Abstract
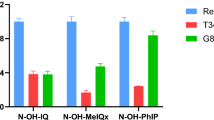
Heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) are primarily produced during the heating of meat or fish. HAAs are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and their toxicity in model systems depend on metabolic activation. This activation is mediated by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, in particular CYP1A2. Some studies have indicated a role of human sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A1 and N-acetyltransferase (NAT) 2 in the terminal activation of HAAs. In this study, we conducted a metabolism/genotoxicity relationship analysis for 16 HAAs and related heterocyclics. We used the γH2AX genotoxicity assay in V79 cells (deficient in CYP, SULT and NAT) and V79-derived cell lines genetically engineered to express human CYP1A2 alone or in combination with human SULT1A1 or NAT2. Our data demonstrated genotoxic properties for 13 out of the 16 compounds tested. A clear relationship between metabolic bioactivation and genotoxicity allowed to distinguish four groups: (1) Trp-P-1 genotoxicity was linked to CYP1A2 bioactivation only—with negligible effects of phase II enzymes; (2) Glu-P-2, Glu-P-1, Trp-P-2, APNH, MeAαC and AαC were bioactivated by CYP1A2 in combination with either phase II enzyme tested (NAT2 or SULT1A1); (3) IQ, 4-MeIQ, IQx, 8-MeIQx, and 4,8-DiMeIQx required CYP1A2 in combination with NAT2 to be genotoxic, whereas SULT1A1 did not enhance their genotoxicity; (4) PhIP became genotoxic after CYP1A2 and SULT1A1 bioactivation—NAT2 had not effect. Our results corroborate some previous data regarding the genotoxic potency of seven HAAs and established the genotoxicity mechanism for five others HAAs. This study also permits to compare efficiently the genotoxic potential of these 13 HAAs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M, Yoshikawa K, Iwase Y, Ishiura S (2014) Usefulness of monitoring gamma-H2AX and cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells for estimating genotoxicity using a high-content analysis system. J Biomol Screen 19(9):1246–1254
Audebert M, Riu A, Jacques C et al (2010) Use of the gammaH2AX assay for assessing the genotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in human cell lines. Toxicol Lett 199(2):182–192
Audebert M, Dolo L, Perdu E, Cravedi JP, Zalko D (2011) Use of the gammaH2AX assay for assessing the genotoxicity of bisphenol A and bisphenol F in human cell lines. Arch Toxicol 85(11):1463–1473
Audebert M, Zeman F, Beaudoin R, Pery A, Cravedi JP (2012) Comparative potency approach based on H2AX assay for estimating the genotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 260(1):58–64
Boobis AR, Lynch AM, Murray S et al (1994) CYP1A2-catalyzed conversion of dietary heterocyclic amines to their proximate carcinogens is their major route of metabolism in humans. Cancer Res 54(1):89–94
Bryce SM, Bemis JC, Mereness JA et al (2014) Interpreting in vitro micronucleus positive results: simple biomarker matrix discriminates clastogens, aneugens, and misleading positive agents. Environ Mol Mutagen 55(7):542–555
Chang CC, Castellazzi M, Glover TW, Trosko JE (1978) Effects of harman and norharman on spontaneous and ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Cancer Res 38(12):4527–4533
Dobbernack G, Meinl W, Schade N et al (2011) Altered tissue distribution of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-DNA adducts in mice transgenic for human sulfotransferases 1A1 and 1A2. Carcinogenesis 32(11):1734–1740
Glatt H (2006) Metabolic factors affecting the mutagenicity of heterocyclic amines. Book Acryl Other Hazard Compd Heat Treat Foods:358–404
Glatt H, Gemperlein I, Setiabudi F, Platt KL, Oesch F (1990) Expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes in propagatable cell cultures and induction of micronuclei by 13 compounds. Mutagenesis 5(3):241–249
Glatt H, Davis W, Meinl W, Hermersdorfer H, Venitt S, Phillips DH (1998) Rat, but not human, sulfotransferase activates a tamoxifen metabolite to produce DNA adducts and gene mutations in bacteria and mammalian cells in culture. Carcinogenesis 19(10):1709–1713
Glatt H, Pabel U, Meinl W, Frederiksen H, Frandsen H, Muckel E (2004) Bioactivation of the heterocyclic aromatic amine 2-amino-3-methyl-9H-pyrido [2,3-b]indole (MeAaC) in recombinant test systems expressing human xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes. Carcinogenesis 25(5):801–807
Graillot V, Takakura N, Hegarat LL, Fessard V, Audebert M, Cravedi JP (2012a) Genotoxicity of pesticide mixtures present in the diet of the French population. Environ Mol Mutagen 53(3):173–184
Graillot V, Tomasetig F, Cravedi JP, Audebert M (2012b) Evidence of the in vitro genotoxicity of methyl-pyrazole pesticides in human cells. Mutat Res 748(1–2):8–16
Hammons GJ, Milton D, Stepps K, Guengerich FP, Tukey RH, Kadlubar FF (1997) Metabolism of carcinogenic heterocyclic and aromatic amines by recombinant human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Carcinogenesis 18(4):851–854
Hoie AH, Monien BH, Glatt H, Hjertholm H, Husoy T (2016) DNA adducts induced by food mutagen PhIP in a mouse model expressing human sulfotransferases 1A1 and 1A2. Toxicol Lett 248:34–38
Holme JA, Soderlund E, Aune T (1985) Effects of harman and norharman on the metabolism and genotoxicity of 2-acetylaminofluorene in cultured rat hepatocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol 1(3):223–239
Husain A, Zhang X, Doll MA, States JC, Barker DF, Hein DW (2007) Identification of N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) transcription start sites and quantitation of NAT2-specific mRNA in human tissues. Drug Metab Dispos 35(5):721–727
IARC (2016) International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/latest_classif.php
Jamin EL, Riu A, Douki T et al (2013) Combined genotoxic effects of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (B(a)P) and an heterocyclic amine (PhIP) in relation to colorectal carcinogenesis. PLoS One 8(3):e58591
Kato T, Ohgaki H, Hasegawa H, Sato S, Takayama S, Sugimura T (1988) Carcinogenicity in rats of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline. Carcinogenesis 9(1):71–73
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2013) Validation of high-throughput genotoxicity assay screening using gammaH2AX in-cell western assay on HepG2 cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 54(9):737–746
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2016a) Complementarity of phosphorylated histones H2AX and H3 quantification in different cell lines for genotoxicity screening. Arch Toxicol 90(8):1983–1995
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2016b) Evaluation of four human cell lines with distinct biotransformation properties for genotoxic screening. Mutagenesis 31(1):83–96
Landsiedel R, Engst W, Scholtyssek M, Seidel A, Glatt H (1996) Benzylic sulphuric acid esters react with diverse functional groups and often form secondary reactive species. Polycycl Aromat Compd 11:341–348
Martignoni M, Groothuis GM, de Kanter R (2006) Species differences between mouse, rat, dog, monkey and human CYP-mediated drug metabolism, inhibition and induction. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2(6):875–894
Meinl W, Tsoi C, Swedmark S, Tibbs ZE, Falany CN, Glatt H (2013) Highly selective bioactivation of 1- and 2-hydroxy-3-methylcholanthrene to mutagens by individual human and other mammalian sulphotransferases expressed in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutagenesis 28(5):609–619
Mizota T, Ohno K, Yamada T (2011) Validation of a genotoxicity test based on p53R2 gene expression in human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res 724(1–2):76–85
Muckel E, Frandsen H, Glatt HR (2002) Heterologous expression of human N-acetyltransferases 1 and 2 and sulfotransferase 1A1 in Salmonella typhimurium for mutagenicity testing of heterocyclic amines. Food Chem Toxicol 40(8):1063–1068
Nishigaki R, Totsuka Y, Kataoka H et al (2007) Detection of aminophenylnorharman, a possible endogenous mutagenic and carcinogenic compound, in human urine samples. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 16(1):151–156
Ohgaki H, Takayama S, Sugimura T (1991) Carcinogenicities of heterocyclic amines in cooked food. Mutat Res 259(3–4):399–410
Quesnot N, Rondel K, Audebert M et al (2016) Evaluation of genotoxicity using automated detection of gammaH2AX in metabolically competent HepaRG cells. Mutagenesis 31(1):43–50
Ripa L, Mee C, Sjo P, Shamovsky I (2014) Theoretical studies of the mechanism of N-hydroxylation of primary aromatic amines by cytochrome P450 1A2: radicaloid or anionic? Chem Res Toxicol 27(2):265–278
Saito K, Kato R (1984) Glutathione conjugation of arylnitroso compound: detection and monitoring labile intermediates in situ inside a fast atom bombardment mass spectrometer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 124(1):1–5
Schmalix WA, Maser H, Kiefer F et al (1993) Stable expression of human cytochrome P450 1A1 cDNA in V79 Chinese hamster cells and metabolic activation of benzo[a]pyrene. Eur J Pharmacol 248(3):251–261
Schut HA, Snyderwine EG (1999) DNA adducts of heterocyclic amine food mutagens: implications for mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 20(3):353–368
Shamovsky I, Ripa L, Borjesson L et al (2011) Explanation for main features of structure-genotoxicity relationships of aromatic amines by theoretical studies of their activation pathways in CYP1A2. J Am Chem Soc 133(40):16168–16185
Shamovsky I, Ripa L, Blomberg N et al (2012) Theoretical studies of chemical reactivity of metabolically activated forms of aromatic amines toward DNA. Chem Res Toxicol 25(10):2236–2252
Skog KI, Johansson MA, Jagerstad MI (1998) Carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in model systems and cooked foods: a review on formation, occurrence and intake. Food Chem Toxicol 36(9–10):879–896
Smart DJ, Ahmedi KP, Harvey JS, Lynch AM (2011) Genotoxicity screening via the gammaH2AX by flow assay. Mutat Res 715(1–2):25–31
Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K, Nakagama H, Nagao M (2004) Heterocyclic amines: mutagens/carcinogens produced during cooking of meat and fish. Cancer Sci 95(4):290–299
Teubner W, Meinl W, Florian S, Kretzschmar M, Glatt H (2007) Identification and localization of soluble sulfotransferases in the human gastrointestinal tract. Biochem J 404(2):207–215
Turesky RJ, Le Marchand L (2011) Metabolism and biomarkers of heterocyclic aromatic amines in molecular epidemiology studies: lessons learned from aromatic amines. Chem Res Toxicol 24(8):1169–1214
Turesky RJ, Constable A, Fay LB, Guengerich FP (1999) Interspecies differences in metabolism of heterocyclic aromatic amines by rat and human P450 1A2. Cancer Lett 143(2):109–112
Westerink WM, Stevenson JC, Horbach GJ, Schoonen WG (2010) The development of RAD51C, Cystatin A, p53 and Nrf2 luciferase-reporter assays in metabolically competent HepG2 cells for the assessment of mechanism-based genotoxicity and of oxidative stress in the early research phase of drug development. Mutat Res 696(1):21–40
Westerink WM, Schirris TJ, Horbach GJ, Schoonen WG (2011) Development and validation of a high-content screening in vitro micronucleus assay in CHO-k1 and HepG2 cells. Mutat Res 724(1–2):7–21
Wild D, Feser W, Michel S, Lord HL, Josephy PD (1995) Metabolic activation of heterocyclic aromatic amines catalyzed by human arylamine N-acetyltransferase isozymes (NAT1 and NAT2) expressed in Salmonella typhimurium. Carcinogenesis 16(3):643–648
Yamazoe Y, Tada M, Kamataki T, Kato R (1981) Enhancement of binding of N-hydroxy-TRP-P-2 to DNA by seryl-tRNA synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 102(1):432–439
Yamazoe Y, Shimada M, Shinohara A, Saito K, Kamataki T, Kato R (1985) Catalysis of the covalent binding of 3-hydroxyamino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole to DNA by a l-proline- and adenosine triphosphate-dependent enzyme in rat hepatic cytosol. Cancer Res 45(6):2495–2500
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chevereau, M., Glatt, H., Zalko, D. et al. Role of human sulfotransferase 1A1 and N-acetyltransferase 2 in the metabolic activation of 16 heterocyclic amines and related heterocyclics to genotoxicants in recombinant V79 cells. Arch Toxicol 91, 3175–3184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1935-8