goto Y, Kimura H (2010) Hydrogen sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative stress in mitochondria. Antioxidants Redox Signal 12(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2282
Koike S, Nishimoto S, Ogasawara Y (2017) Cysteine persulfides and polysulfides produced by exchange reactions with H(2)S protect SH-SY5Y cells from methylglyoxal-induced toxicity through Nrf2 activation. Redox Biol 12:530–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.03.020
Lan A, Liao X, Mo L et al (2011) Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells. PloS One 6(10):e25921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025921
Li L, Fau WM, Guan YY et al (2008) Characterization of a novel, water-soluble hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule (GYY4137): new insights into the biology of hydrogen sulfide. Circulation 117(18):2351–2360. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.753467
Li B, Cui W, Liu J et al (2013) Sulforaphane ameliorates the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antagonizing oxidative stress and Th17-related inflammation in mice. Exp Neurol 250(4):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.10.002
Li L, Jiang H, Li Y, Guo Y (2015) Hydrogen sulfide protects spinal cord and induces autophagy via miR-30c in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Biomed Sci 22(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-015-0135-1
Li XH, Deng YY, Li F, Shi JS, Gong QH (2016) Neuroprotective effects of sodium hydrosulfide against β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Med 38(4):1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2701
Li L, Xiao T, Li F et al (2017) Hydrogen sulfide reduced renal tissue fibrosis by regulating autophagy in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep 16(2):1715–1722. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6813
Liu YY, Bian JS (2010) Hydrogen sulfide protects amyloid-beta induced cell toxicity in microglia. J Alzheimers Dis 22(4):1189–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.09.006
Liu W, Wang D, Liu K, Sun X (2012) Nrf2 as a converging node for cellular signaling pathways of gasotransmitters. Med Hypotheses 79(3):308–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2012.05.016
Liu Y, Deng Y, Liu H, Yin C, Li X, Gong Q (2016a) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates learning memory impairment in APP/PS1 transgenic mice: a novel mechanism mediated by the activation of Nrf2. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 153:150–151;207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2016.11.00
Liu H, Wang Y, Xiao Y, Hua Z, Cheng J, Jia J (2016b) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates tissue plasminogen activator-induced cerebral hemorrhage following experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res 7(3):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0459-5
Liu J, Wu J, Sun A et al (2016c) Hydrogen sulfide decreases high glucose/palmitate-induced autophagy in endothelial cells by the Nrf2-ROS-AMPK signaling pathway. Cell Biosci 6(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-016-0099-1
Lu M, Hu LF, Hu G, Bian JS (2008) Hydrogen sulfide protects astrocytes against H(2)O(2)-induced neural injury via enhancing glutamate uptake. Free Radic Biol Med 45(12):1705–1713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.09.014
Lu R, Wang S, Xing G et al (2009) Effects of acrylonitrile on antioxidant status of different brain regions in rats. Neurochem Int 55(7):552–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.05.009
Mariño G, López-Otín C (2004) Autophagy: molecular mechanisms, physiological functions and relevance in human pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(12):1439–1454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4012-4
Medeiros JV, Bezerra VHGomes AS (2009) Hydrogen sulfide prevents ethanol-induced gastric damage in mice: role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330(3):764–770. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.109.152801
Meng JL, Mei WY, Dong YF et al (2011) Heat shock protein 90 mediates cytoprotection by H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced injury in PC12 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38(1):42–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2010.05462.x
Meng G, Zhao S, Xie L, Han Y, Ji Y (2017) Protein S-sulfhydration by hydrogen sulfide in cardiovascular system. Br J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13825
Moore PK, Bhatia M, Moochhala S (2003) Hydrogen sulfide: from the smell of the past to the mediator of the future? Trends Pharmacol Sci 24(12):609 – 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2003.10.007
Mustafa AK, Gadalla MM, Sen N et al (2009) H2S signals through protein S-sulfhydration. Sci Signal 2(96):ra72. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000464
Paul BD, Sbodio JI, Xu R et al (2014) Cystathionine γ-lyase deficiency mediates neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. Nature 509(7498):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13136
Perniss A, Preiss K, Nier M, Althaus M (2017) Hydrogen sulfide stimulates CFTR in Xenopus oocytes by activation of the cAMP/PKA signalling axis. Sci Rep 7:3517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03742-5
Pu X, Kamendulis Lm Fau - Klaunig JE, Klaunig JE (2009) Acrylonitrile-induced oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci 111(1):64–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp133
Pu X, Wang Z, Zhou S, Klaunig JE (2016) Protective effects of antioxidants on acrylonitrile-induced oxidative stress in female F344 rats. Environ Toxicol 31(12):1808–1818. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22182
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Fau-Davies JE, Davies Je Fau, Futter M et al (2010) Regulation of mammalian autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 90(4):1383 – 435. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2009
Reiffenstein RJ, Hulbert WC, Roth SH (1992) Toxicity of hydrogen sulfide. Annu Rev Pharmacol 32(1):109–134. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.000545
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2199
Scott A (2013) Acrylonitrile fumes kill one in Belgium. In: Business concentrates. http://cen.acs.org/articles/91/i19/Acrylonitrile-Fumes-Kill-One-Belgium.html?type=paidArticleContent Accessed 21 June 2017
Shen B, Wang W, Ding L et al (2015) Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 rescues the oxidative stress induced by di-N-butylphthalate in testicular Leydig cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 34(2):145 – 52. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327114530744
Specia M (2015) Thousands evacuated after train carrying toxic chemicals derails in Tennessee. In. http://mashable.com/2015/07/02/train-derailment-tennessee/#wdowKufr38qW Accessed 21 June 2017
Sun Y, Huang Y, Yu W et al (2017) Sulfhydration-associated phosphodiesterase 5A dimerization mediates vasorelaxant effect of hydrogen sulfide. Oncotarget 8(19):31888–31900. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16649
Takuma K, Baba A, Matsuda T (2004) Astrocyte apoptosis: implications for neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 72(2):111–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2004.02.001
Tan BH, Wong PT, Bian JS (2010) Hydrogen sulfide: a novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system. Neurochemistry international 56(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.08.008
Tang X, Yang C, Chen J et al (2008) Effect of hydrogen sulphide on beta-amyloid-induced damage in PC12 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35(2):180–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04799.x
Tsai CY, Wen SY, Shibu MA et al (2015) Diallyl trisulfide protects against high glucose-induced cardiac apoptosis by stimulating the production of cystathionine gamma-lyase-derived hydrogen sulfide. Int J Cardiol 195:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.111
Wang S, Lu R, Xu W et al (2010) Induction or inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 modifies the acute toxicity of acrylonitrile in rats: biochemical evidence. Arch Toxicol 84(6):461–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0519-7
Wu Y, Xin W, Guo H et al (2013) Synthesis and screening of 3-MA derivatives for autophagy inhibitors. Autophagy 9(4):593–603. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.23641
Xiao F, Zhang P, Chen AH et al (2016) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits MPP(+)-induced aldehyde stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC12 cells: involving upregulation of BDNF. Exp Cell Res 348(1):106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.09.006
Xie H, Xu Q, Jia J et al (2015) Hydrogen sulfide protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by activating AMP-activated protein kinase torestore autophagic flux. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(3):632–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.017
Xie L, Gu Y, Wen M et al (2016) Hydrogen sulfide induces Keap1 S-sulfhydration and suppresses diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis via Nrf2 activation. Diabetes 65(10):3171. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-0020
Xing G, Lu R, Xu W et al (2010) Curcumin pretreatment protects against acute acrylonitrile-induced oxidative damage in rats. Toxicology 267(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.11.001
Xue X, Bian JS (2015) Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in Parkinson’s disease animal models: methods and protocols. Methods Enzymol 554:169. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mie.2014.11.015
Yadav V, Gao XH, Willard B, Hatzoglou M, Banerjee R, Kabil O (2017) Hydrogen sulfide modulates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha) phosphorylation status in the integrated stress-response pathway. J Biol Chem 292(32):13143–13153. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.778654
Yang G, Zhao K, Fau-Ju Y, Ju Y, Fau - Mani S et al (2013) Hydrogen sulfide protects against cellular senescence via S-sulfhydration of Keap1 and activation of Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(15):1906–1919. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4645
Yang H, Mao Y, Tan B, Luo S, Zhu Y (2015) The protective effects of endogenous hydrogen sulfide modulator, S-propargyl-cysteine, on high glucose-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes: A novel mechanism mediated by the activation of Nrf2. Eur J Pharmacol 761:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.001
Yin Z, Lee E, Ni M et al (2011) Methylmercury-induced alterations in astrocyte functions are attenuated by ebselen. Neurotoxicology 32(3):291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2011.01.004
Yin J, Tu C, Zhao J et al (2013) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in rats. Brain Res 1491:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.046
Yoshida E, Toyama T, Shinkai Y, Sawa T, Akaike T, Kumagai Y (2011) Detoxification of methylmercury by hydrogen sulfide-producing enzyme in mammalian cells. Chem Res Toxicol 24(10):1633. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx200394g
Zhang H, Zhang A, Guo C et al (2011) S-diclofenac protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice via ameliorating cardiac gap junction remodeling. PloS one 6(10):e26441. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026441
Zhang MY, Shan HY, Chang P et al (2014) Hydrogen sulfide offers neuroprotection on traumatic brain injury in parallel with reduced apoptosis and autophagy in mice. PloS one 9(1):e87241. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087241
Zhang M, Shan H, Pan C et al (2017) Upregulation of 3-MST relates to neuronal autophagy after traumatic brain injury in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0369-9
Zheng Q, Su H, Ranek MJ, Wang X (2011) Autophagy and p62 in cardiac proteinopathy. Circ Res 109(3):296. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.244707
Zheng J, Zhao T, Yuan Y, Hu N, Tang X (2015) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) attenuates uranium-induced acute nephrotoxicity through oxidative stress and inflammatory response via Nrf2-NF-κB pathways. Chem Biol Interact 242:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.10.021
Zhou X, An G, Chen J (2014) Hydrogen sulfide improves left ventricular function in smoking rats via regulation of apoptosis and autophagy. Apoptosis 19(6):998–1005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-0978-z
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30872139, 81273124, 81302459) and by grants from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS R01ES07331, NIEHS R01ES10563 and NIEHS R01ES020852). We thank Barry Patel, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (http://www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Bai, Y., Yin, C. et al. Activation of autophagic flux and the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway by hydrogen sulfide protects against acrylonitrile-induced neurotoxicity in primary rat astrocytes. Arch Toxicol 92, 2093–2108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2208-x