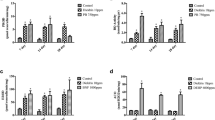
Abstract
Perfluorocarboxylic acids (PFCAs) including perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) are environmental pollutants showing high accumulation, thermochemical stability and hepatocarcinogenicity. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α is suggested to mediate their toxicities, but the precise mechanism remains unclear. Previous reports also imply a possible role of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), a key transcription factor for the xenobiotic-induced expression of various genes involved in drug metabolism and disposition as well as hepatocarcinogenesis. Therefore, we have investigated whether PFCAs activate CAR. In wild-type but not Car-null mice, mRNA levels of Cyp2b10, a CAR target gene, were increased by PFOA treatment. PFCA treatment induced the nuclear translocation of CAR in mouse livers. Since CAR activators are divided into two types, ligand-type activators and phenobarbital-like indirect activators, we investigated whether PFCAs are CAR ligands or not using the cell-based reporter gene assay that can detect CAR ligands but not indirect activators. As results, neither PFCAs nor phenobarbital increased reporter activities. Interestingly, in mouse hepatocytes, pretreatment with the protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid prevented an increase in Cyp2b10 mRNA levels induced by phenobarbital as reported, but not that by PFOA. Finally, in human hepatocyte-like HepaRG cells, PFOA treatment increased mRNA levels of CYP2B6, a CAR target gene, as did phenobarbital. Taken together, our present results suggest that PFCAs including PFOA are indirect activators of mouse and human CAR and that the mechanism might be different from that for phenobarbital. The results imply a role of CAR in the hepatotoxicity of PFCAs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TCPOBOP:
-
1,4-Bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene
- PFCA:
-
Perfluorocarboxylic acid
- PFOA:
-
Perfluorooctanoic acid
- PFHA:
-
Perfluoroheptanoic acid
- PFNA:
-
Perfluorononanoic acid
- PFDA:
-
Perfluorodecanoic acid
- CITCO:
-
6-(4-Chlorophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole-5-carbaldehyde O-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)oxime
- PPARα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α
- CAR:
-
Constitutive androstane receptor
- RXRα:
-
Retinoid X receptor α
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- Acox1 :
-
Acyl-CoA oxidase 1
- Acat1 :
-
Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1
- Hmgcs2 :
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2
- Aldh1 :
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1
- Pck1 :
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1
- Cpt1a :
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a
- G0s2 :
-
G0/G1 switch gene 2
References
Abbott BD, Wood CR, Watkins AM, Tatum-Gibbs K, Das KP, Lau C (2012) Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) and nuclear receptor-regulated genes in fetal and postnatal CD-1 mouse tissues. Reprod Toxicol 33:491–505. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.11.005
Abdellatif AG, Préat V, Taper HS, Roberfroid M (1991) The modulation of rat liver carcinogenesis by perfluorooctanoic acid, a peroxisome proliferator. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 111:530–537. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(91)90257-F
Aninat C, Piton A, Glaise D, Le Charpentier T, Langouët S, Morel F, Guguen-Guillouzo C, Guillouzo A (2006) Expression of cytochromes P450, conjugating enzymes and nuclear receptors in human hepatoma HepaRG cells. Drug Metab Dispos 34:75–83. doi:10.1124/dmd.105.006759
Butler WH (1978) Long-term effects of phenobarbitone-Na on male Fischer rats. Br J Cancer 37:418–423
Cheng X, Klaassen CD (2008) Perfluorocarboxylic acids induce cytochrome P450 enzymes in mouse liver through activation of PPAR-alpha and CAR transcription factors. Toxicol Sci Off J Soc Toxicol 106:29–36. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn147
Dong B, Saha PK, Huang W, Chen W, Abu-Elheiga LA, Wakil SJ, Stevens RD, Ilkayeva O, Newgard CB, Chan L, Moore DD (2009) Activation of nuclear receptor CAR ameliorates diabetes and fatty liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18831–18836. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909731106
Emmett EA, Zhang H, Shofer FS, Freeman D, Rodway NV, Desai C, Shaw LM (2006) Community exposure to perfluorooctanoate: relationships between serum levels and certain health parameters. J Occup Environ Med 48:771–779. doi:10.1097/01.jom.0000233380.13087.37
Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang YX (2004) PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med 10:355–361. doi:10.1038/nm1025
Ferré P (2004) The biology of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors relationship with lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 53(suppl 1):S43–S50
Gao J, He J, Zhai Y, Wada T, Xie W (2009) The constitutive androstane receptor is an anti-obesity nuclear receptor that improves insulin sensitivity. J Biol Chem 284:25984–25992. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.016808
Hays T, Rusyn I, Burns AM, Kennett MJ, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ, Peters JM (2005) Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) in bezafibrate-induced hepatocarcinogenesis and cholestasis. Carcinogenesis 26:219–227. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh285
Heuvel JPV, Kuslikis BI, Peterson RE (1992) Covalent binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to proteins in the plasma, liver and testes of rats. Chem Biol Interact 82:317–328. doi:10.1016/0009-2797(92)90003-4
Honkakoski P, Negishi M (1998) Protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors suppress phenobarbital-induced Cyp2b10 gene transcription in mouse primary hepatocytes. Biochem J 330:889–895. doi:10.1042/bj3300889
Imai J, Yamazoe Y, Yoshinari K (2013) Novel cell-based reporter assay system using epitope-tagged protein for the identification of agonistic ligands of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR). Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28:290–298. doi:10.2133/dmpk.DMPK-12-RG-112
Inoue S, Yoshinari K, Sugawara M, Yamazoe Y (2011) Activated sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 suppresses hepatocyte nuclear factor-4-mediated Cyp3a11 expression in mouse liver. Mol Pharmacol 79:148–156. doi:10.1124/mol.110.068577
Kachaylo EM, Yarushkin AA, Pustylnyak VO (2012) Constitutive androstane receptor activation by 2,4,6-triphenyldioxane-1,3 suppresses the expression of the gluconeogenic genes. Eur J Pharmacol 679:139–143. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.01.007
Kawamoto T, Sueyoshi T, Zelko I, Moore R, Washburn K, Negishi M (1999) Phenobarbital-responsive nuclear translocation of the receptor CAR in induction of the CYP2B gene. Mol Cell Biol 19:6318–6322. doi:10.1128/MCB.19.9.6318
Kodama S, Koike C, Negishi M, Yamamoto Y (2004) Nuclear receptors CAR and PXR cross talk with FOXO1 to regulate genes that encode drug-metabolizing and gluconeogenic enzymes. Mol Cell Biol 24:7931–7940. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.18.7931-7940.2004
Koike C, Moore R, Negishi M (2007) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase is an endogenous signal retaining the nuclear constitutive active/androstane receptor (CAR) in the cytoplasm of mouse primary hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol 71:1217–1221. doi:10.1124/mol.107.034538
Lee H, D’Eon J, Mabury SA (2010) Biodegradation of polyfluoroalkyl phosphates as a source of perfluorinated acids to the environment. Environ Sci Technol 44:3305–3310. doi:10.1021/es9028183
Lee YJ, Lee HG, Yang JH (2013) Perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells is mediated by ERK 1/2 pathway. Chemosphere 90:1597–1602. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.033
Lu Y, Luo B, Li J, Dai J (2016) Perfluorooctanoic acid disrupts the blood-testis barrier and activates the TNFalpha/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Arch Toxicol 90:971–983. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1492-y
Maglich JM, Parks DJ, Moore LB, Collins JL, Goodwin B, Billin AN, Stoltz CA, Kliewer SA, Lambert MH, Willson TM, Moore JT (2003) Identification of a novel human constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) agonist and its use in the identification of CAR target genes. J Biol Chem 278:17277–17283. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300138200
Martin JW, Asher BJ, Beesoon S, Benskin JP, Ross MS (2010) PFOS or PreFOS? Are perfluorooctane sulfonate precursors (PreFOS) important determinants of human and environmental perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure? J Environ Monit 12:1979–2004. doi:10.1039/c0em00295j
Mutoh S, Sobhany M, Moore R, Perera L, Pedersen L, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M (2013) Phenobarbital indirectly activates the constitutive active androstane receptor (CAR) by inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Sci Signal 6(274):ra31. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2003705
Ohmori K, Kudo N, Katayama K, Kawashima Y (2003) Comparison of the toxicokinetics between perfluorocarboxylic acids with different carbon chain length. Toxicology 184:135–140. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00573-5
Osabe M, Negishi M (2011) Active ERK1/2 protein interacts with the phosphorylated nuclear constitutive active/androstane receptor (CAR; NR1I3), repressing dephosphorylation and sequestering CAR in the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 286:35763–35769. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.284596
Pastoor TP, Lee KP, Perri MA, Gillies PJ (1987) Biochemical and morphological studies of ammonium perfluorooctanoate-induced hepatomegaly and peroxisome proliferation. Exp Mol Pathol 47:98–109. doi:10.1016/0014-4800(87)90011-6
Post GB, Cohn PD, Cooper KR (2012) Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), an emerging drinking water contaminant: a critical review of recent literature. Environ Res 116:93–117. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2012.03.007
Rosen MB, Lee JS, Ren H, Vallanat B, Liu J, Waalkes MP, Abbott BD, Lau C, Corton JC (2008) Toxicogenomic dissection of the perfluorooctanoic acid transcript profile in mouse liver: evidence for the involvement of nuclear receptors PPAR alpha and CAR. Toxicol Sci Off J Soc Toxicol 103:46–56. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn025
Rosen MB, Schmid JR, Corton JC, Zehr RD, Das KP, Abbott BD, Lau C (2010) Gene expression profiling in wild-type and PPARalpha-null mice exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate reveals PPARalpha-independent effects. PPAR Res. doi:10.1155/2010/794739
Saito K, Kobayashi K, Mizuno Y, Fukuchi Y, Furihata T, Chiba K (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) agonists induce constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and cytochrome P450 2B in rat primary hepatocytes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 25:108–111. doi:10.2133/dmpk.25.108
Saito K, Moore R, Negishi M (2013) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates nuclear receptor CAR that activates the CYP2B6 gene. Drug Metab Dispos 41:1170–1173. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.051623
Seglen PO (1976) Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol 13:29–83
Shizu R, Abe T, Benoki S, Takahashi M, Kodama S, Miayata M, Matsuzawa A, Yoshinari K (2016) PXR stimulates growth factor-mediated hepatocyte proliferation by cross-talk with the FOXO transcription factor. Biochem J 473:257–266. doi:10.1042/BJ20150734
Sueyoshi T, Negishi M (2001) Phenobarbital response elements of cytochrome P450 genes and nuclear receptors 1. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:123–143. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.123
Tolson AH, Wang H (2010) Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes by xenobiotic receptors: PXR and CAR. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1238–1249. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2010.08.006
Wei P, Zhang J, Egan-Hafley M, Liang S, Moore DD (2000) The nuclear receptor CAR mediates specific xenobiotic induction of drug metabolism. Nature 407(6806):920–923. doi:10.1038/35038112
Williams GM, Whysner J (1996) Epigenetic carcinogens: evaluation and risk assessment. Exp Toxicol Pathol 48:189–195. doi:10.1016/s0940-2993(96)80041-8
Yeung LW, Loi EI, Wong VY, Guruge KS, Yamanaka N, Tanimura N, Hasegawa J, Yamashita N, Miyazaki S, Lam PK (2009) Biochemical responses and accumulation properties of long-chain perfluorinated compounds (PFOS/PFDA/PFOA) in juvenile chickens (Gallus gallus). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57:377–386. doi:10.1007/s00244-008-9278-3
Yoshinari K, Kobayashi K, Moore R, Kawamoto T, Negishi M (2003) Identification of the nuclear receptor CAR: HSP90 complex in mouse liver and recruitment of protein phosphatase 2A in response to phenobarbital. FEBS Lett 548:17–20. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00720-8
Zhang H, Lu Y, Luo B, Yan S, Guo X, Dai J (2014) Proteomic analysis of mouse testis reveals perfluorooctanoic acid-induced reproductive dysfunction via direct disturbance of testicular steroidogenic machinery. J Proteome Res 13:3370–3385. doi:10.1021/pr500228d
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from Food Safety Commission, Japan (#1302). The authors are grateful to Dr. Satoru Kakizaki (Gunma University Maebashi, Japan) for Car-null mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in this article involving animals were in strict accordance with the ethical standard guidelines of Tohoku University and University of Shizuoka. The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, T., Takahashi, M., Kano, M. et al. Activation of nuclear receptor CAR by an environmental pollutant perfluorooctanoic acid. Arch Toxicol 91, 2365–2374 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1888-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1888-3